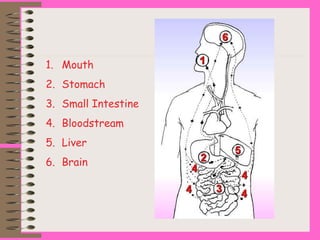
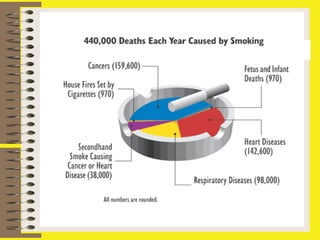
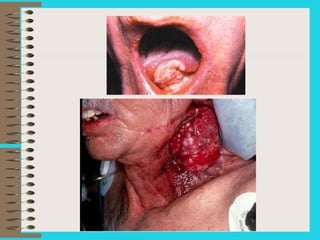
The document discusses various types of drugs including stimulants, depressants, and hallucinogens, emphasizing their effects on the body and mind. It highlights the dangers of alcohol and nicotine, detailing their physical and mental health impacts, particularly among young people. Additionally, the document outlines risk and protective factors related to drug use, stressing the importance of healthy activities and positive relationships.