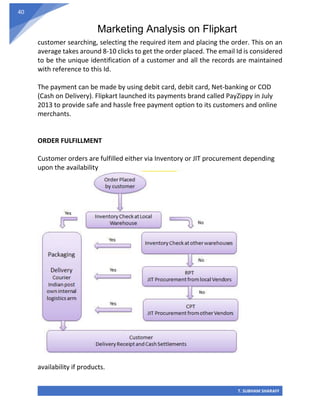
The document is a marketing analysis project on Flipkart conducted by T. Subham Sharaff as part of his B.Com degree. It explores Flipkart's business model evolution, including its transition from a consignment to a marketplace model, and highlights the company's growth in the Indian e-commerce sector. The report also includes a detailed analysis of Flipkart's supply chain management, marketing strategies, and customer service practices.