1) The study aimed to develop an automated routine for precise brain volume measurement in patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) using magnetic resonance (MR) images.
2) A k-nearest neighbor (kNN) classification approach was used, which requires manually segmented training data. The routine included brain extraction, inhomogeneity correction, and kNN classification to generate probability maps for different brain structures.
3) The routine was evaluated on MR images from 39 aSAH patients and 25 controls. Evaluation showed fractional similarity indices of 0.98, 0.93 and 0.92 for intracranial volume, total brain and lateral ventricles respectively, comparable to
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 1
Automated Measurement of Brain Volume
in Patients after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid
Hemorrhage
Anne Kaspers, Biomedical Image Sciences, University Medical Centre Utrecht
Abstract—Accurate and precise brain segmentations of cerebral abnormalities present in patients after aSAH, like
Magnetic Resonance (MR) brain images from patients after enlarged ventricles. k-Nearest Neighbor-based probabilistic
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) are hard to
segmentation (kNN) [8] is a supervised pattern recognition
acquire by an automated routine due to presence of various
cerebral abnormalities, like enlarged ventricles. Available method which can perform precise and accurate brain volume
routines neither dealt with theses abnormalities nor were suited measurement [7], for which training data can be obtained from
for MR images with high magnetic field strength or used different high resolution MR brain scans containing variety of
techniques with limited accuracy and precision. In order to
perform accurate and precise brain volume measurements for 3 cerebral abnormalities.
T aSAH MR images, we created a new routine in which we tried In this study we aimed therefore to design a new, automatic
to deal with these cerebral abnormalities. Measurements of routine for quantification of cerebral structure volumes in
intracranial volume, total brain, lateral ventricles and peripheral
patients after aSAH, based on kNN using manually segmented
cerebrospinal fluid were performed on T1 and T2 weighted MR
images of 39 patients and 25 control participants using k-Nearest MR image training data.
Neighbor (kNN) classification. Evaluation showed a fractional
Similarity Index (fSI) of 0.98, 0.93 and 0.92 for respectively intra-
cranial volume, total brain and lateral ventricles, which are
equally good as the inter-observer results.
II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
A. Data
Index Terms—Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage; k-
Nearest Neighbor classification; Magnetic Resonance imaging;
Segmentation For training 10 and for validation 12 scans of patients after
aSAH and of age- and sex-matched control participants were
included, which were obtained between 2005 and 2007.
I. INTRODUCTION
Patients who were screened on aneurysmata were included as
control participants.
A
NEURYSMAL SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHA-
Patients were excluded if they had additional aneurysms
GE (aSAH) is a type of stroke, caused by a ruptured
treated with neurosurgical clips that either contained
intracranial aneurysm [1]. The annual incidence of a
ferromagnetic material or were located less than 20 mm from
non-traumatic aSAH varies from 6 - 8 cases per 100,000
the coiled aneurysm, had a cardiac pacemaker, were
person-years [2]. Almost half died within thirty days [3] while
claustrophobic or younger than 18 years [9].
almost half of the survivors suffered from significant cognitive
MRI scans were acquired on a 3T Philips magnetic
and neurological or cognitive deficits after a year [4]. It is
resonance imaging system using a standardized protocol (24
assumed that the size of neuropsychological deficits,
contiguous slices, voxel size: 0.45 × 0.45 × 4.0 mm) and
commonly detected after treatment of ruptured intracranial
consisted of an axial T1-weighted (repetition time in ms [TR]:
aneurysms is associated with the loss of cerebral volume [5].
500, echo time in ms [TE]: 10) and T2-weighted sequence
Study by Bendel showed enlargement of cerebrospinal fluid
(TR: 3000, TE: 80).
(CSF) and ventricular volume in patients after aSAH, using
the technique of voxel-based morphometry (VBM) [6].
