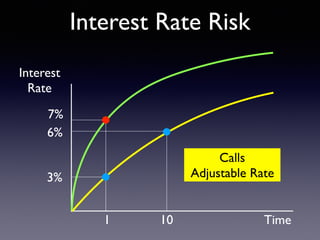
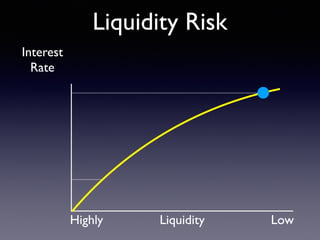
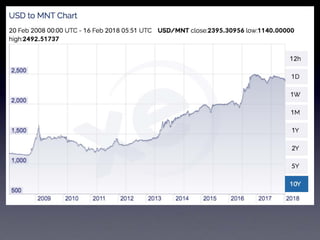
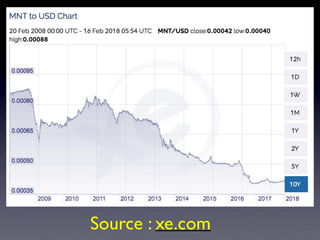
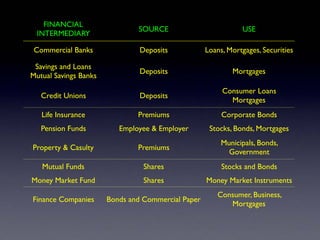
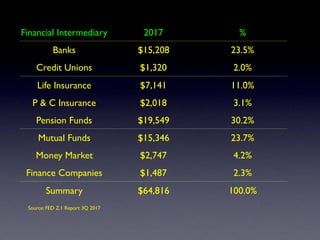
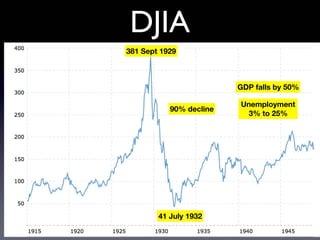
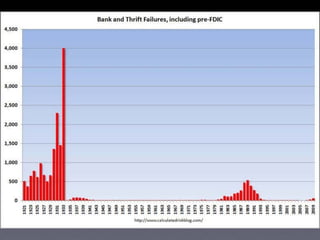
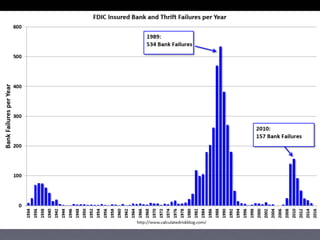
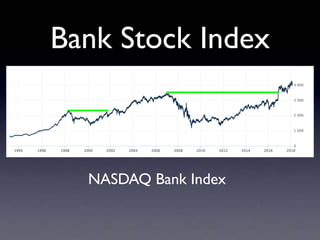
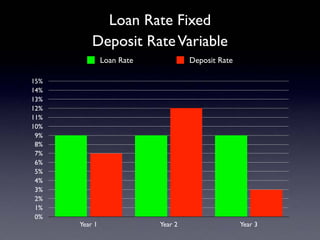
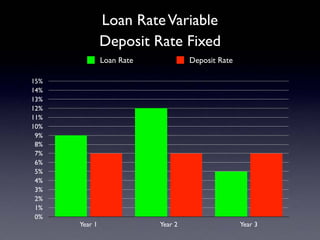
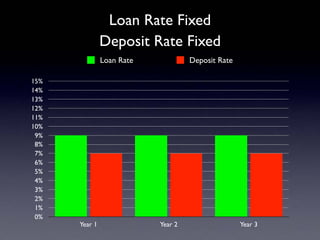
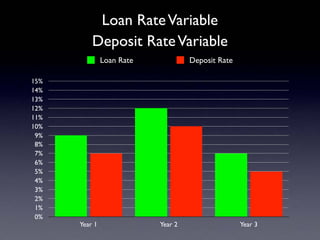
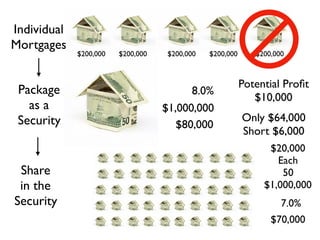
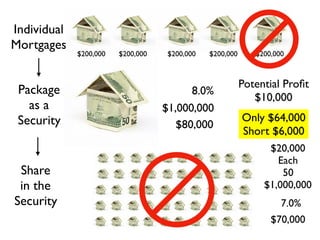
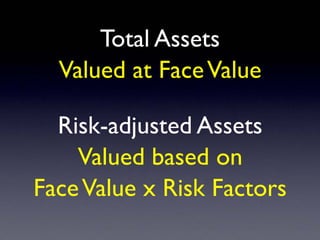
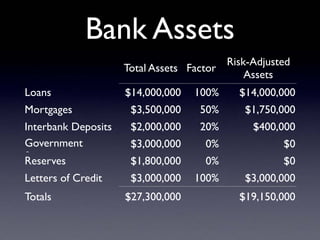
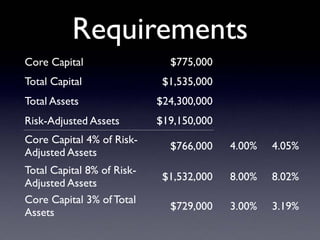
The document provides an overview of several lectures on money, banking, and financial intermediaries. It discusses topics like financial intermediaries and the risks they face, innovations in financial instruments, and regulation of the banking system. Slides cover money market instruments, risks faced by financial institutions, and the roles of various financial intermediaries and regulatory agencies.