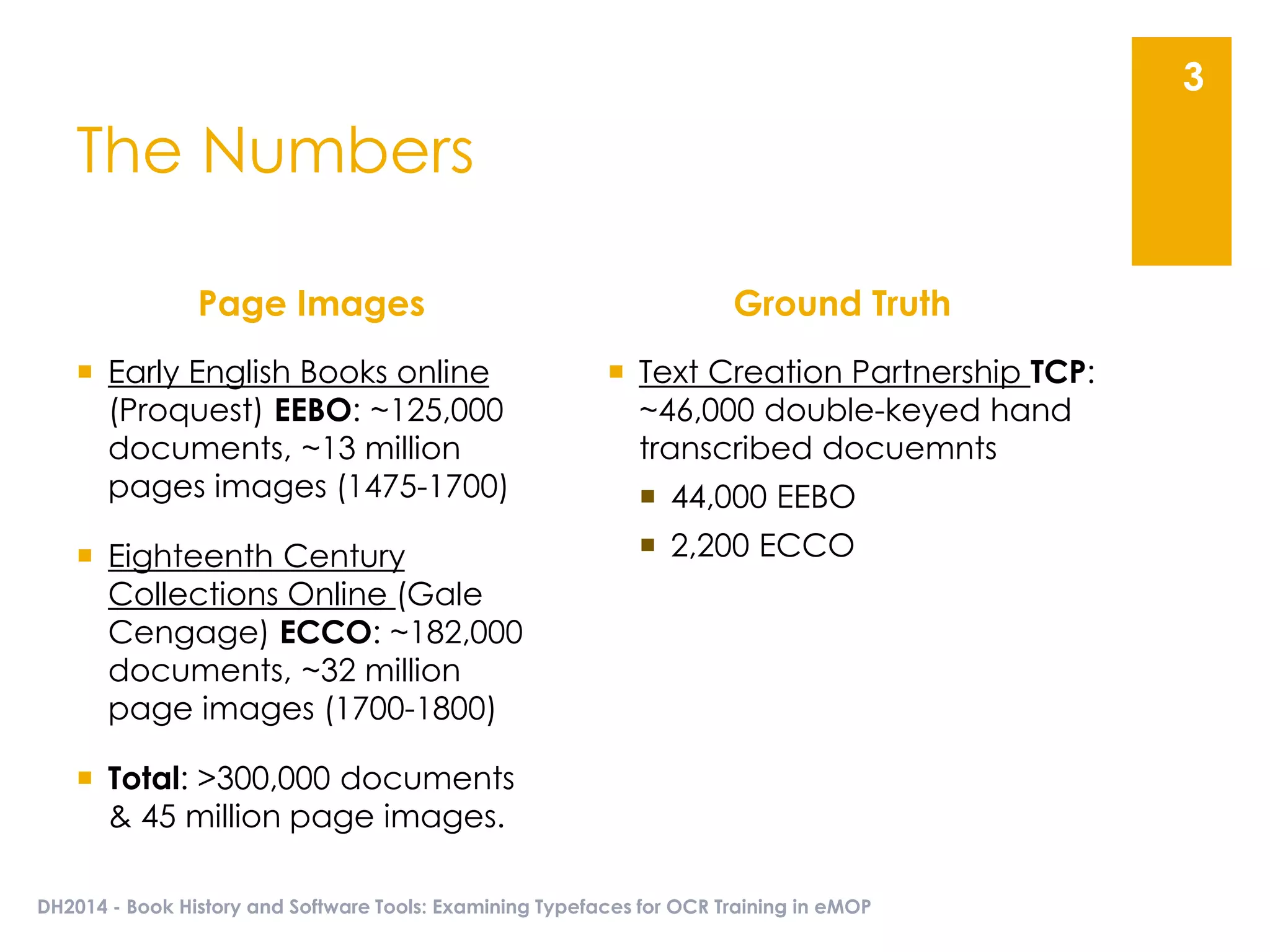
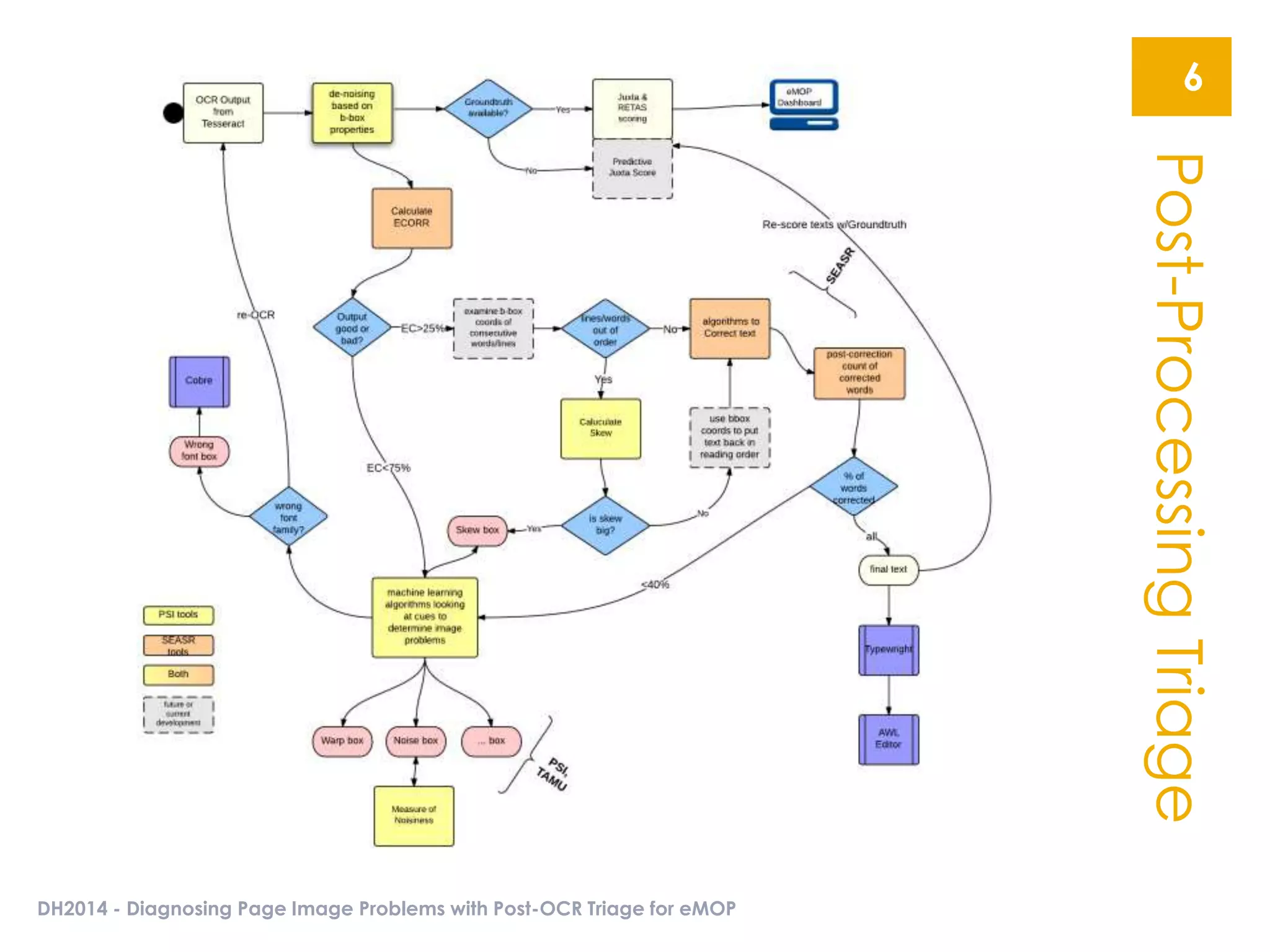
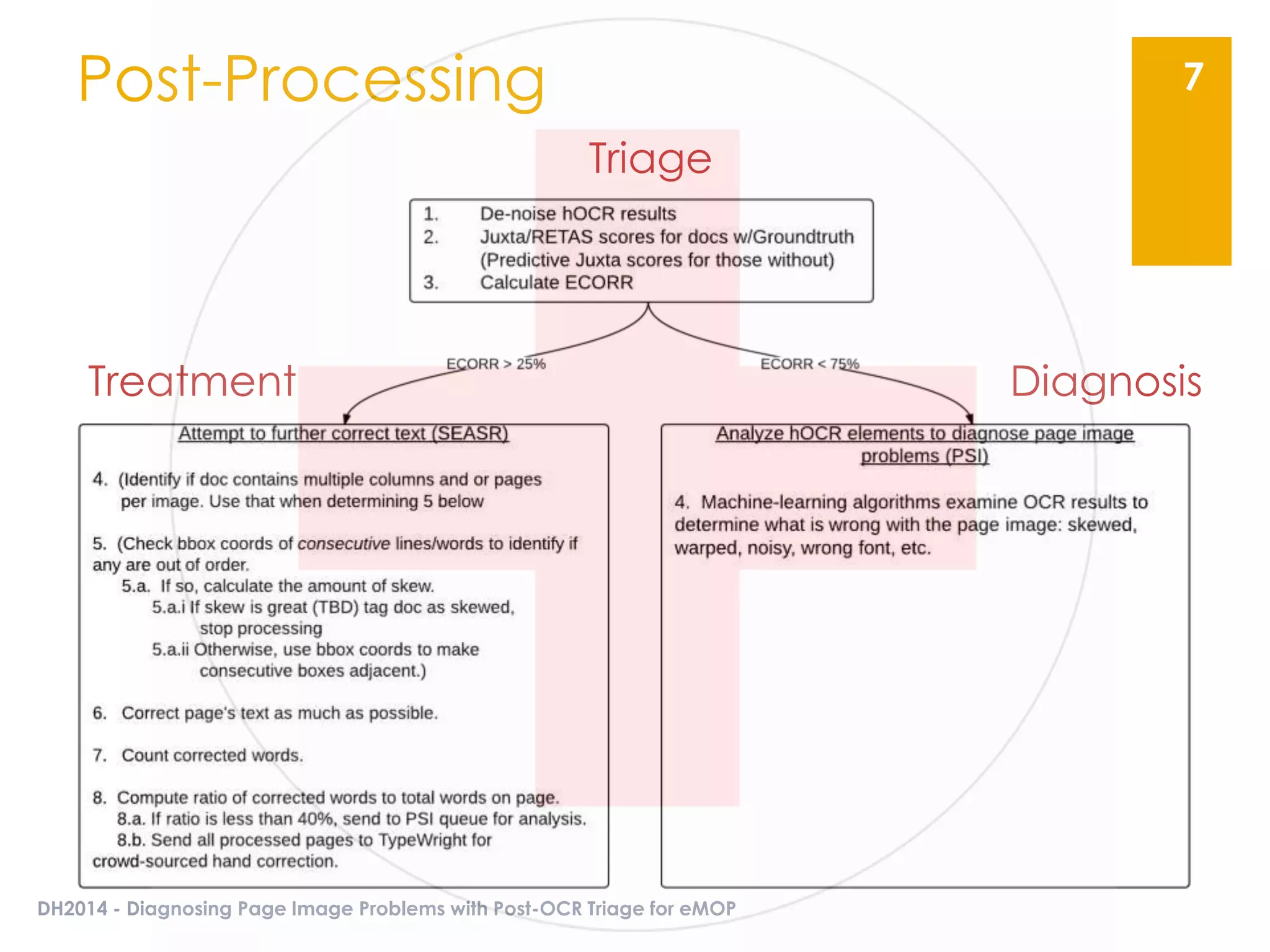