However, the accuracy and precision of VBM is limited since
its measurements are based on an average brain, which is not B. Image processing
specific for aSAH patients [7]. Existing routines, which are
based on training data of Magnetic Resonance (MR) brain Routine steps
images, were not suited to measure significant volume
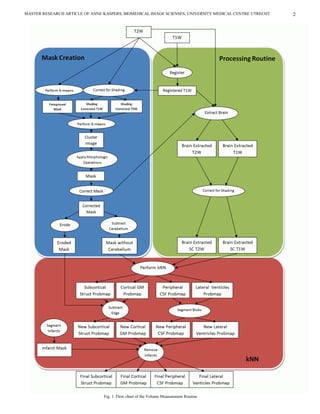
differences in scans of patients after aSAH. This is partly In figure 1, all routine steps from provided images to
because they were made for MR image data with too low resulting probability maps are schematically visualized.
magnetic field strength, and partly because they lacked](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/75/Master-research-article-1-2048.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 3
First, the T1-weighted image was rigidly registered to the threshold, were summed to get a basic mask (figure 2D).
T2-weighted image by using Elastix [10]. To exclude remaining non-brain structures and fill holes, a
To exclude hyper-intense non-brain structures like skull and number of morphological operations were performed. An
fatty tissue, a brain mask was created by an automated routine, erosion with a round, 11 voxels wide kernel separated non-
based on the k-means algorithm [11], which used both the T1- brain structures from the brain. These structures were removed
and T2-weighted image (figure 2A). The first non-empty slice by segmenting groups of attaching mask voxels, further
was used 5 times to get more hyper-intense background mentioned as blobs, and keeping only the largest blob.
information for k-means clustering. A foreground mask was Dilation with the same kernel as used for erosion restored the
created using k-means clustering with a small sample set, old borders (figure 2E). A set of 6 dilations with a round, 9
previous to full k-means clustering (figure 2B). Scan voxels wide kernel filled holes while kept the shape of the
inhomogeneities were corrected by a shading correction mask edge intact. The mask was brought back within its
algorithm using a multiplicative 4th order correction model on original borders by 7 erosions with the same kernel (figure
all voxels covered by the foreground mask [12]. In full k- 2F). A maximum of the brain mask with holes and the eroded
means clustering, all shading corrected T1 and T2 intensities mask restored the old borders while holes remained filled
were taken as samples in a 2D feature space, which only (figure 2G). At the end of the routine 3 dilations with a 7
contained intensity parameters. The algorithm tried to find 10 voxels wide, round kernel increased the margin to include all
means, which minimized the sum of Euclidean distance of all CSF below the skull. Since only the cerebral volume was
samples to their nearest mean. Each voxel was classified to the important for our study, the cerebellum was manually
cluster number of their nearest mean, which resulted in 10 segmented (figure 2H).
brain clusters and 1 background cluster, derived from the The T2 image and the registered T1 image were multiplied
foreground mask (figure 2C). voxelwise by their corresponding mask including cerebellum
To select clusters suitable for the brain mask, cluster and inhomogeneities were corrected [12], resulting in brain
numbers were counted for a fixed selection of approximately extracted shading corrected images, which were used for kNN
1/3 of the voxels located in the center of the cluster image. classification (figure 1, processing routine).
