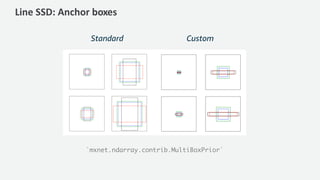
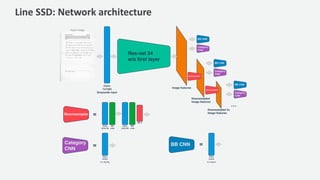
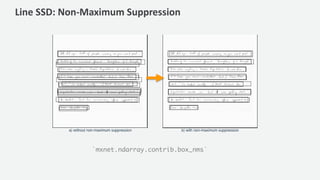
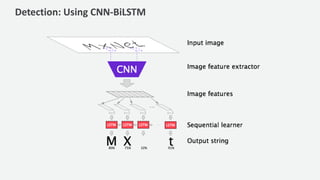
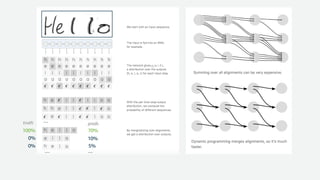
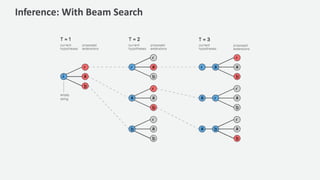
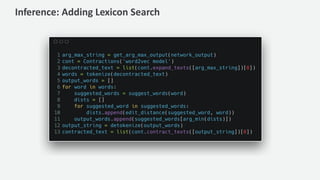
The document discusses a handwriting recognition pipeline using AWS MXNet and Gluon, focusing on optical character recognition through various methods including page and line segmentation using CNN and SSD. It elaborates on the challenges of labeling and alignment in handwriting recognition, proposing solutions like connectionist temporal classification loss and inference methods such as beam search and lexicon search. Results highlight a character error rate improvement through these techniques, emphasizing the effectiveness of the developed model.