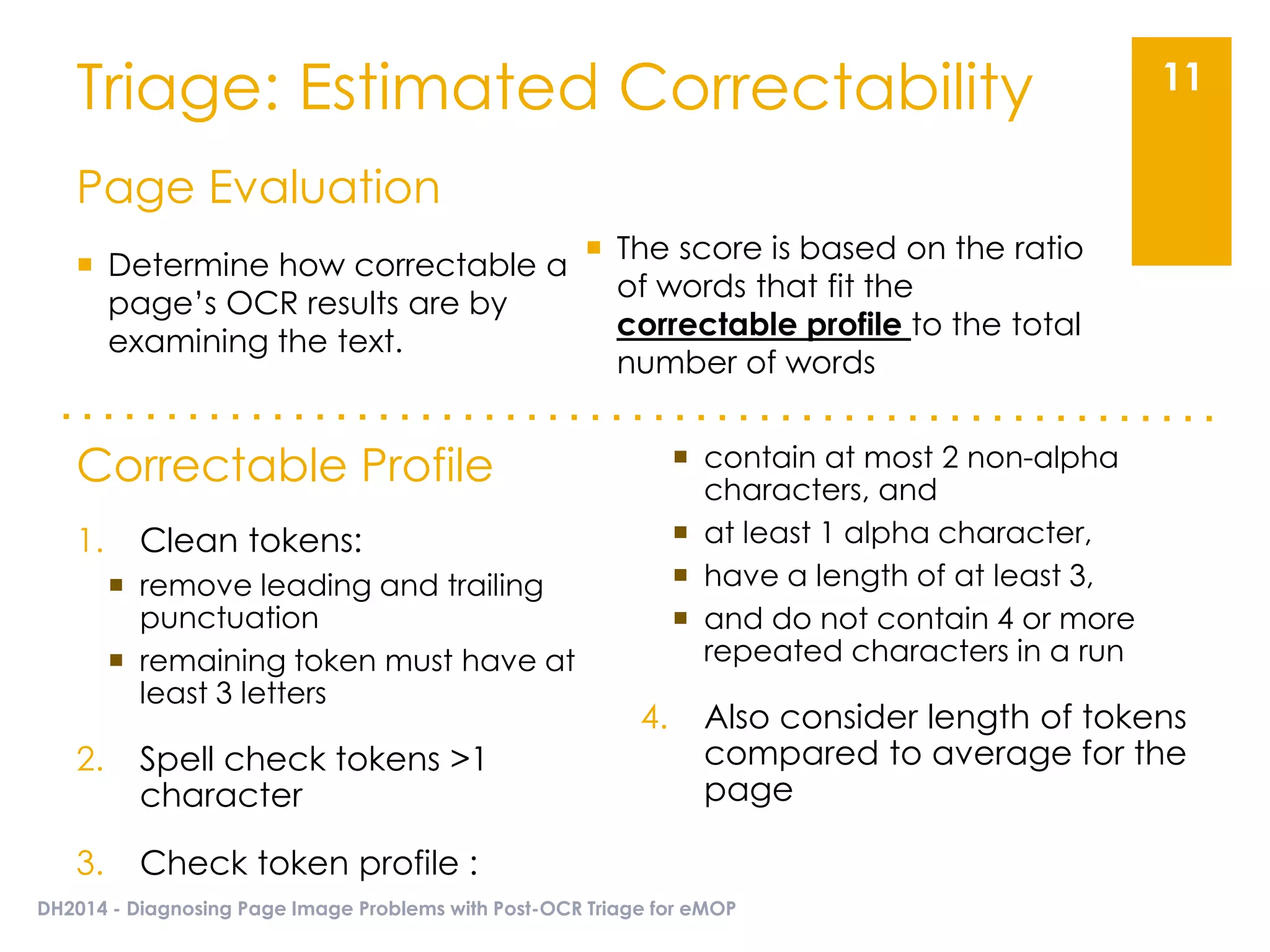
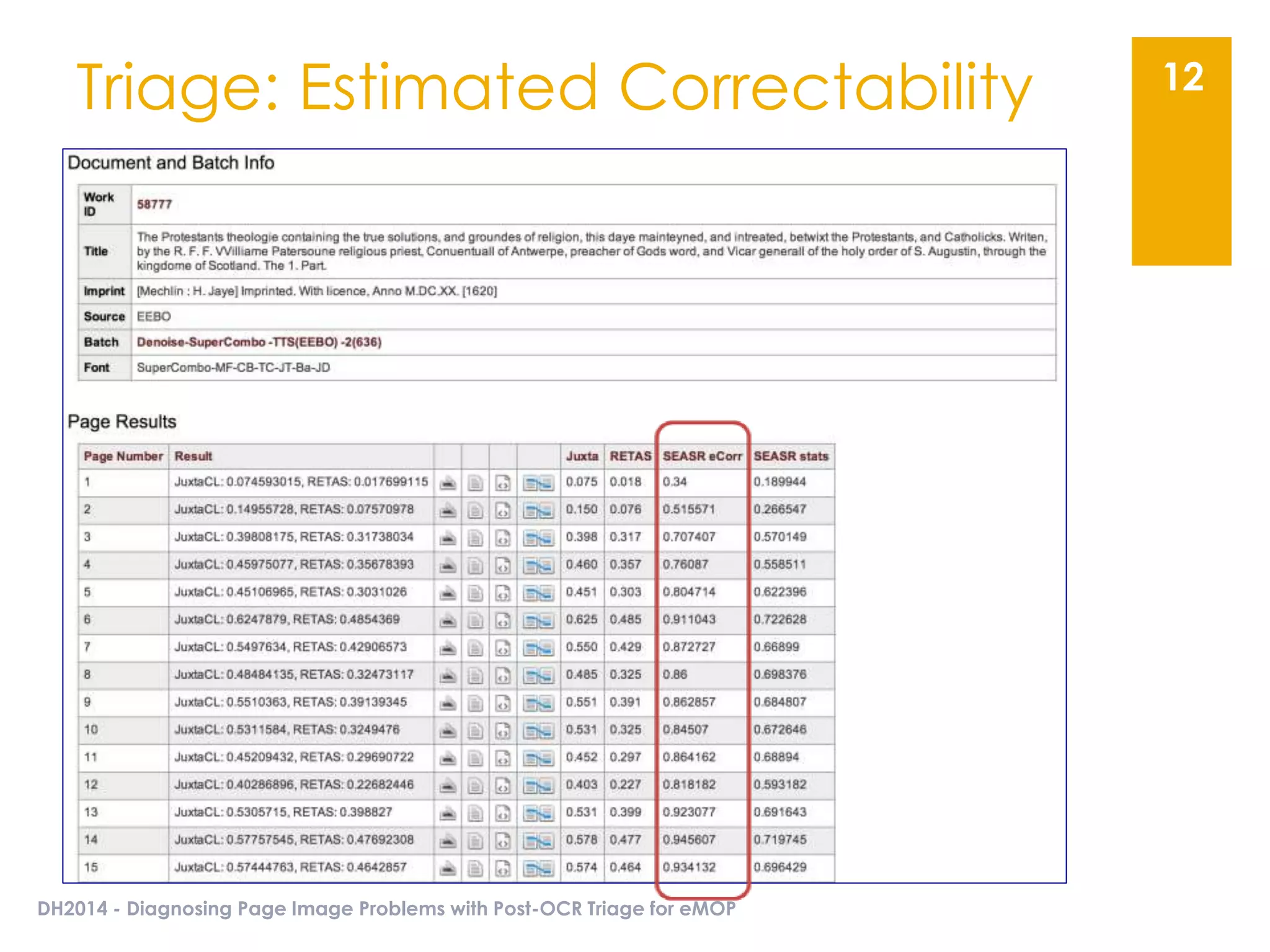
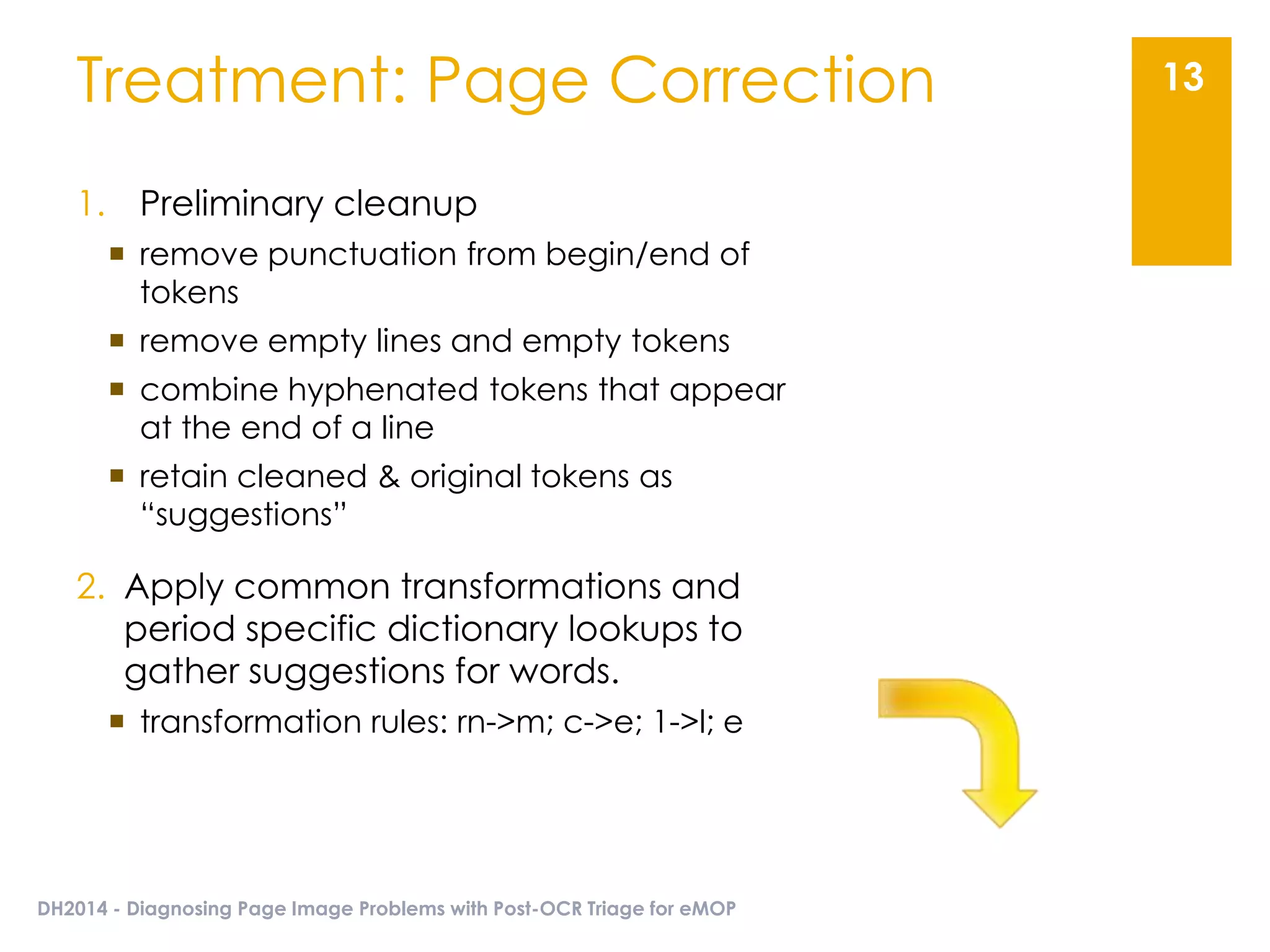