The 4 largest clusters and extra clusters, which size exceeded a As post-processing, small groups of attaching probabilities,
Fig. 2. k-Means mask routine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-3-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 4
further mentioned as blobs, were transferred from the lateral inclusion of a representative selection of all shading areas in
ventricles to the peripheral CSF probability map; only the the training data, which would enlarge the overlap of structure
largest blob was not transferred. Afterwards, a visual check samples in feature space. In figure 4, T1 and T2 weighted
was done to move back wrongly transferred blobs. intensities of samples from a training data patient with
To remove as subcortical structures and cortical grey matter numerous parenchymal high-signal intensity lesions on T2-
misclassified background outside the brain, the mask was weighted MRI are shown before and after inhomogeneity
eroded 2 times with a round, 7 voxels wide, kernel and voxels correction. Both the T1 and T2 weighted image added
of subcortical structures and cortical grey matter outside the information, which showed the different range of structures on
eroded mask were excluded. Infarcts, drain trajectories, the x- and y-axis. After correction, intensities of all structures
meningiomas, etcetera, significantly diminished classification were more concentrated and distinctive. Cortical grey matter,
outcome and were manually segmented and removed from the peripheral CSF and parenchymal lesion intensities were better
probability maps. In figure 3, an example classification separated from each other while there was still overlap
outcome of one participant is shown. between subcortical structures and cortical grey matter, which
could be explained by the unclear border in both the T1 and
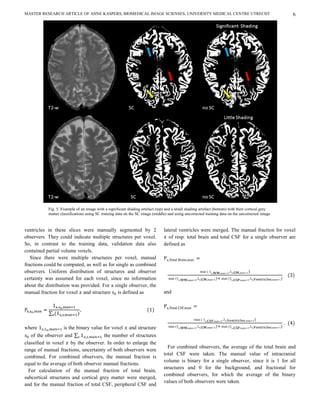
T2 weighted image. The effect of inhomogeneity correction to
Routine choices cortical grey matter classification is shown in figure 5 for a
participant scan with little and one with significant shading.
In this study, volume measurements of subcortical After correction, cortical grey matter was better classified on
structures, cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF and lateral the shading area, which made the segmentation more uniform.
ventricles were performed. Besides these structures, other To create a proper brain mask, we designed an automated
structures were included in the masked area, further mentioned routine, based on the k-means algorithm [11]. It was extended
as background, which needed to be included in the training with cluster selection and a set of morphological operations to
data to prevent misclassification. Assignment of all not fill holes, caused by exclusion of small clusters in the brain,
classified voxels as background in the training data would while original borders were maintained. Parameters for cluster
incorrectly assign partial volume brain structure voxels to the selection were determined by testing values close to the
background. Assignment of only hypo-intense voxels as settings which were used in a study by Jongen [13] on our
background would lead to misclassification of hyper-intense training data. In contrast to the mask routine used by Jongen,
background to closely located brain structures with similar we automated cluster selection by setting a cluster size
intensity. Therefore, we put a manual selection of non-partial threshold, which provided good cluster selection for 9 of the
hypo- and hyper-intense background in the training data. 10 training data images. After cluster selection, a large number
Remaining misclassified skull and fatty tissue classified as of small dilations, followed by one more number of small
subcortical structures and cortical grey matter was removed if erosions was used instead of a large morphologic closing, to
it was located within 6 voxels of the edge of the brain mask, fill large holes without loss of border detail. Holes close to the
under the assumption that only peripheral CSF could be border were filled while the original border was kept intact by
located there. taking voxelwise the maximum of the unclosed mask and the
The provided T1 and T2 weighted MR brain images closed, eroded mask.
contained a shading artefact, which diminished intensity For a selection of participants, results of k-means and the
homogeneity for each brain structure. We applied Brain Extraction Tool (BET) were compared [14]. In normal
inhomogeneity correction [12], assuming its effect to the cases BET performed similar to k-means, but in cases with
classification could be large since the orientation of the shaded large infarcts k-means performed better. In k-means we could
area is different for each scan, which makes it hard to handle determine the number and selection of clusters to be classified.
by kNN. Preventive removal of shading seemed better than
Fig. 3. A registered T1 and T2 weighted image and corresponding kNN probability maps of subcortical structures, cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF and
lateral ventricles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-4-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 5
Fig. 4 A. Scatter plot of voxel intensities of the original T2W image relative to the registered original T1WFFE image of one patient from the
training data. Five structures are indicated: subcortical structures (SCS), cortical grey matter (CGM), peripheral (per.) CSF, lateral (lat.) ventricles
and parenchymal (par.) lesions B. Same for shading corrected intensities.
