This document discusses the importance of mathematics in engineering. It makes three key points:
1. Mathematics is used at every stage of the engineering design process, from modeling problems mathematically to simulating and analyzing designs. Mathematical thinking is important for engineering.
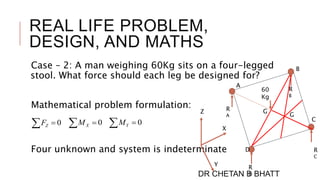
2. Several examples are given showing how engineering problems can be formulated mathematically, such as calculating load distributions on stools. This demonstrates how mathematics is applied to solve real-life engineering problems.
3. Emerging areas like wavelets, compressed sensing, and eigenvectors illustrate how advances in mathematical sciences have driven new technologies with important engineering applications in areas like imaging, search engines, and animation.