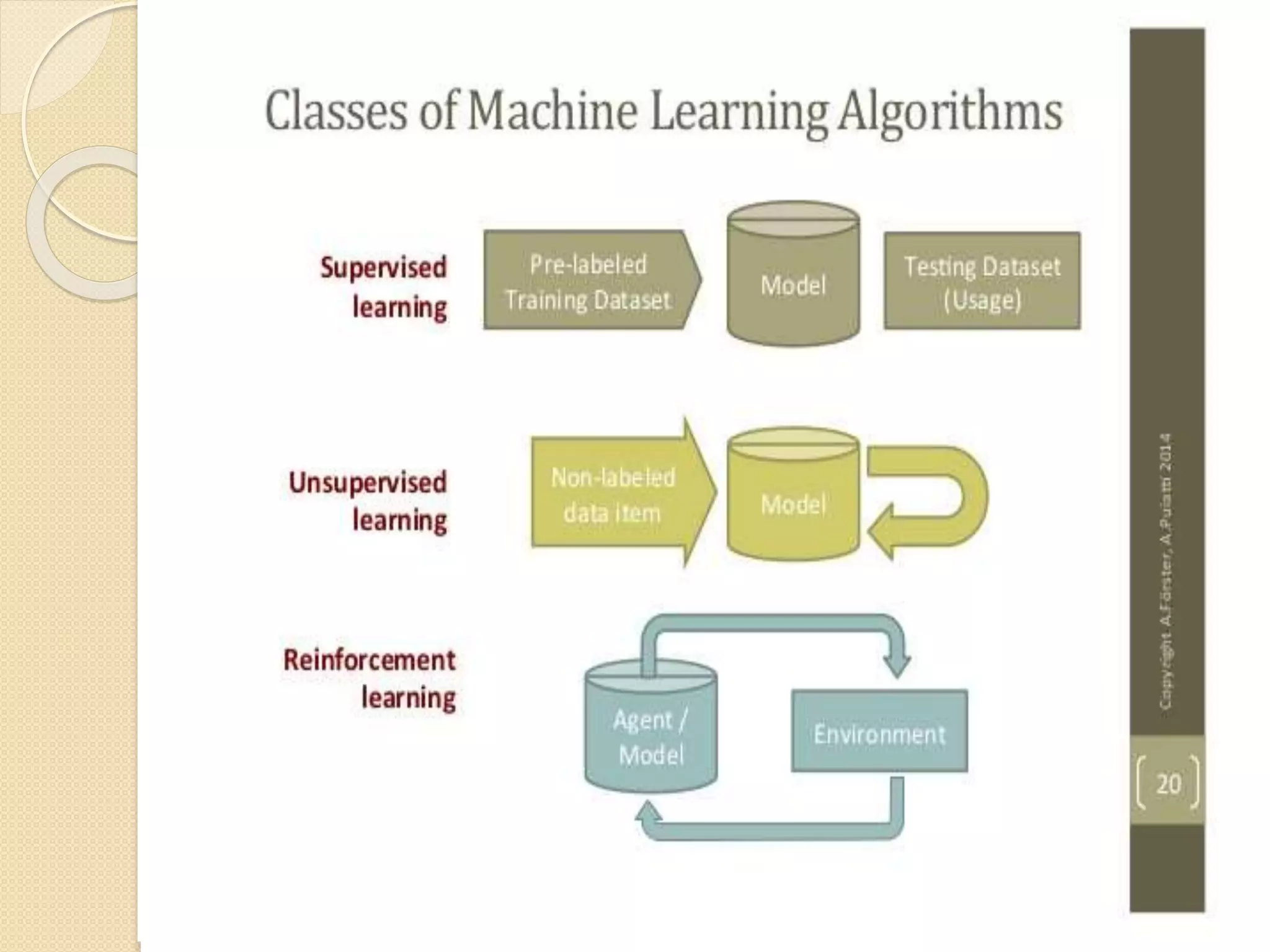
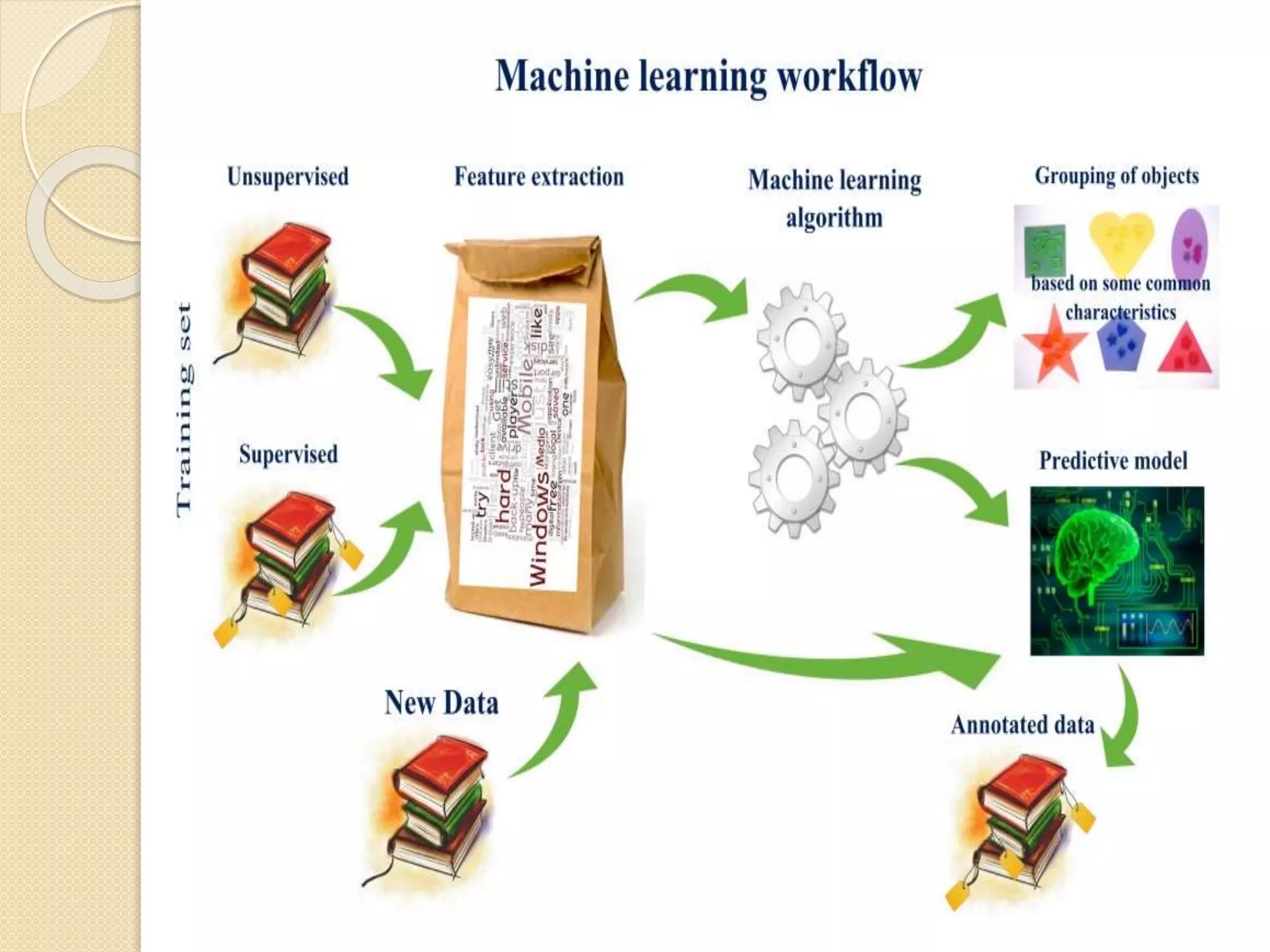
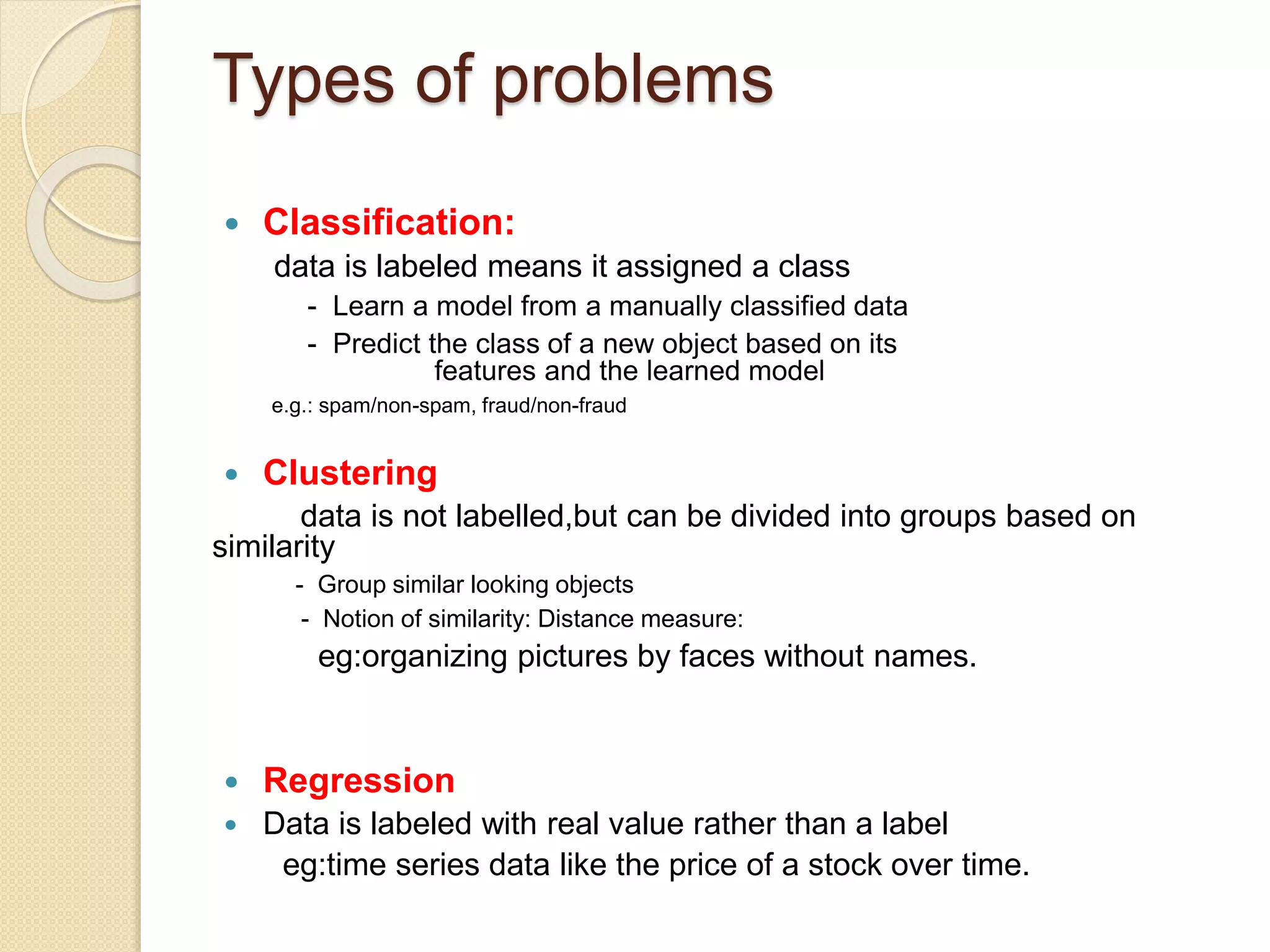
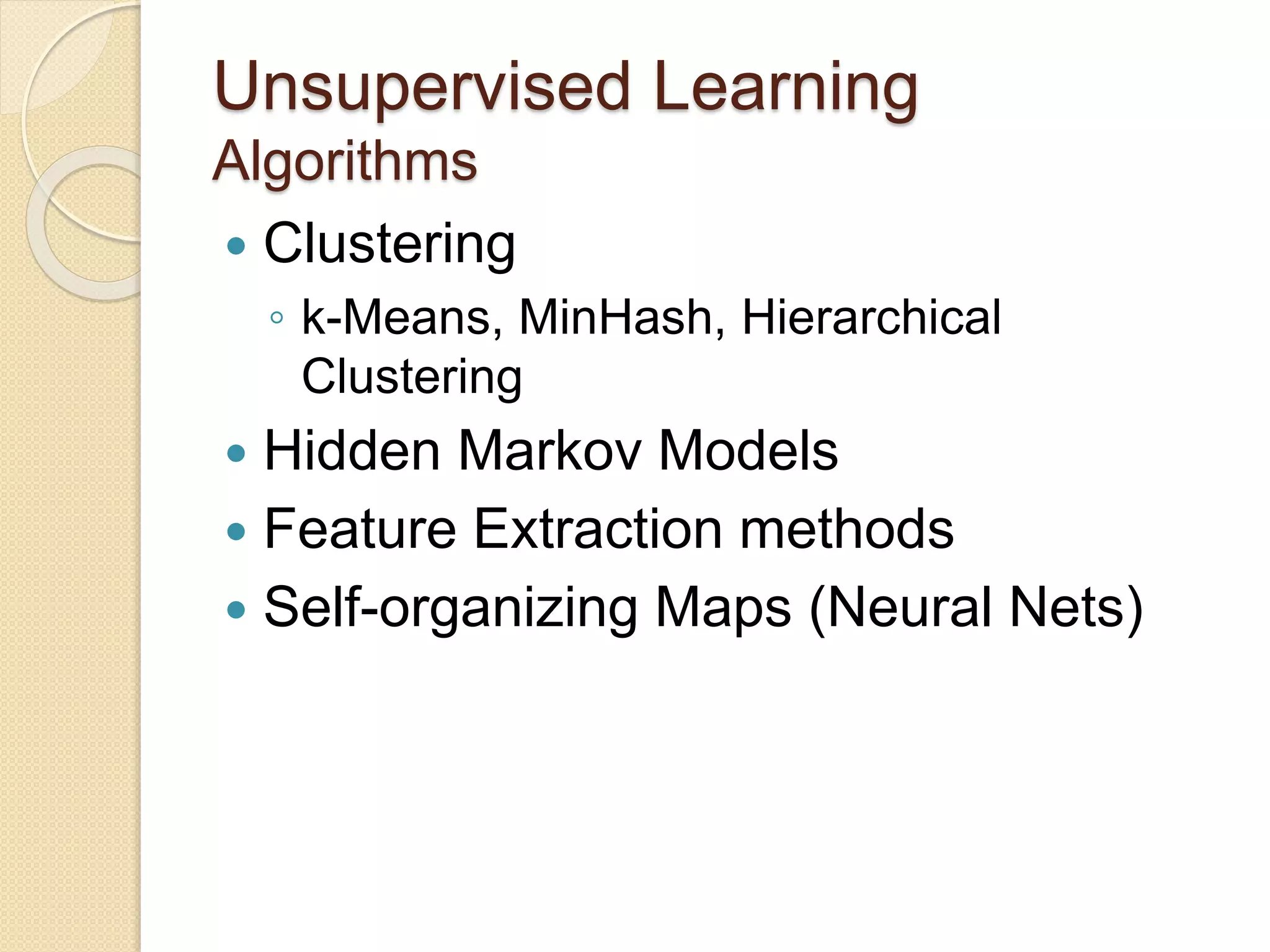
This document discusses machine learning and the use of MapReduce and Apache Mahout for scalable machine learning. It provides an introduction to machine learning concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning. It then describes how MapReduce can be used to parallelize machine learning algorithms across large datasets. Finally, it discusses Apache Mahout, an open source machine learning library that provides implementations of popular algorithms optimized for MapReduce.