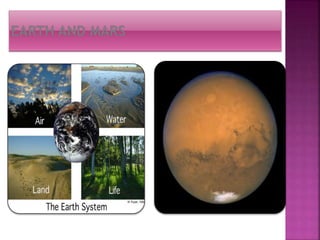
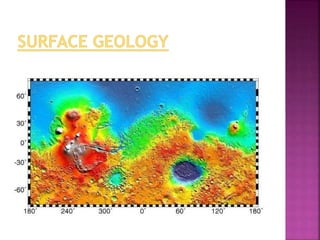
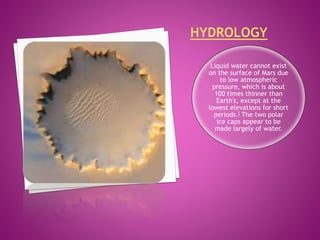
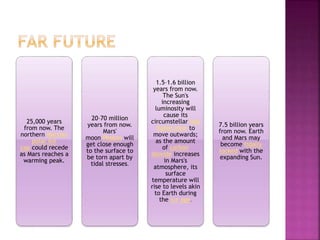
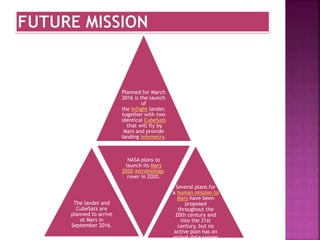
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and has characteristics that make it similar yet different from Earth. It has a thin atmosphere, seasonal changes, polar ice caps, the largest volcano in the solar system called Olympus Mons, and evidence of ancient rivers and lakes. Future missions are planned to further explore Mars, including the InSight lander in 2016 and Mars 2020 rover. The Curiosity rover has been exploring Gale Crater since 2012 and found environmental conditions that may have once supported microbial life.



















![Curiosity is a car-
sized robotic
rover exploring Gale
Crater on Mars as part
of NASA's Mars Science
Laboratory mission
(MSL).[3] As of March 20,
2016, Curiosity has been on
Mars for
1287 sols (1322 total days)
since landing on August 6,
2012.
The rover's goals include:
investigation of the
Martian climate andgeology;
assessment of whether the
selected field site inside Gale
Crater has ever
offered environmental
conditions favorable
for microbial life, including
investigation of the role of
water; and planetary
habitabilitystudies in
preparation for future human
exploration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mars-copy-170910154512/85/Mars-36-320.jpg)