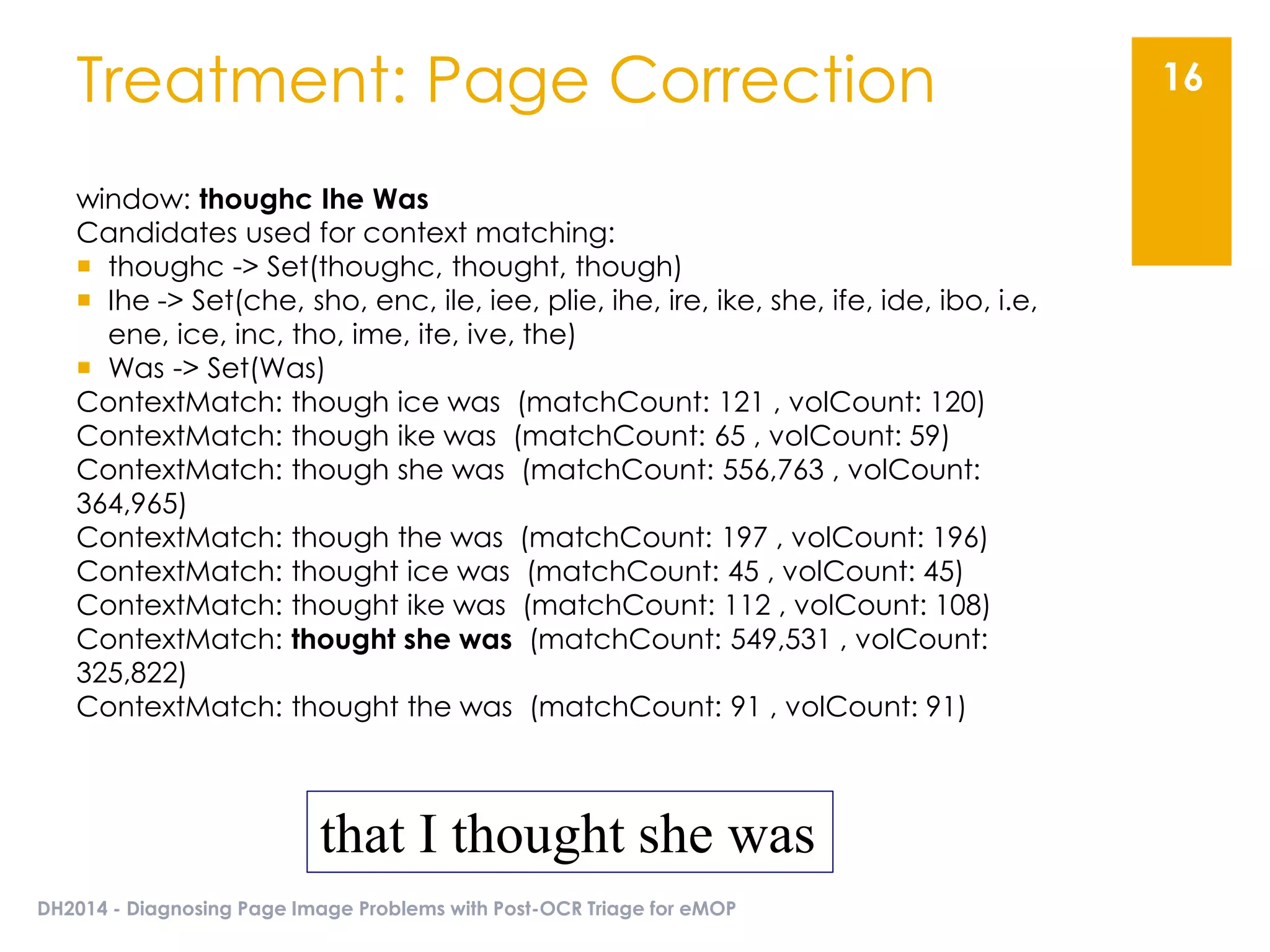
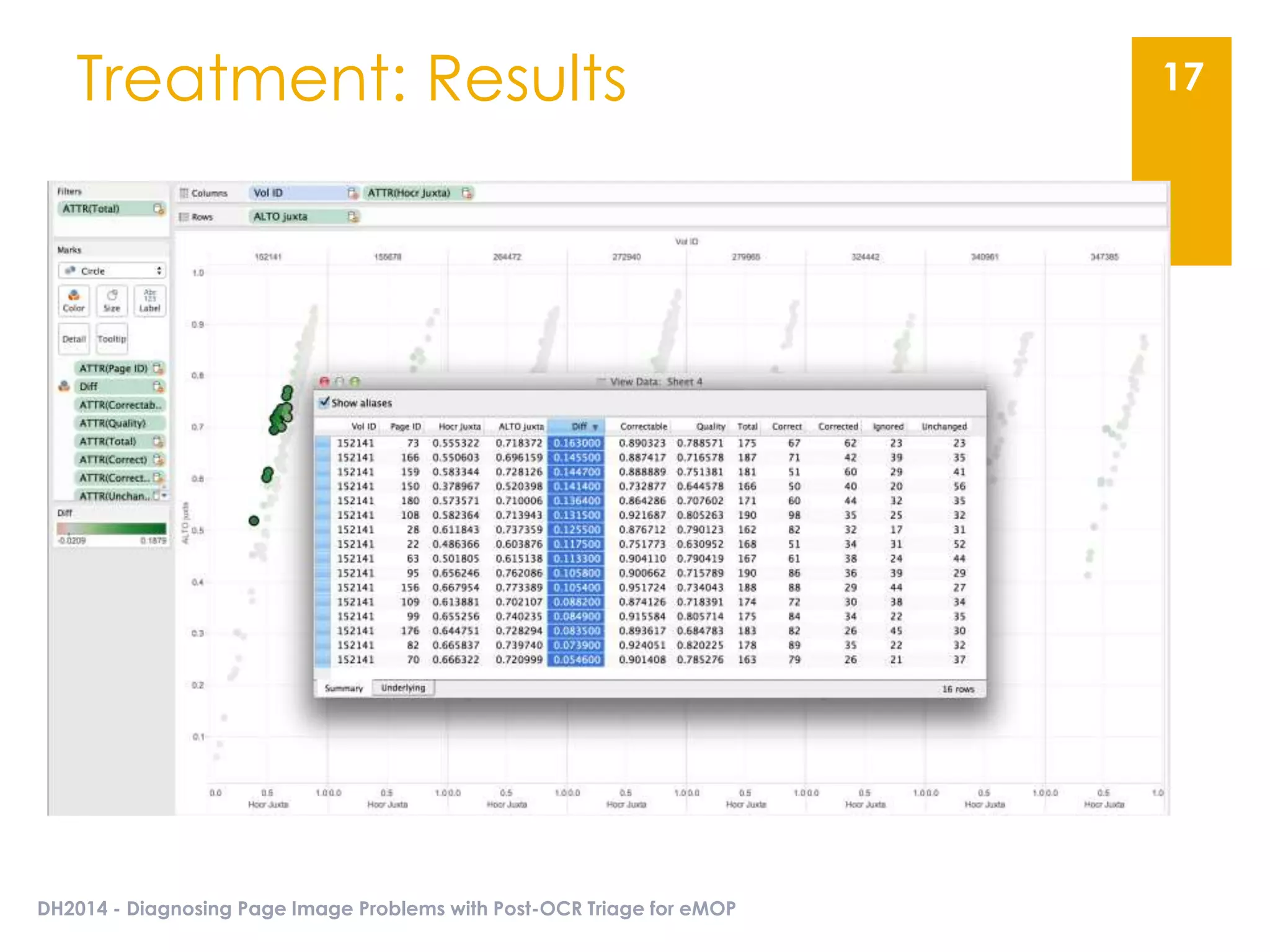
