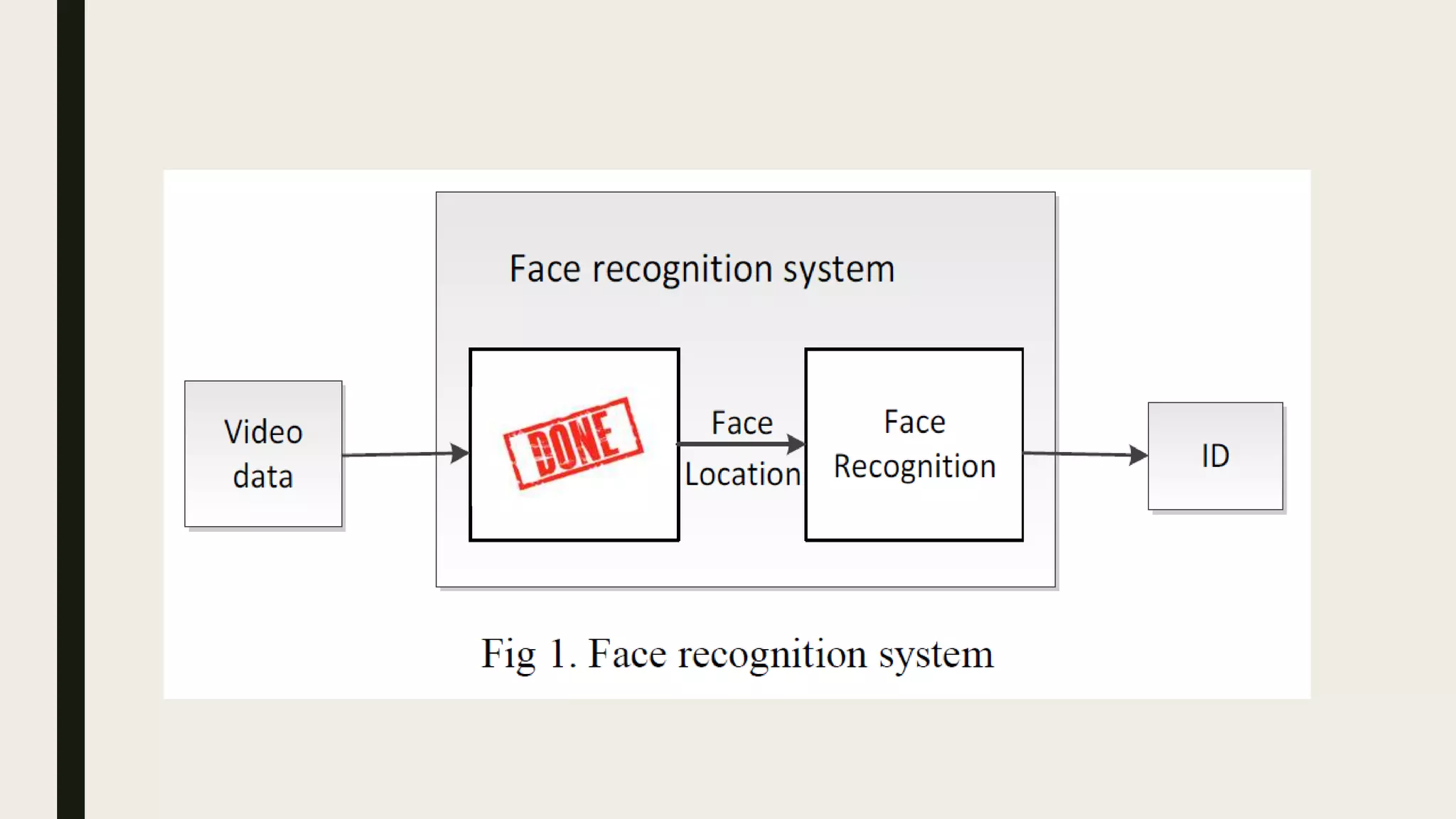
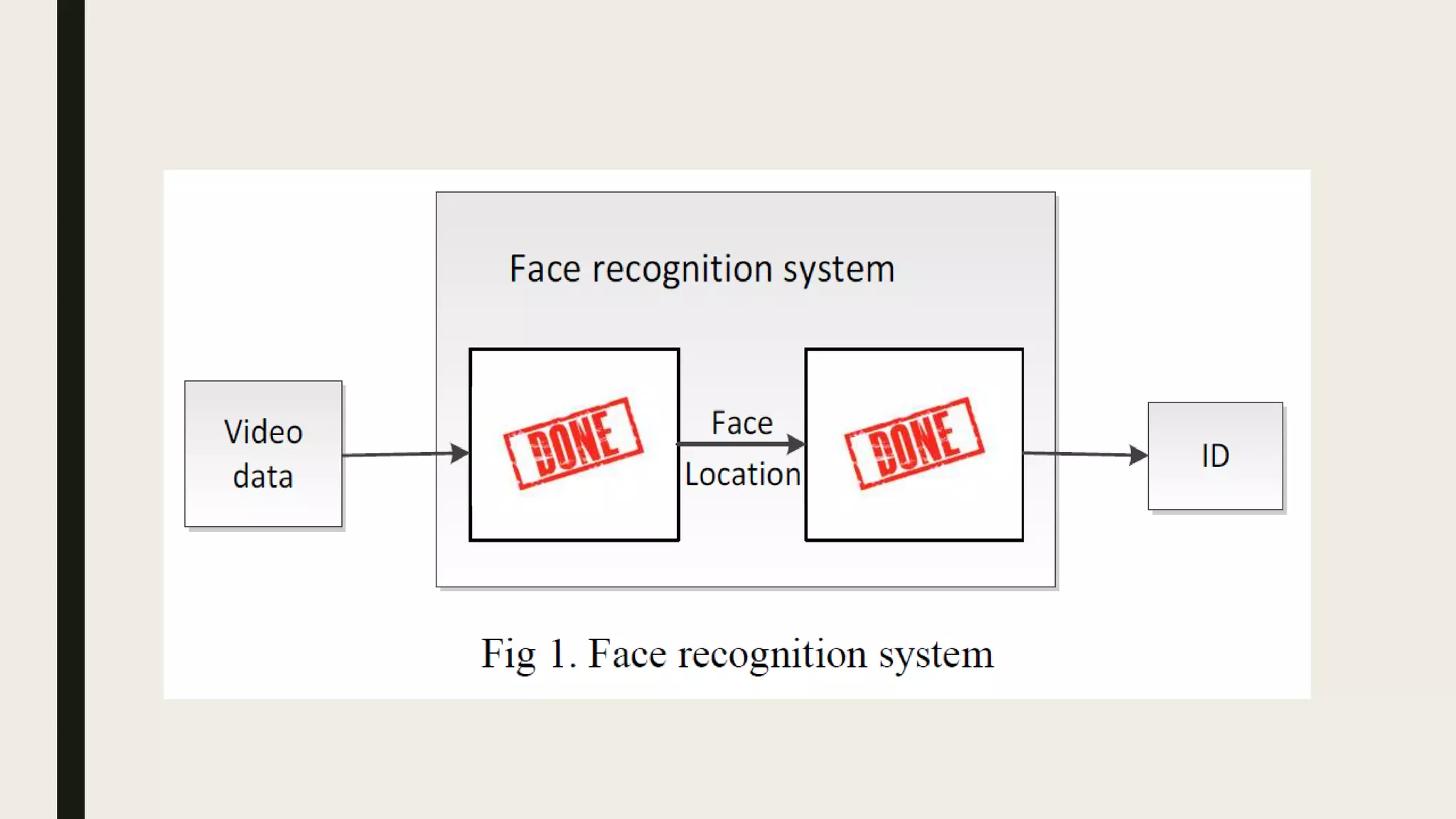
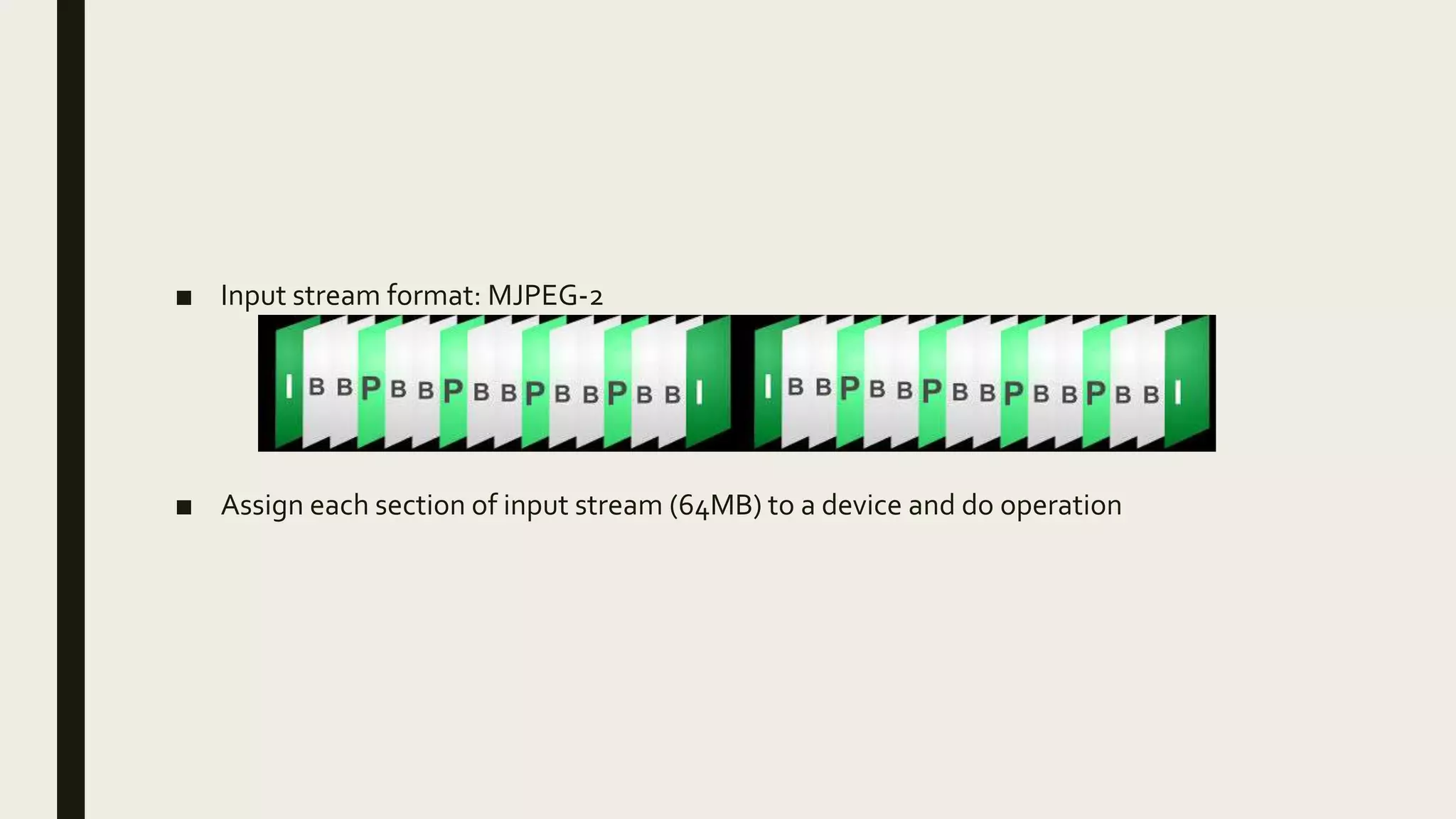
This document describes how to use MapReduce to process video