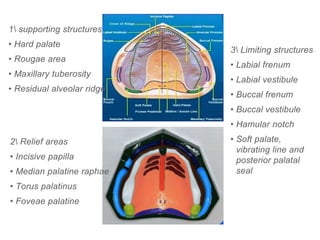
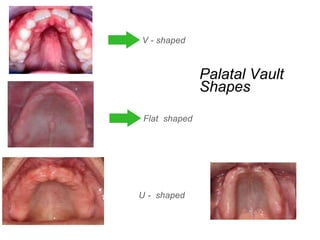
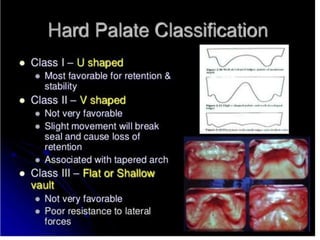
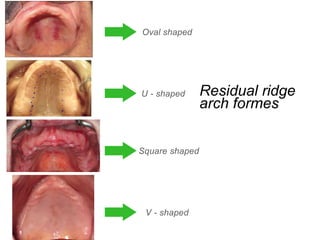
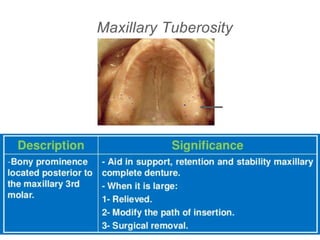
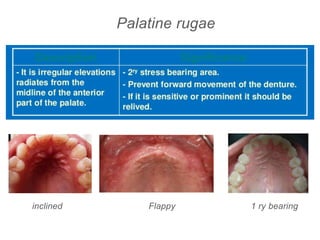
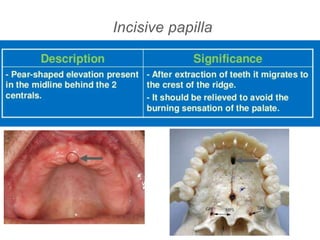
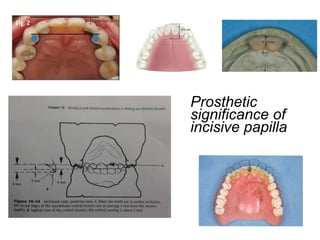
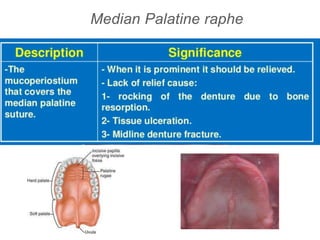
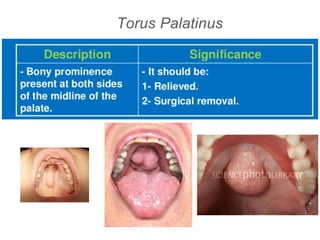
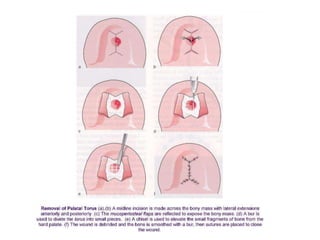
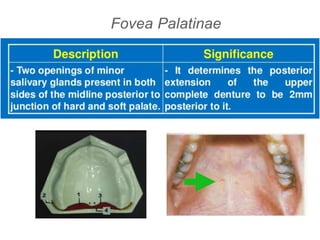
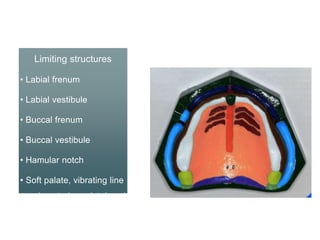
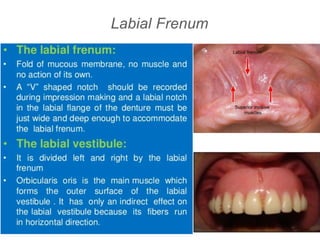
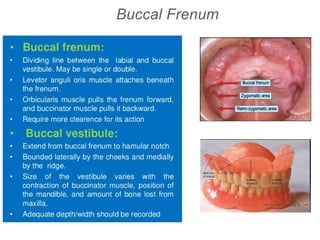
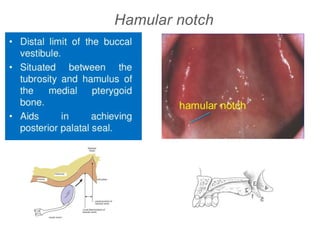
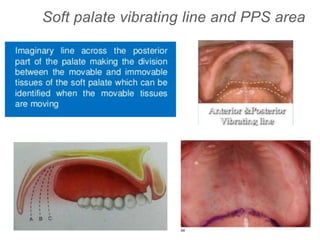
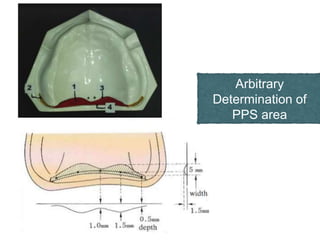
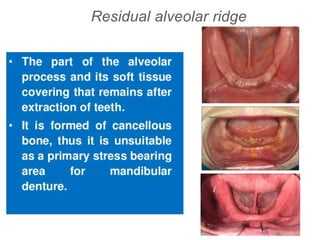
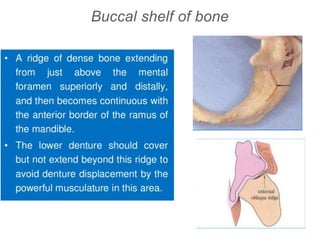
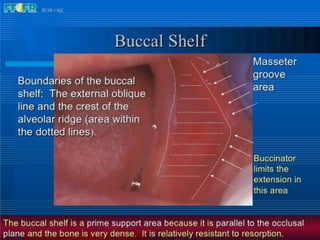
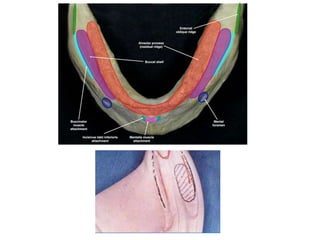
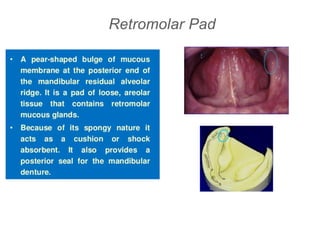
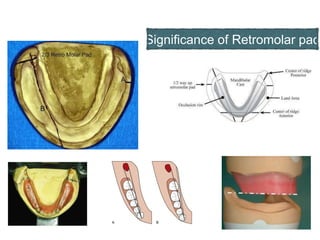
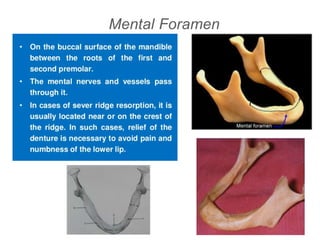
