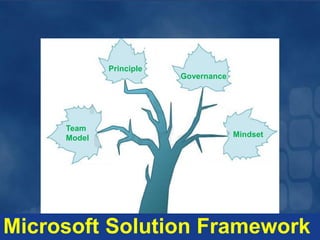
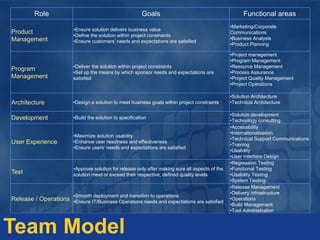
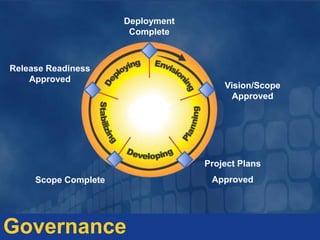
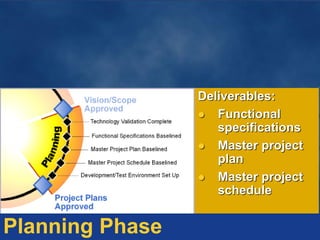
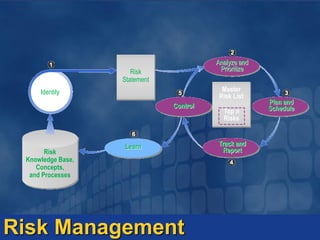
The document outlines principles and frameworks for effective project management, emphasizing the importance of governance, communication, accountability, and customer collaboration. It highlights the need for a shared vision and adaptive team structures to enhance agility and quality in technology solutions. Key roles and deliverables within the Microsoft Solutions Framework (MSF) are detailed, aiming to minimize project risks and optimize value delivery.