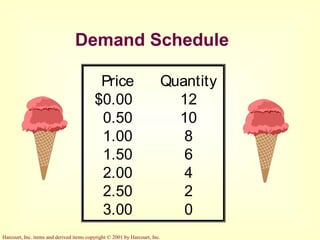
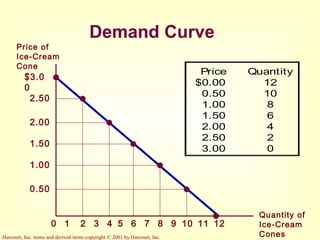
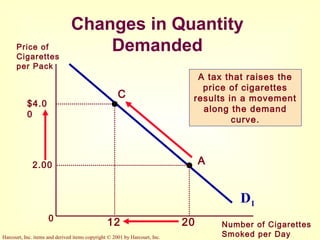
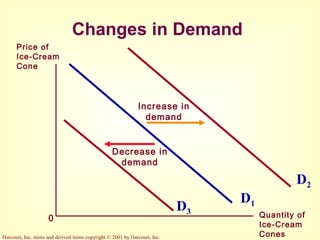
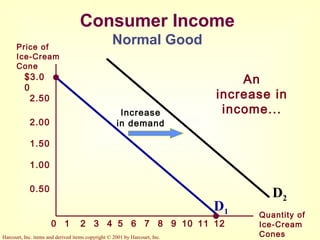
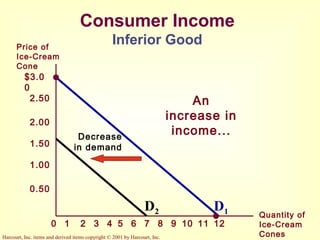
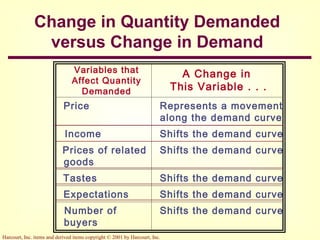
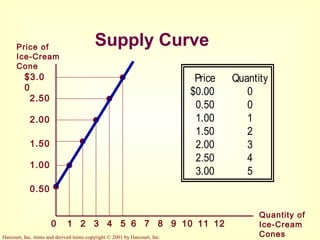
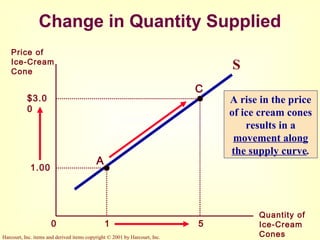
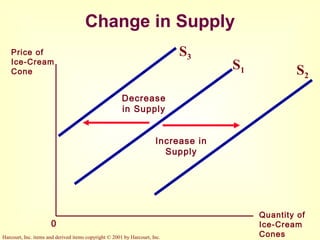
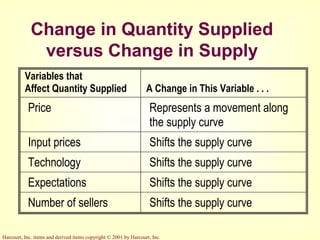
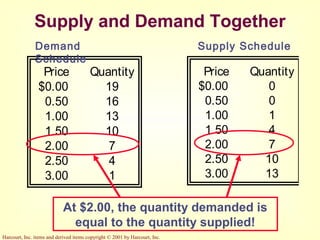
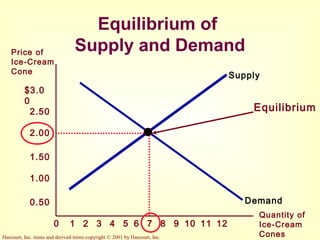
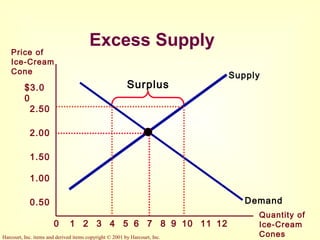
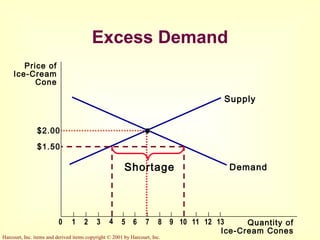
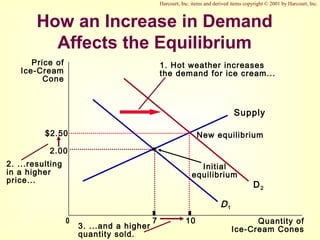
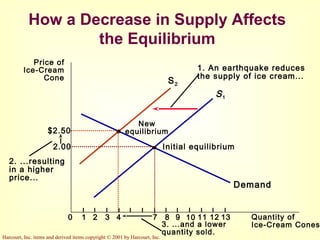
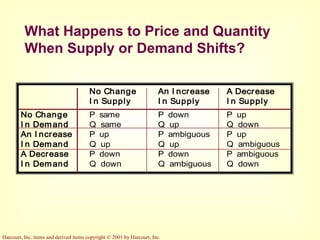
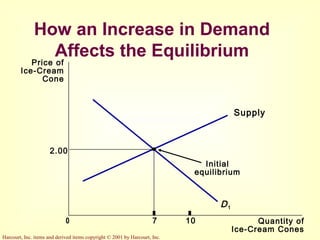
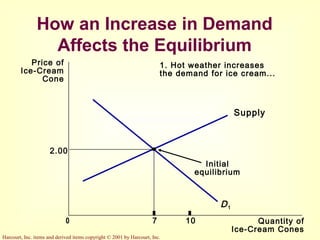
