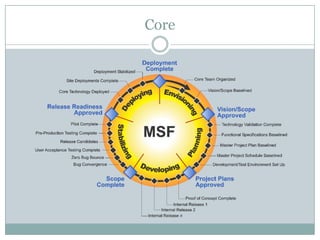
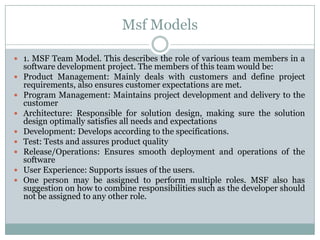
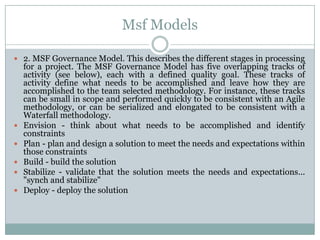
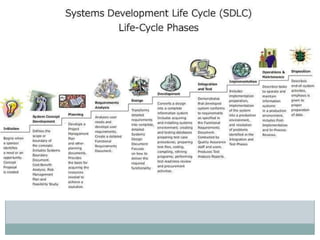
This document discusses Microsoft Solutions Frameworks. It outlines 8 foundational principles that form the backbone of MSF models and disciplines, including open communication, shared vision, empowerment, accountability, business value, agility, quality, and learning from experiences. It describes 2 MSF models: the team model which defines roles like product management, program management, architecture, development, test, release/operations, and user experience. It also describes the governance model which defines 5 overlapping activity tracks - envision, plan, build, stabilize, and deploy - that can be performed quickly for agile methodologies or serialized for waterfall. Finally, it provides a brief definition of agile software development which uses iterative development, collaboration between cross-functional teams