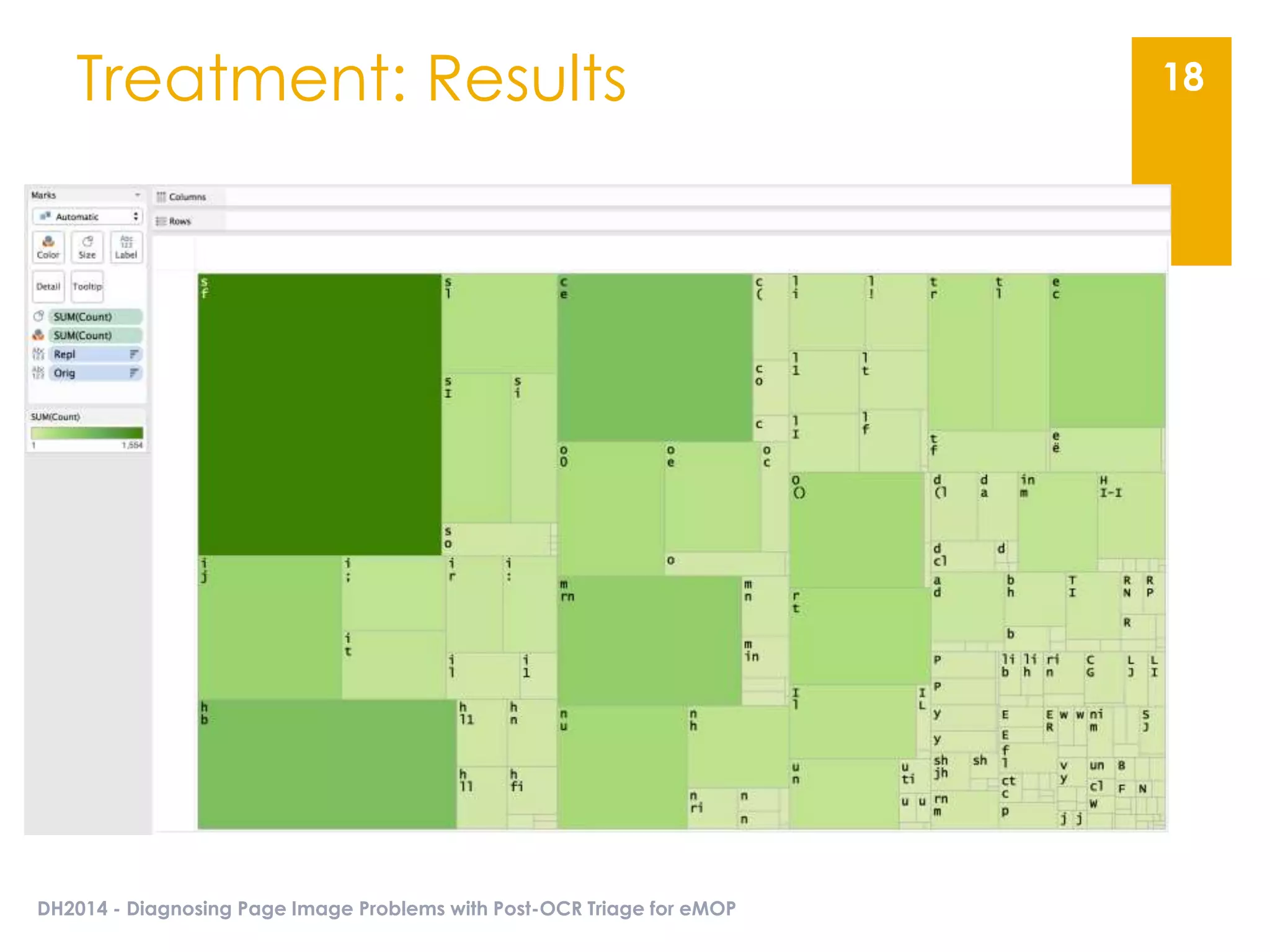
The document presents an overview of the EMOP (Early Modern OCR Project) triage process for diagnosing issues in page images resulting from OCR. It highlights the project's focus on post-processing corrections and the development of a triage system to evaluate and improve OCR outputs, aiming for high-quality results in processing over 45 million page images. The methodology includes techniques for noise reduction, token correction, and tagging problematic pages, with the goal of comprehensive analysis and improved digitization quality.