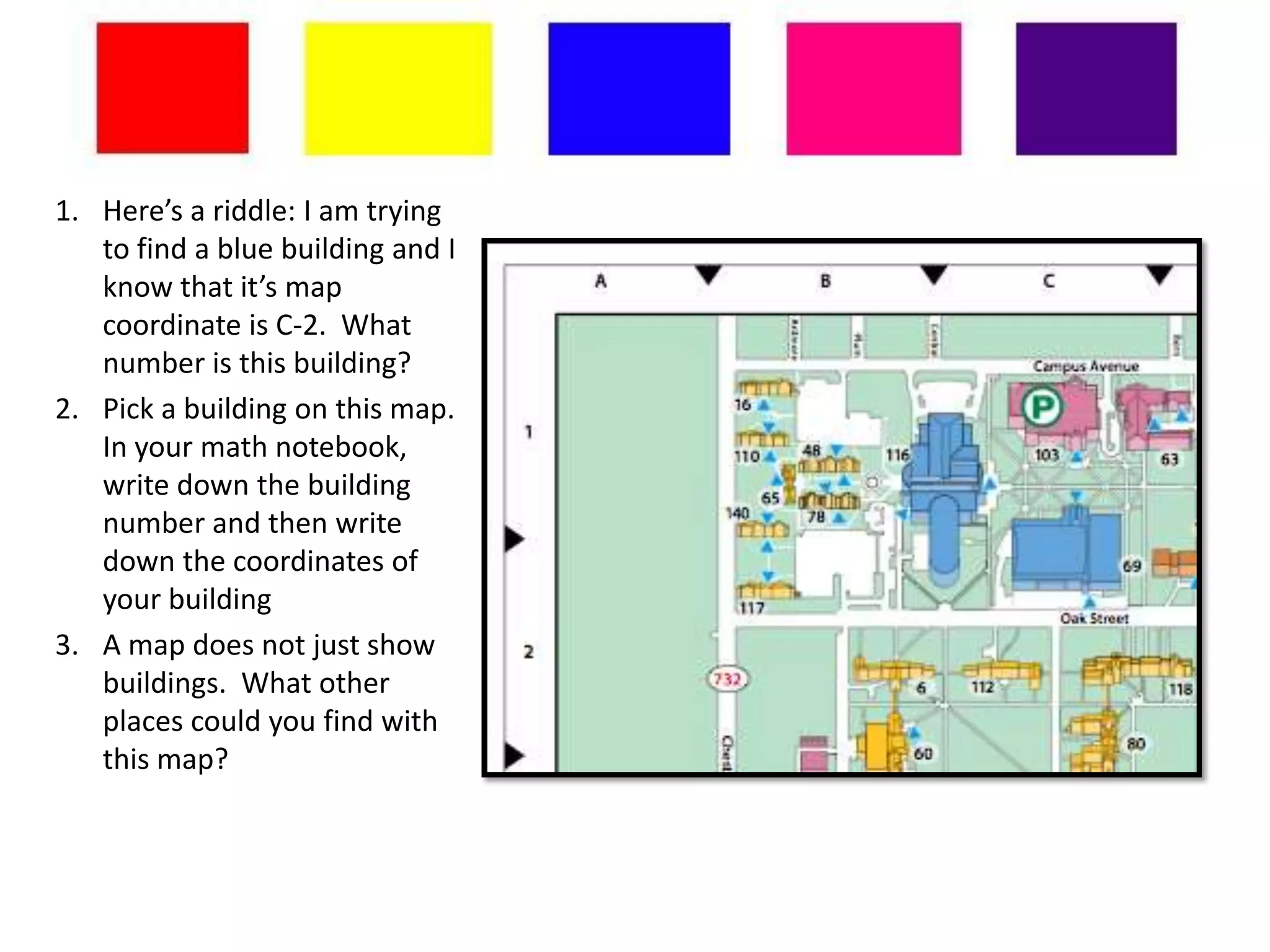
Here are the summaries for each picture in the first and second grade sections:
First Grade:
Picture 1 - Identifying 2D shapes and their properties
Picture 2 - Identifying 3D shapes and their faces
Picture 3 - Using location words like near and far
Picture 4 - Identifying and sorting 2D shapes
Picture 5 - Creating new shapes by combining or cutting other shapes
Second Grade:
Picture 6 - Identifying symmetrical shapes
Picture 7 - Determining if shapes are congruent or similar
Picture 8 - Predicting new shapes formed by combining or cutting others
Picture 9 - Identifying, describing and comparing 3D shapes
Picture 10 - Sorting and comparing 2D and 3D shapes by