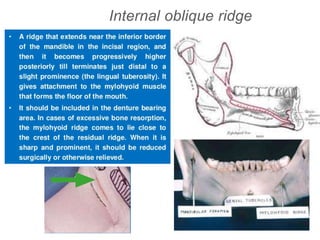
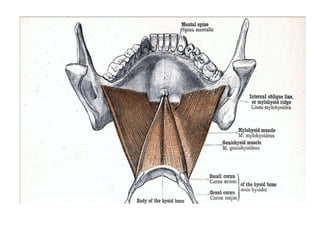
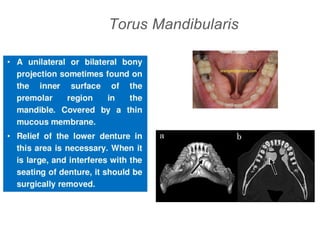
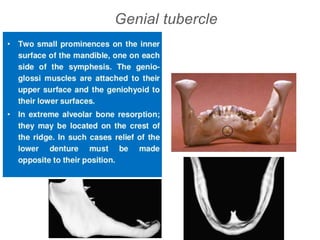
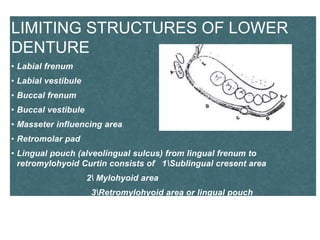
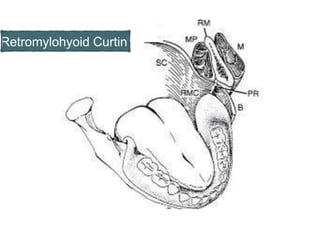
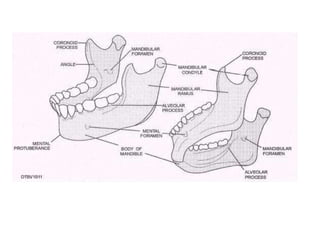
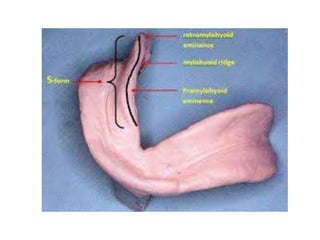
This document discusses the anatomical landmarks important for complete denture construction in the maxilla and mandible. It outlines the supporting, relief, and limiting structures within the oral cavity. In the maxilla, key supporting structures include the hard palate, palatal rugae, maxillary tuberosity, and residual alveolar ridge. Relief areas are the incisive papilla, median palatine raphe, and torus palatinus. Limiting structures incorporate the labial and buccal frenums and vestibules. Similarly, the mandible's supporting structures comprise the buccal shelf, residual ridge, and external oblique ridge, while relief areas contain the mental foramen and internal oblique ridge