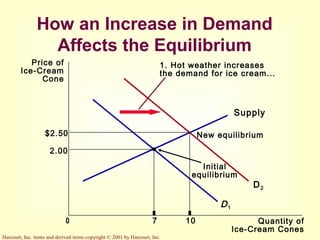
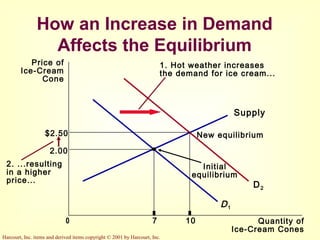
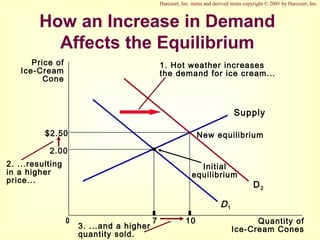
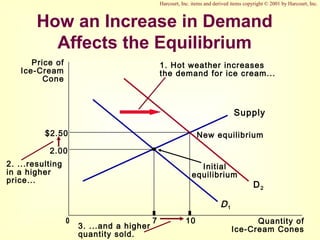
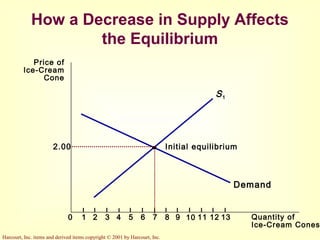
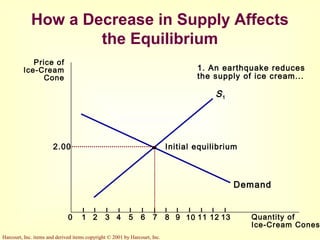
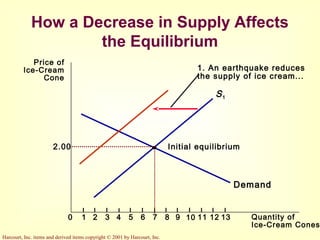
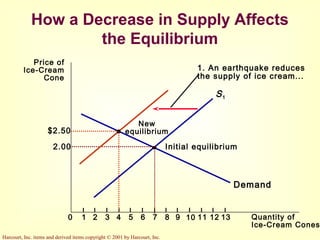
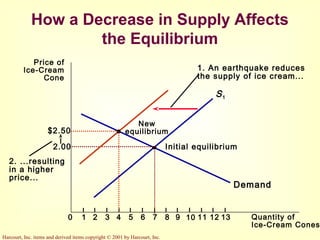
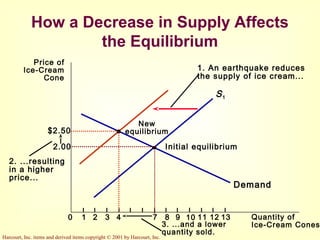
This document provides an overview of supply and demand economics. It defines key terms like markets, demand curves, supply curves, and equilibrium. Supply and demand are determined by buyers and sellers interacting in markets. The quantity demanded is influenced by price and other factors, while quantity supplied depends on price and production costs. When supply and demand are equal at a single price, the market reaches equilibrium.