This allowed us to include large infarcts and exclude hyper- C. Training data routine
intense background. BET often considered infarcts as non-
brain structures, which caused large gaps in the mask. Since a The training data consisted of non-partial volume
larger part of the patients after aSAH had infarcts (n = 40), we segmentations of 10 participant scans (JB). It is a
chose to use k-means instead of BET. representative selection of the dataset (Appendix A),
All blobs in the lateral ventricles probability map, except the composed of scans of patients after aSAH and control
largest were transferred from the lateral ventricles to the participants, which varied in modified Rankin Scale [15] and
peripheral CSF probability map, under the assumption that all size of the lateral ventricles. The segmentations contained
lateral ventricle voxels attach to each other. However, this background and 4 brain structures: subcortical structures,
assumption was not valid in all cases because of the large slice cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF and lateral ventricles. For
thickness. Manual adjustment was needed for some posterior all training data participants pre-processing was performed
and inferior ventricle horns. Nevertheless, this operation was (section C). A fixed, random selection of 40% of the manually
an easy way to get improvement. segmented structures and background was saved by their brain
Since we were only interested in volume measurements of extracted shading corrected T1 and T2 weighted intensity and
brain structures in the cerebrum, we needed to segment the spatial parameters. The kNN algorithm could calculate
cerebellum. However, presence of subcortical structures, distances in feature space to obtain structure probabilities of
cortical grey matter and peripheral CSF in both cerebrum and partial volume samples.
cerebellum complicated kNN classification and search for
better methods exceeded the project scope, so we segmented
the cerebellum manually. Because the border between
cerebrum and cerebellum was unclear, specific segmentation D. Validation routine
rules had to be defined to guaranty consistency.
Right or left hemispheres were selected randomly
throughout the brain from 12 participant scans of whom 6
were from the training data and 6 from other data. Subcortical
structures, cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF and lateral](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-5-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 7
E. Evaluation
where is the sum of minima of the
The agreement of observer segmentations and the automatic reference and segmentation probabilities, equivalent to the
segmentation, acquired by kNN classification, and the inter- sum of true positives, is the sum of reference
observer agreement, were measured by a variant of the Dice probabilities, equivalent to the sum of true positives and false
similarity index (SI) [16, 17] . The SI formula assumes binary negatives, is the number of
values for both the reference and the segmentation. It is voxels minus the maxima of the reference and segmentation
defined as probabilities, equivalent to the sum of true negatives, and
is the number of voxels minus the sum of
reference probabilities, equivalent to the sum of true negatives
and false positives.
The reference and segmented volume were determined by
multiplication of and to the volume of 1
voxel in milliliters. The difference was examined to detect
over- or under-segmentation of the automated structure
where “Ref” denotes the volume of the binary reference,
volumes.
“Seg” is the volume of the binary segmentation, “Ref ∩ Seg”
Inter-observer and routine fSI and sensitivity scores of
denotes the volume of the intersection of the binary reference
subcortical structures, cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF,
and binary segmentation, is the sum over all voxels
lateral ventricles, total brain, total CSF and intracranial
in the binary reference, is the sum over all voxels, volume were analyzed. To investigate if inclusion of training
where in the binary reference the intensity value equals 1 and data in the validation data improved validation scores, fSI
idem for the binary segmentation. scores were compared for a validation set of only training data
Because we calculated manual fractions for the observer to a validation set of non training data.
segmentations, and kNN classification provided probabilistic
segmentations, the fractional Similarity Index (fSI) was
measured [18]. It is defined as III. RESULTS
Table I shows the inter-observer validation results for all
structures. Apart from peripheral CSF, fSI scores of all
structures are good with a score of 0.82 for cortical grey
matter and total CSF, 0.95 for lateral ventricles and total brain
and even 0.98 for intracranial volume. Contrary to their high
where is the manual fraction, computed for single fSI score, sensitivity of cortical grey matter is moderate with a
observers (formula 1) or combined observers (formula 2). score of 0.77.
