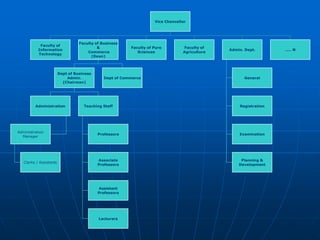
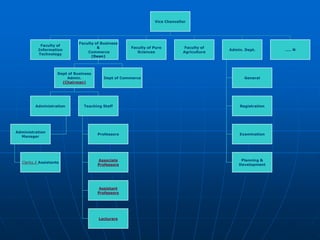
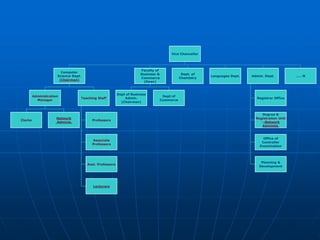
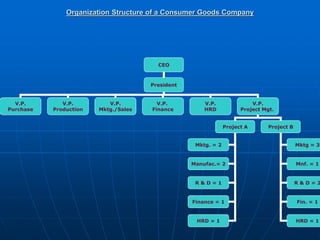
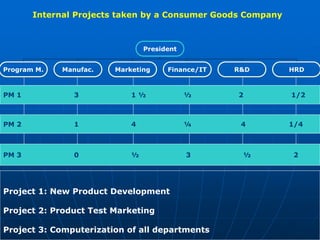
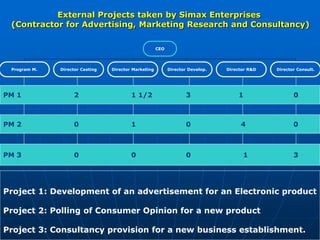
The document describes a functional organization structure for projects. In this structure, projects are undertaken by one or more functional departments within the organization. Team members maintain their regular roles but take on project work as an additional responsibility. While this provides flexibility and maximum staff utilization, it can result in a lack of coordinated effort and sub-optimization when project issues fall outside functional areas' expertise.