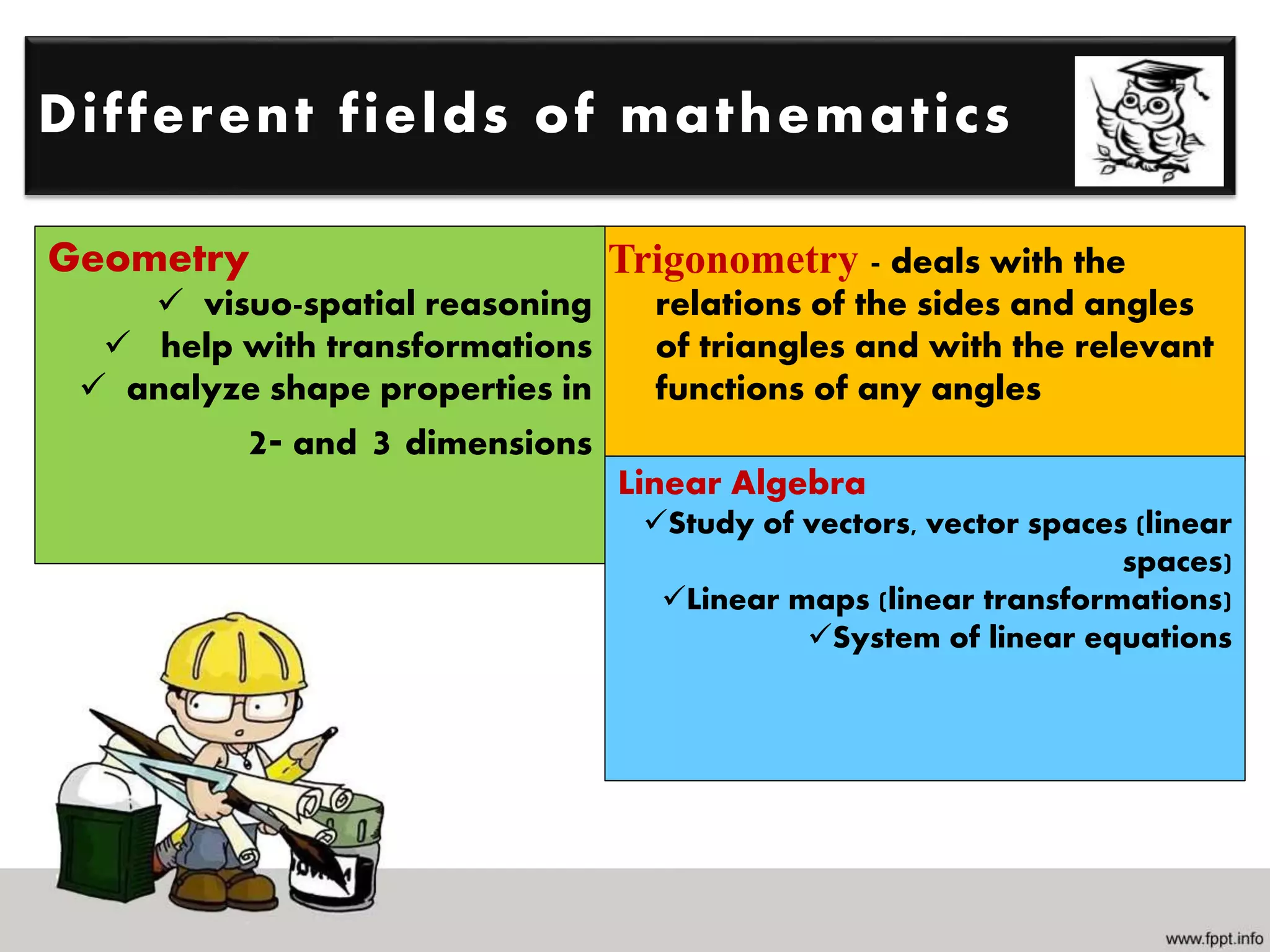
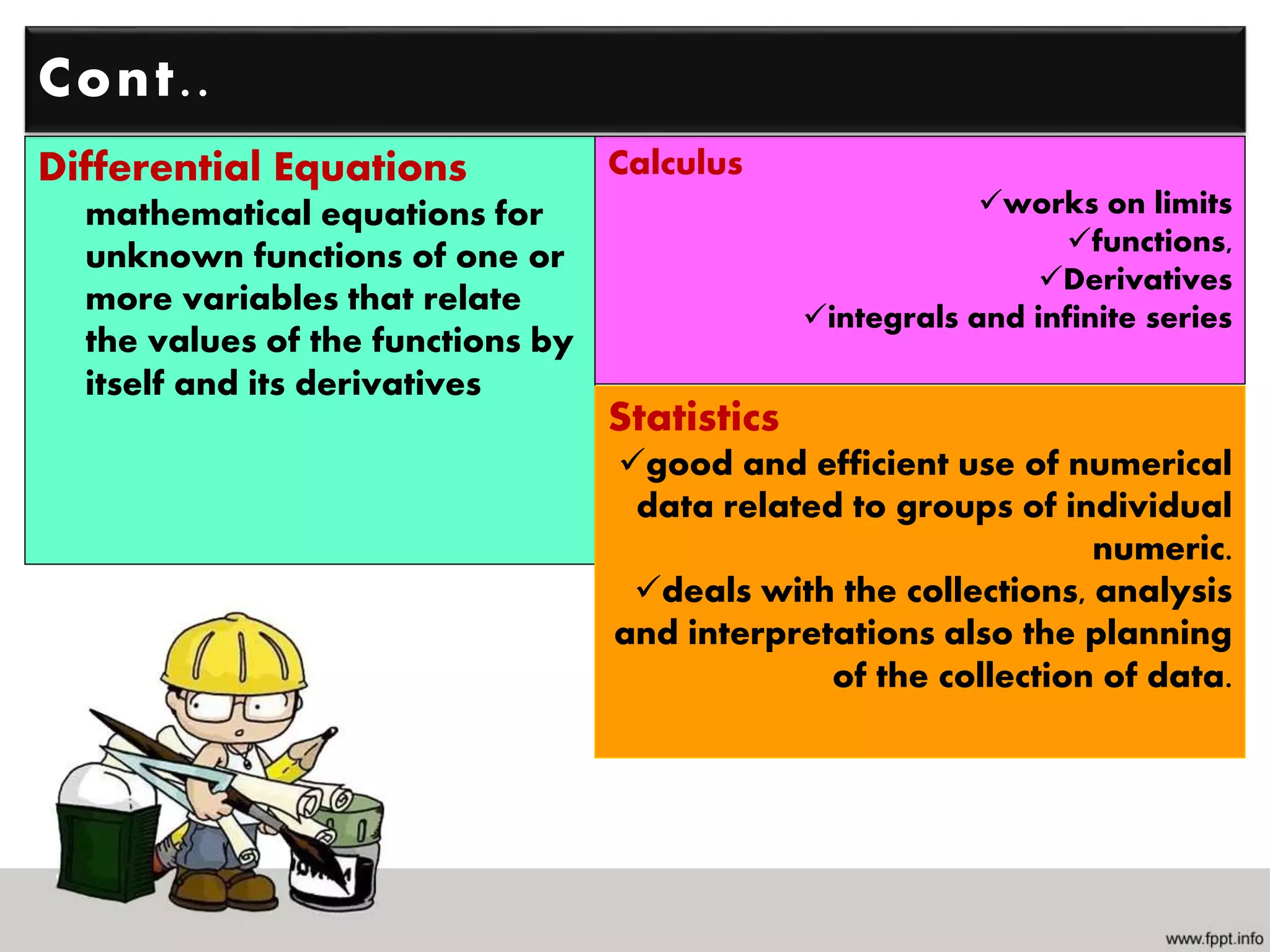
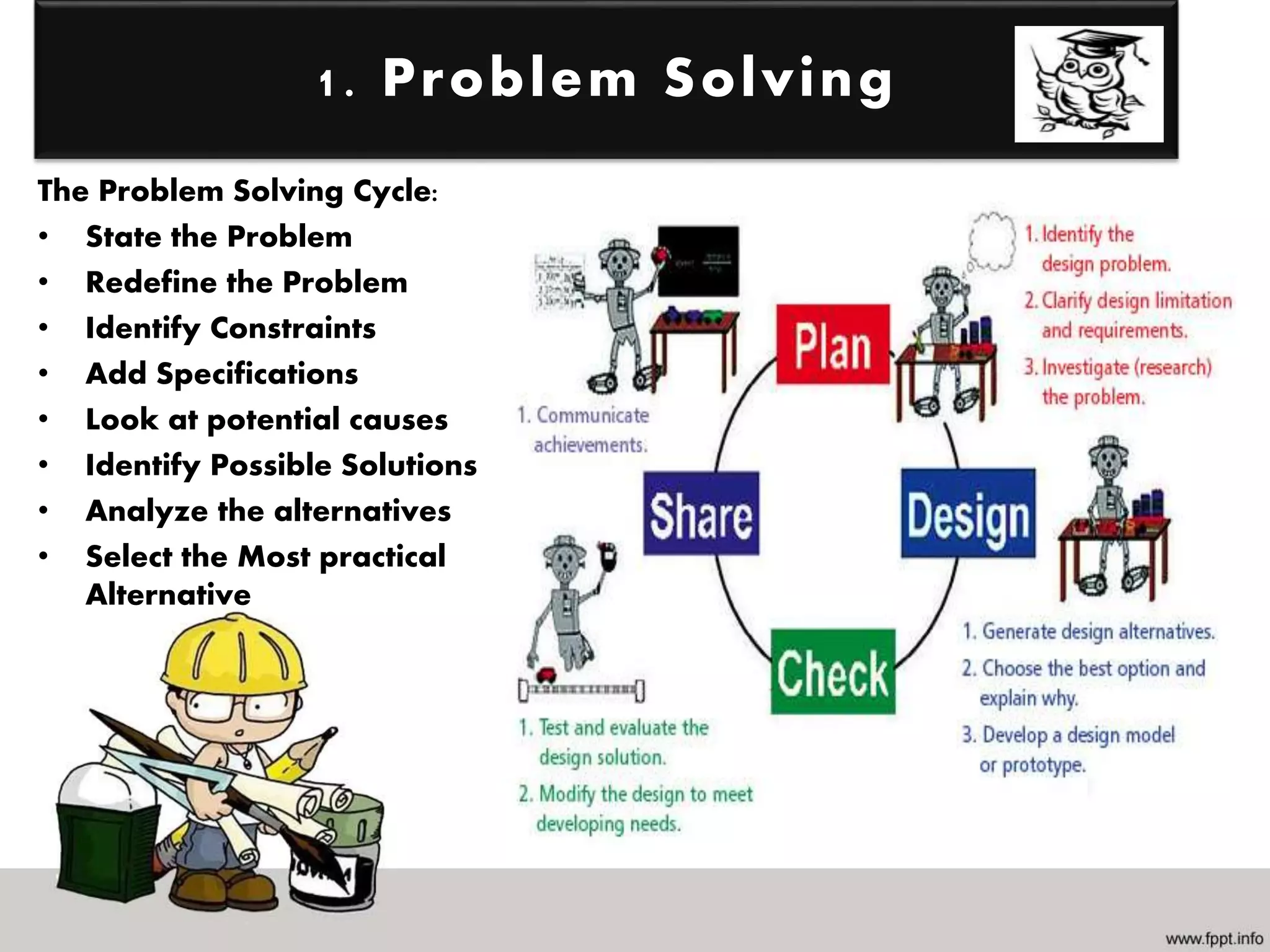
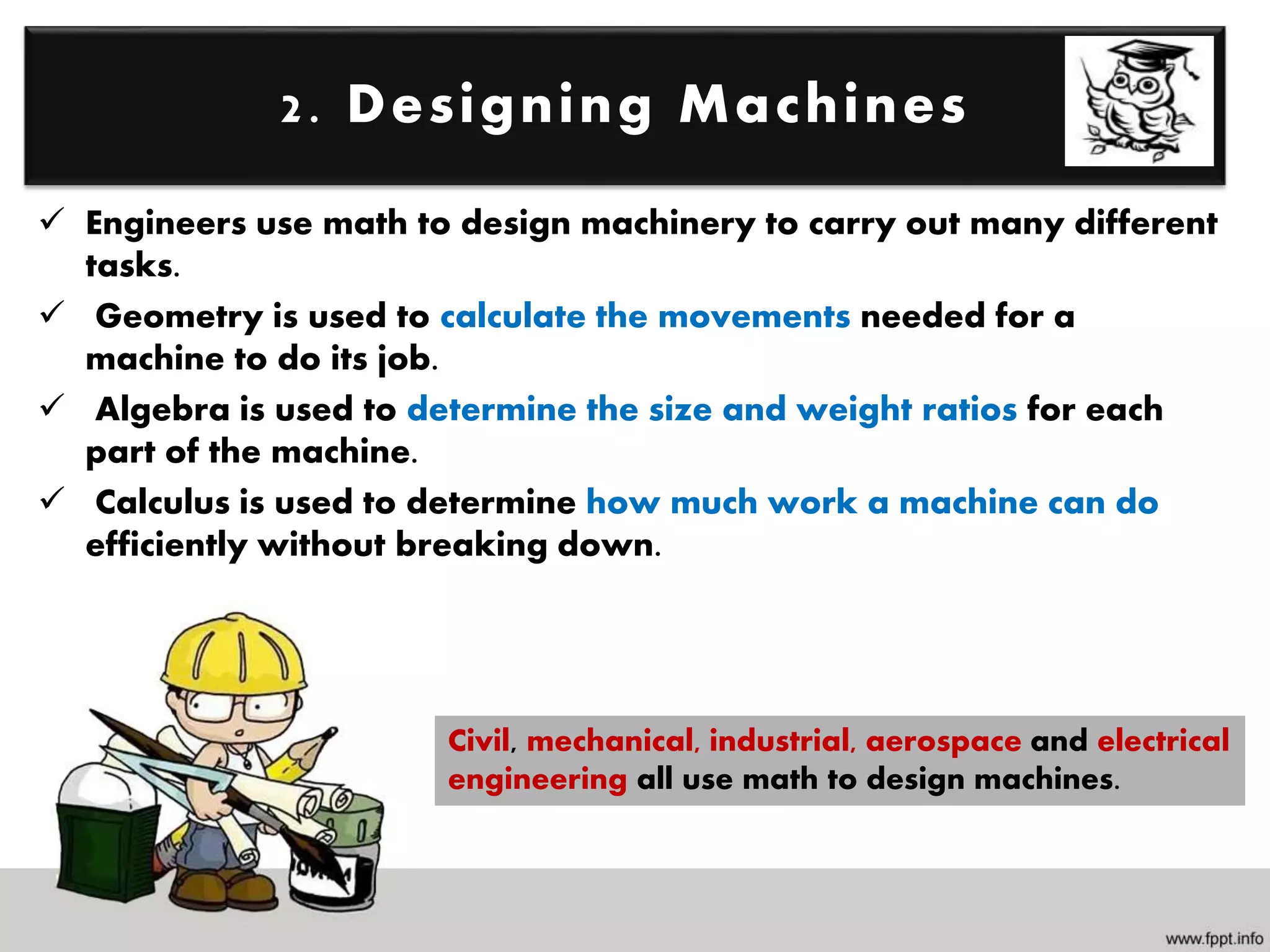
