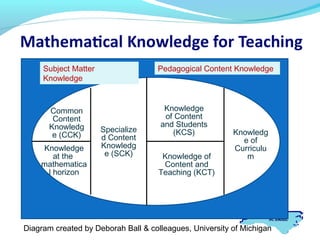
This document discusses the differences between mathematical knowledge for teaching and other specialized knowledge. It begins by asking critical questions about what mathematics is important for teaching and how it differs from mathematics used in other fields. It then defines mathematical knowledge for teaching as having two components: common mathematical knowledge that all should know, and specialized knowledge for teaching mathematics, such as representing ideas, providing explanations, and appraising unusual student solutions. The document provides examples of these different types of knowledge and knowledge used in pedagogical situations versus pure content knowledge. It concludes by introducing a diagram that further categorizes the specialized knowledge needed for teaching mathematics.