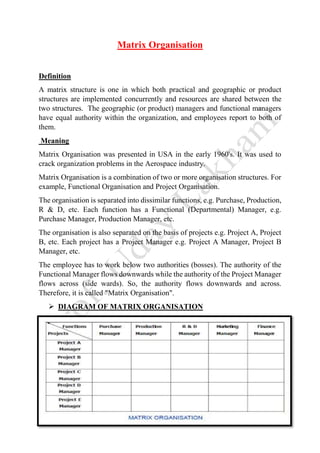
A matrix organization combines functional and project-based reporting structures so that employees report to both a functional manager in their department and a project manager. This allows for specialization between functional experts and project managers while also facilitating collaboration across departments for projects. However, it can increase complexity and potentially cause conflicts between managers as employees have dual reporting lines. Matrix structures are well-suited for large organizations operating in dynamic environments with multiple concurrent projects.