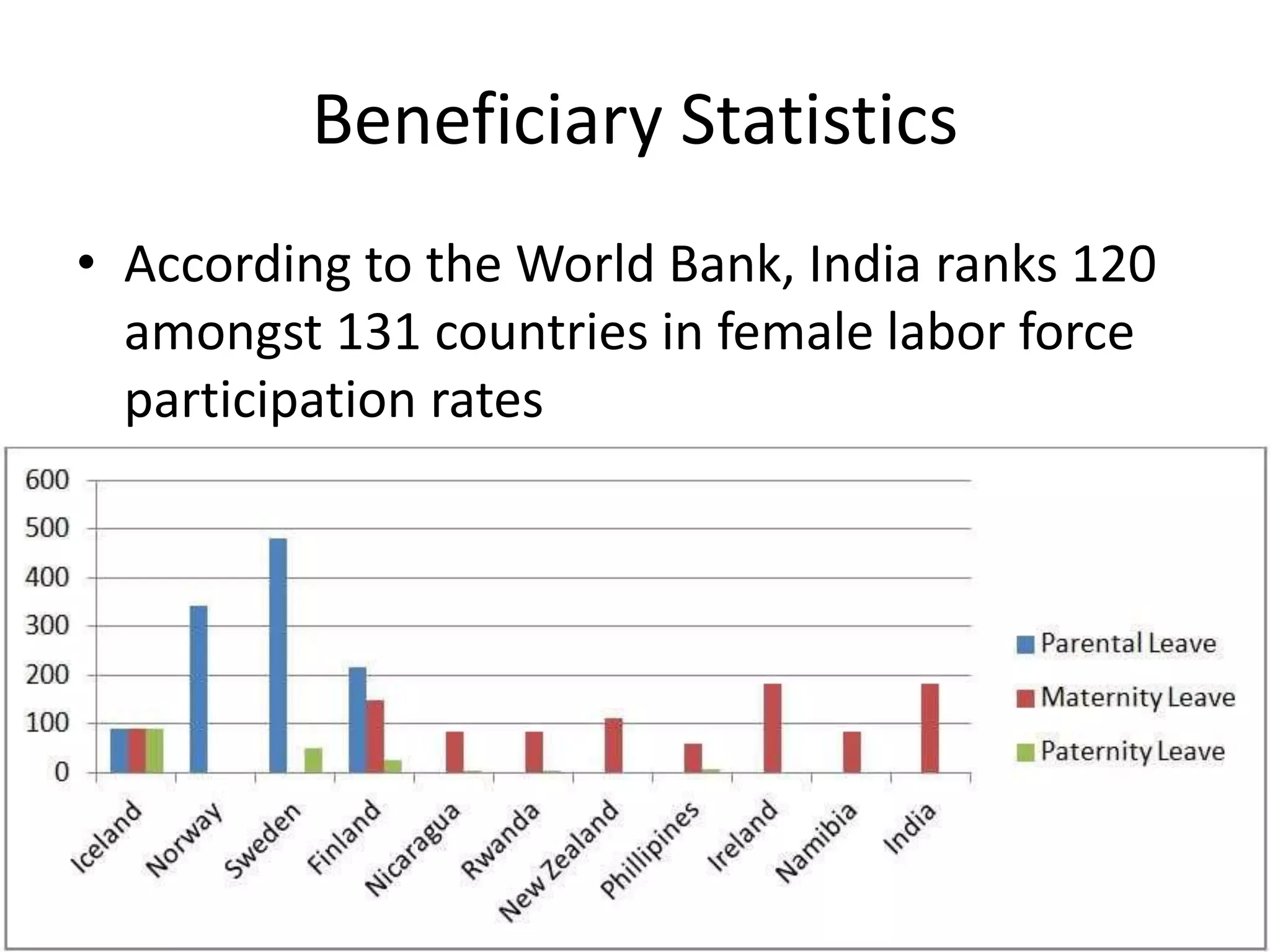
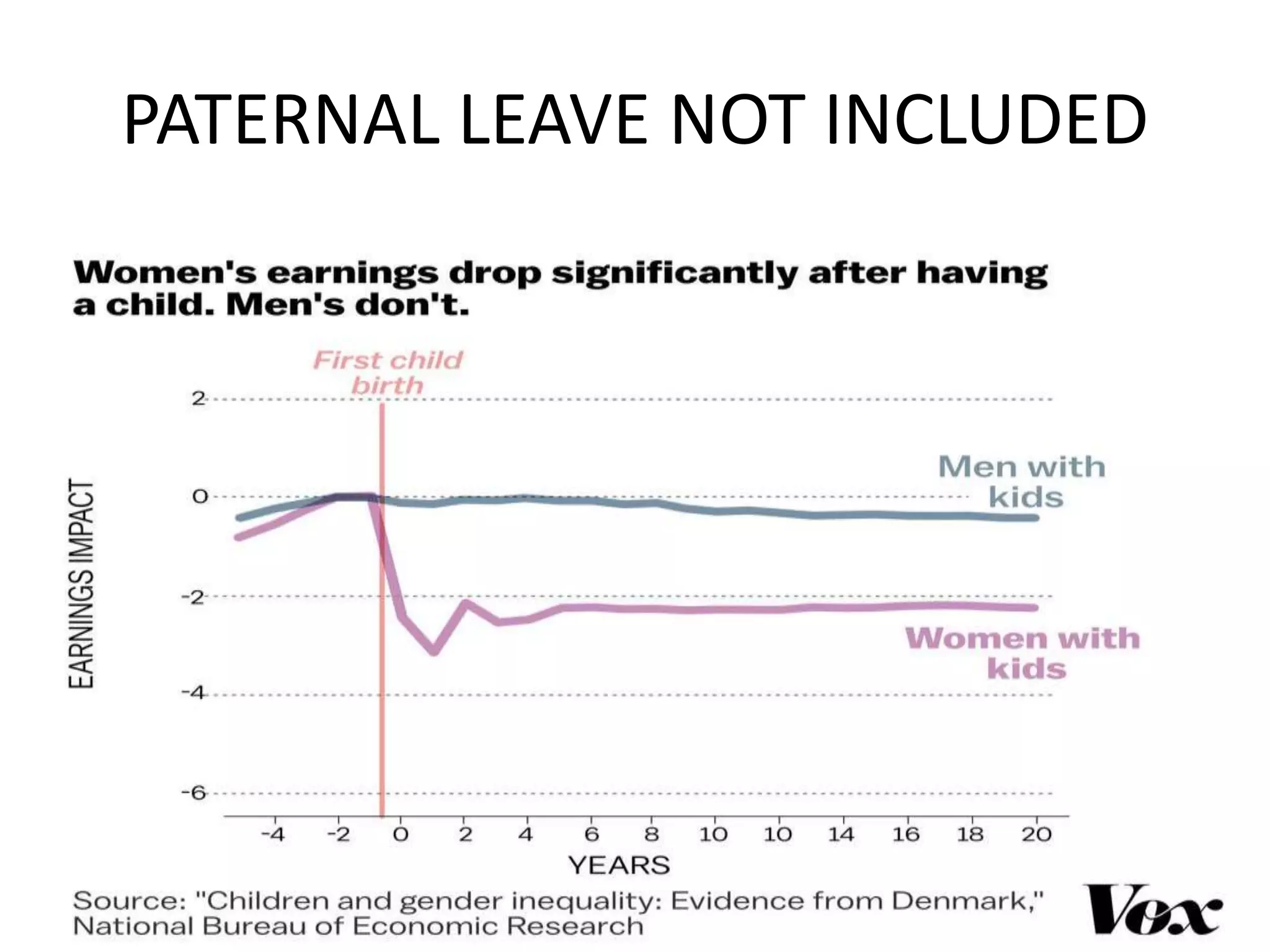
The Maternity Benefit Act, 1961 aims to protect the dignity of motherhood by providing financial and non-cash benefits to pregnant women, including paid leave before and after childbirth. The Maternity Benefit (Amendment) Act, 2017 expanded these benefits to include increased maternity leave and provisions for adoptive mothers. Challenges for women include gender inequality in hiring, resignation post-pregnancy, and lack of childcare facilities, highlighting the need for further support in balancing work and family responsibilities.