Notice that in case probabilistic values are substituted for Table II shows the routine validation results for all
binary values, the fSI formula is equal to the SI formula. The structures. Intracranial volume, total brain and lateral
agreement of the probabilistic manual segmentations with the ventricles scored well with fSI scores of resp. 0.98, 0.93, 0.92
automatic segmentation and the inter-observer agreement were and similar sensitivity scores. Subcortical structures scored
measured with the fSI. less with a fSI score of 0.83 and a sensitivity score of 0.88.
Besides the fSI, also the sensitivity and specificity were Total CSF, cortical grey matter and peripheral CSF scored
measured, which are more common quality indicators and moderately with fSI scores of resp. 0.77, 0.76 and 0.71.
therefore makes the validation outcome comparable to other
studies. They are defined as
and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-7-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 8
TABLE I TABLE II
INTER-OBSERVER VALIDATION RESULTS ROUTINE VALIDATION RESULTS
Tissue type Sensitivity Specificity fSI Tissue type Sensitivity Specificity fSI
Subcortical structures 0.89 0.99 0.87 Subcortical structures 0.88 0.98 0.83
Cortical grey matter 0.77 0.99 0.82 Cortical grey matter 0.70 0.98 0.76
Peripheral CSF 0.87 0.99 0.77 Peripheral CSF 0.74 0.99 0.71
Lateral Ventricles 0.95 1.00 0.95 Lateral Ventricles 0.92 1.00 0.92
Total Brain 0.93 1.00 0.95 Total Brain 0.92 0.99 0.93
Total CSF 0.90 0.99 0.82 Total CSF 0.80 0.99 0.77
Intracranial 0.98 1.00 0.98 Intracranial 0.98 0.99 0.98
IV. DISCUSSION segmentation was not feasible, since parenchymal high-signal
intensity lesions and lateral ventricles were both hyper-intense
In this paper we proposed a kNN based routine to segment on T2-weighted MRI and closely located to each other, and
subcortical structures, subcortical grey matter, peripheral CSF occur on different locations and in different amounts.
and lateral ventricles on 3T T1 and T2 MR brain images of Therefore, they were combined with subcortical structures to
patients after aSAH. To measure subtle differences in brain which they belong anatomically.
volumes, high accuracy and precision were required.
Therefore, we based our routine on the kNN algorithm, which
is an accurate and precise method, and used accurate training B. Validation issues
data of an expert and automated most routine steps for optimal
precision. The fSI scores of intracranial volume, total brain In order to fully exploit the observer segmentations, they
and lateral ventricles were good, while subcortical structures, were combined into manual fractions, which take partial
total CSF, cortical grey matter and peripheral CSF scores were volume into account. Both observers got equal share, even if
lower. one observer did not assign any structure. Information about
the distribution of multiple structures in a voxel was not
indicated by the observers, so we considered equal importance
of all structures. For example, three structures in a voxel all
A. Classification issues
got a probability of 1/3, in case of one observer. In reality, one
of the three structures could be dominant and should have a
The low scores of cortical grey matter, peripheral and total
higher probability. For all partial volume voxels where
CSF are partially explained by the slice thickness (4 mm),
structures were not equally distributed, manual fractions
which exceeded the thickness of cortical grey matter (2-4 mm)
deviate, which caused lower classification scores. However,
and peripheral CSF (± 2 mm) [19], which made it largely
consist of partial volume. Subcortical structures and especially
cortical grey matter both have a lower fSI score than total
brain. This is partly explained by the large overlapping area
between subcortical structures and cortical grey matter, where
partial volume correction caused rounding errors, and partly
by the perivascular spaces, which were misclassified as
cortical grey matter (figure 6).
