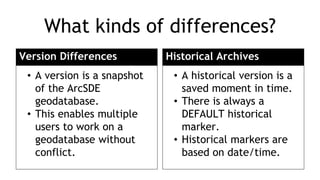
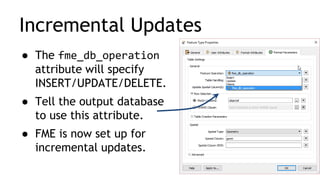
The document discusses enhancements in FME 2016.1 for managing various database formats, including ESRI geodatabase, PostGIS, and Microsoft SQL Server. It highlights new functionalities such as SQL editing, extracting differences between database versions and snapshots, and automating synchronization processes. Additionally, it provides resources and webinars for users to enhance their skills in working with geodatabases.