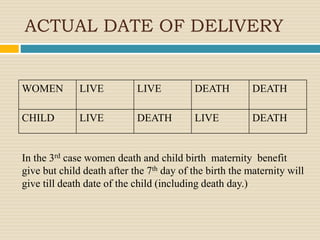
The Maternity Benefit Act 1961 aims to regulate the employment of women during pregnancy and after childbirth. It provides for maternity leave, wages, and other benefits. Key provisions include:
- Women are entitled to 26 weeks of paid maternity leave, including 8 weeks before and after delivery.
- Employers cannot dismiss a woman or give her notice of dismissal during her absence on maternity leave.
- Women are entitled to medical bonus of Rs. 3,500 if the employer does not provide pre-natal and post-natal care free of charge.
- Employers with over 50 employees must provide childcare facilities. Women can breastfeed children under 15 months with two additional breaks per day