Several studies showed that fluid attenuation inversion
recovery (FLAIR) images were more suitable for classification
of parenchymal high-signal intensity lesions on T2-weighted
MRI since it showed them hyper-intense and ventricles hypo-
intense [20]–[23]. In a study by Anbeek, its optimal SI score
decreased from 0.81 to 0.63 when FLAIR images were
excluded from training data, which consisted of inverse
recovery (IR), proton-density (PD), T1 and T2 weighted Fig. 6. Example of perivascular spaces misclassified as cortical grey matter.
images [24]. Because we did not have FLAIR images, good](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-8-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 9
we assumed that in a voxel, dominant structures will always strongly on the composition of the training data, in which
be noticed by both observers and inferior structures could be cerebral abnormalities were included. Samples of the training
missed by one observer, which will compensate for some of data were consistently used by kNN for precise classification.
the deviation. Because kNN effectively measured spatial and intensity
Manual fractions could only take a limited number of values, distances in feature space, only a small training set of non-
while kNN output had a wide range. Hence there was always partial voxels was enough to deal with partial volume. The k-
an error margin added, which decreased our fSI scores. We means algorithm, which was used for brain mask creation, is
chose not to threshold kNN output to the range of manual also simple and provides precise cluster images, under
fractions because it would change results for validation assumption that sufficient samples were taken. With the use of
reasons, while the unadjusted results were used for volume our defined set of morphological operations, cluster images
measurement. could be transformed into closed masks, which kept original
Using fSI instead of SI is an improvement because it could borders unchanged. Hence, the core of our routine is clear and
deal better with partial volume. Probabilistic outcome of our simple so we could focus on application specific processing
kNN routine did not have to be rounded and information of for improvement of kNN results. Apart from cerebellum
multiple structures of both observers could be utilized segmentation, all steps in our routine were automated.
effectively. However, fSI scores were not used in other studies Selection of appropriate training data may require lots of
so far and could therefore not be compared. Measurement of expensive man hours, although a study by Vrooman showed
the SI and fSI between observers was possible, since their that automatic training with kNN is possible and routine steps
segmentations are binary and could be transformed to need only little adaption for general use [25]. Hence, its
fractions. The relation of fSI to SI scores could therefore be application is feasible and additions and changes could be
examined. Generally, the fSI scores were lower than SI scores, tested without much human intervention.
especially for structures with lots of partial volume, like
peripheral CSF and total CSF, because the SI formula did not
correct for partial volume. Usually a SI of 0.80 or higher is D. Strengths and limitations
considered a good segmentation and given that fSI is probably
stricter than SI, we considered the same for fSI. Compared to The strength of the present study is the usage of non-partial
the optimal SI values of the kNN based routine used by volume samples in the training data for kNN classification.
Anbeek, which were based on PD, T1 and T2 weighted scans, Accuracy of brain volume was evaluated using small,
the present routine scored similar and even higher for lateral representative manual segmentations, which contained partial
ventricles. This is true while fSI is stricter and PD weighted volume information, while other brain volume measurement
images were not included [24]. The high fSI score for lateral studies use binary manual segmentations. Precision of brain
ventricles could be explained by the larger ventricle volume of volume could be evaluated because data was selected from a
patients after aSAH. Larger ventricles consist mostly of non- significant number of scans with variety of cerebral
partial voxels, which could better be classified than partial abnormalities. For optimal precision, a standardized scanning
volume voxels. An even lower optimal SI for cortical grey protocol was used for acquiring images of the data set.
matter, compared to our fSI score, indicated that our routine Automated routine steps ensured consistency whereas manual
did not fail but performed well using the kNN algorithm and steps were consequently performed, like cerebellum
the provided imagery. segmentation.
Validation scores of the single observers versus the A limitation of the present routine is that many cerebral
automatic routine were approximately similar as the combined abnormalities, like infarcts and perivascular spaces, could not
observers versus the automatic routine. Adding extra be processed automatically. However, we had accurate manual
information of uncertainty did not improve the scores. Leaving segmentations of those cerebral abnormalities to our disposal,
training data out of the validation data did not change the so this limitation did not hinder accurate brain volume
scores significantly, which indicated good classification measurements. The small number of observers limited the
quality for new participant scans. evaluation because only 6 different values could be assigned
