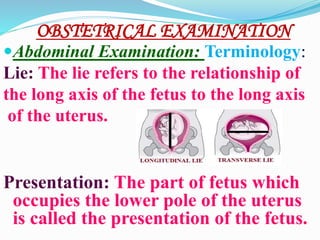
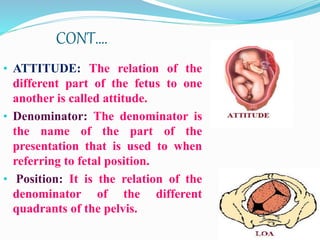
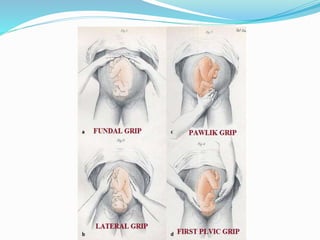
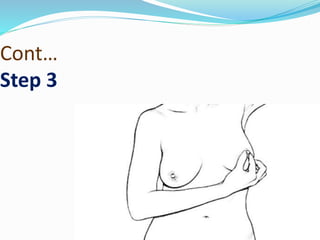
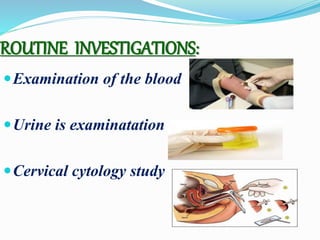
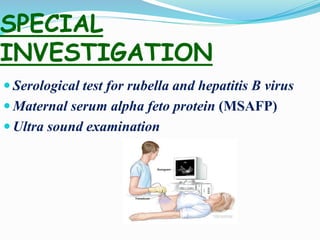
This document outlines maternal assessment measures during antenatal care. It defines antenatal care and states its aims to monitor the mother's and fetus's health and provide support and information. The objectives are to assess health status, screen for high-risk pregnancies, formulate management plans, and obtain baseline information. Components of assessment include history taking, obstetric examination including abdominal and vaginal exams, and routine tests of blood, urine, and cervical cytology along with special tests like ultrasounds. Key terms related to fetal position, lie, and presentation are also defined.