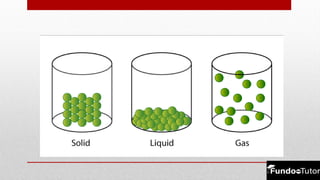
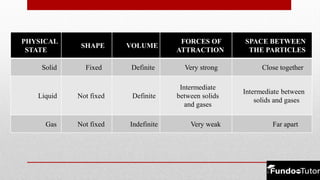
Matter is composed of tiny particles called molecules, which are groups of atoms bonded together. The physical states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—reflect differences in shape, volume, and the forces of attraction between the particles. Matter can change states through processes like melting, freezing, evaporation, and condensation, depending on temperature changes affecting the molecular arrangement.