to the manual fractions, while kNN probabilities could have
100 different values, but it is still better than using binary
C. Application manual values.
Present routine is based on the kNN algorithm, which can
deliver precise and accurate results, while it is also simple and
fast. Its quality depends apart from the quality of the images,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-9-320.jpg)
![MASTER RESEARCH ARTICLE OF ANNE KASPERS, BIOMEDICAL IMAGE SCIENSES, UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE UTRECHT 10
V. CONCLUSION A.2 Cross-sectional routine
In this paper, we proposed an automated routine for brain For all participants in the SAH database, pre-processing was
volume measurements on MR brain images from patients after performed as mentioned. In two cases, only 3 clusters were
aSAH. We extended kNN classification with processing steps, taken in k-means and in 5 cases an extra cluster was added
which we described and evaluated. Lateral ventricles, total when a good cluster image initially did not result in a good
brain and intracranial volume, have good validation scores mask. For some masks, eyes were removed, moderate
while structures with more partial volume scored worse. It imperfections were adjusted or k-means was performed with
could be explained by validation limitations, since visual fewer clusters because of movement artifacts, infarcts,
inspection showed good performance for structures with much bleedings or without clear reason.
partial volume, like peripheral CSF. Post-processing on kNN probability maps were performed,
where in 18 cases, one or two ventricle horns, which voxels
did not attach to the lateral ventricles voxels, had to be
VI. FUTURE PROSPECTS manually moved back from peripheral CSF to lateral
ventricles.
Most cerebral abnormalities present in patients after aSAH Automated segmented volumes of all structures were
were manually segmented, but could be automated after more calculated by multiplication of the size of one voxel in
study or under other conditions. For accurate automatic milliliters to the sum of all probabilities. For the validation
cerebellum segmentation, sagittal images may be needed, data, the difference between the automated and manual
since they show the border between cerebrum and cerebellum volume and the average volume for all validation participants
clearer. Validation scores of structures with much partial were calculated.
volume should increase with the number of observers, because The total volumes of structures were calculated by
it makes the manual fraction more accurate. These multiplication of the sum of their probabilities to the voxel
assumptions need to be addressed in further studies. volume in milliliters.
The results of the probabilistic classification of all
structures were visually checked for all participants, and
incorrectly classified images were excluded. Also total brain
APPENDIX A
and total CSF volume were calculated. The mean and standard
deviation of the total brain, total CSF, subcortical structures,
A.1 Data cortical grey matter, peripheral CSF, and lateral ventricular
volume were measured for patients after aSAH and control
For cross-sectional volume measurements, 39 patients after participants.
aSAH and 30 control participants from the COMET study
were selected. Inclusion criteria were mentioned in chapter
Materials and Methods, section Data. Additionally, control
A.3 Cross-sectional volume measurements
participants with symptomatic ischemia were excluded. One
control participant had a large infarct because of a
neurotrauma and 3 control participants had clinically manifest Table A.I shows the mean and standard deviation of
infarcts. automated volume measurements for control participants and
patients after aSAH. As expected, patients after aSAH had
larger lateral ventricles and infarcts than control participants.
TABLE A.I
MEAN VOLUMES AND STANDARD DEVIATION OF VOLUMES IN PATIENTS WITH SAH AND CONTROL PARTICIPANTS
Peripheral CSF Lateral ventricles Total brain Total CSF Intracranial Infarct1
Control participants
232 ± 52.5 26.6 ± 10.6 978 ± 80.8 259 ± 57.4 1235 ± 125 1.10 [0.67, 1.53]
Volume (ml)
Patients with SAH
200 ± 40.4 48.0 ± 25.4 956 ± 112 248 ± 39.4 1194 ± 134 5.92 [1.49, 20.8]
Volume (ml)
Data are unadjusted mean brain volumes ± SD or 1 median infarct volumes and interquartile range](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artikelannekaspers-13081411114209-phpapp02-110615073746-phpapp02/85/Master-research-article-10-320.jpg)