from CCTV cameras to identify faces and their locations. The process involves:
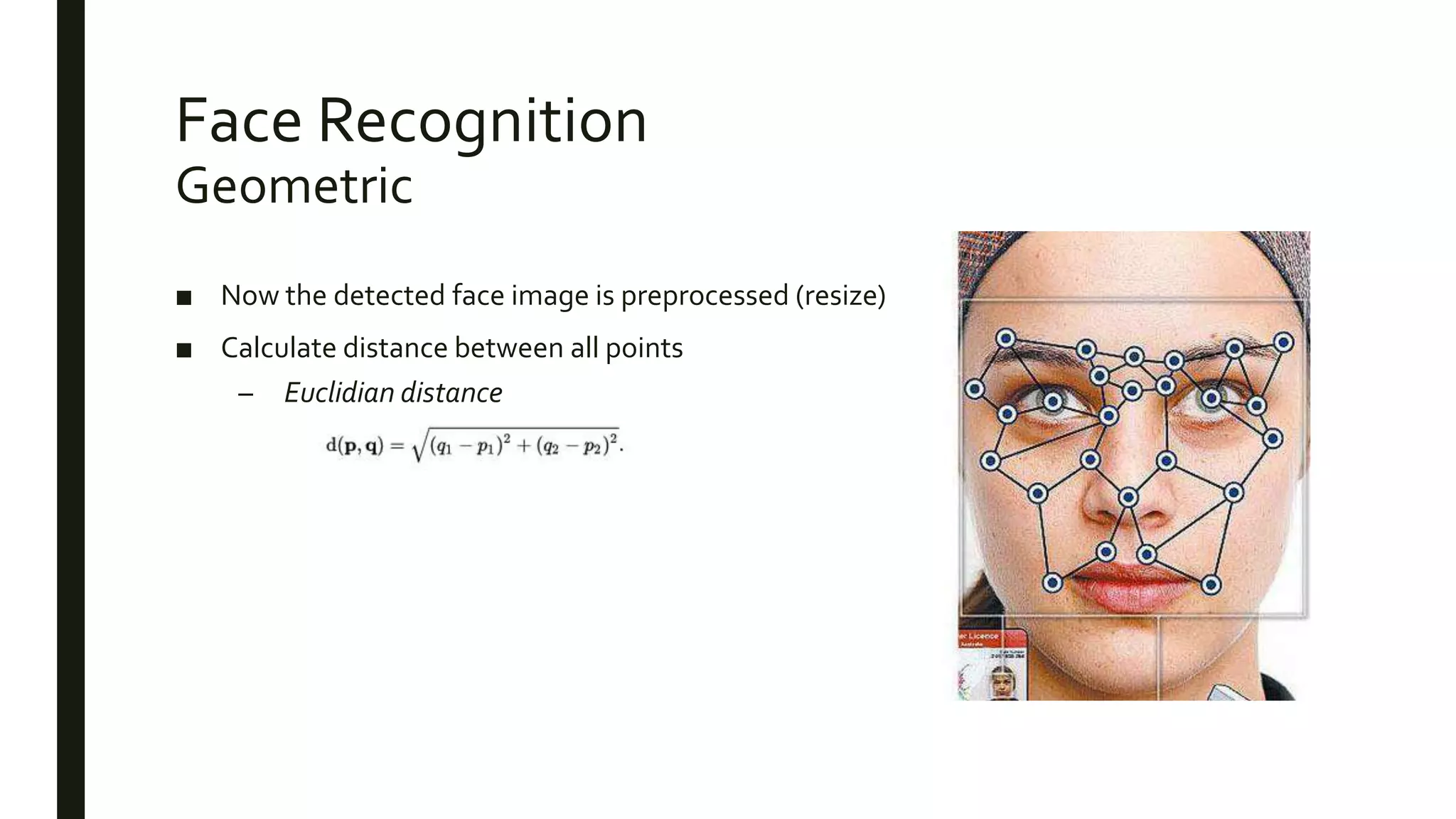
1. The mappers take chunks of video as input, detect faces, extract features, and output face data with identifiers.
2. A shuffler redistributes the face data to reducers based on the identifiers.
3. The reducers calculate distances between the extracted features and a database of known faces. Faces that match are output along with their locations from the video frames. This allows identifying 20 people across 470,000 cameras in Beijing.