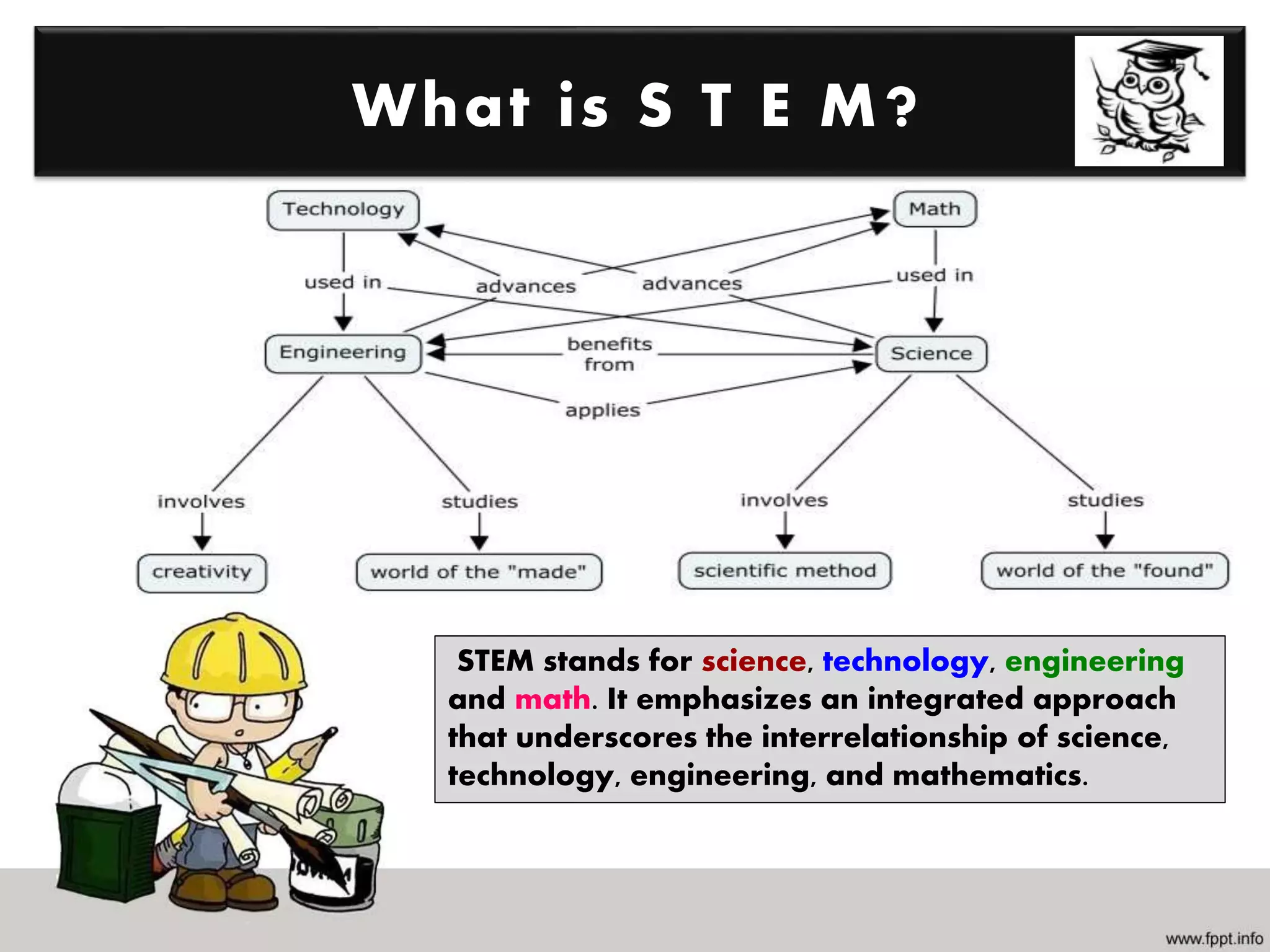
Mathematics is the study of quantities, relations, and symbols, while engineering designs and manufactures products to make life simpler, faster, and more efficient. Several fields of mathematics, including trigonometry, geometry, linear algebra, calculus, differential equations, and statistics are important for engineering. Engineering fields apply mathematics to problem solving, designing machines, creating structures, analyzing simulations, and developing models. STEM emphasizes the integrated relationship between science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, and it is impossible to engineer something without using mathematics in various applications.