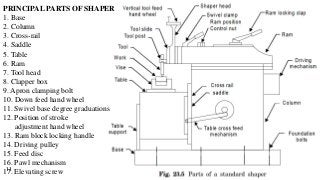
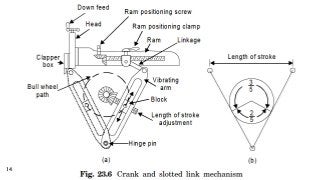
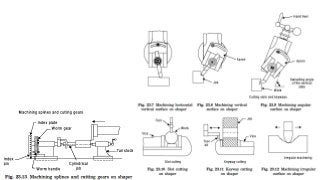
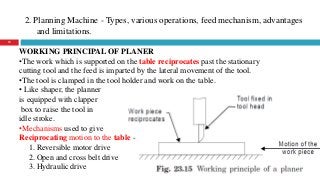
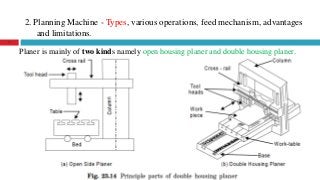
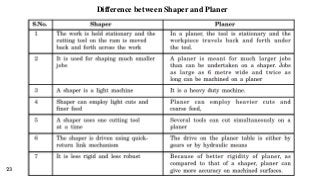
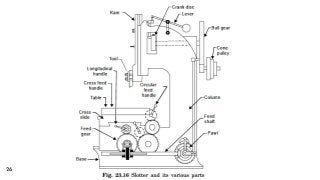
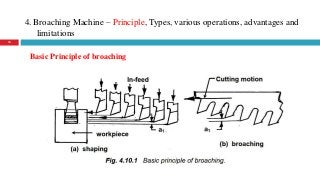
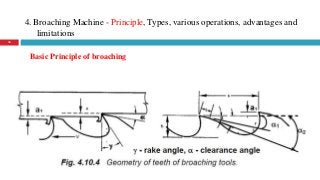
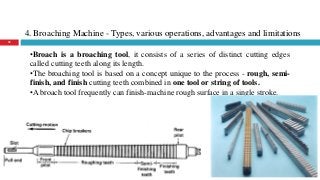
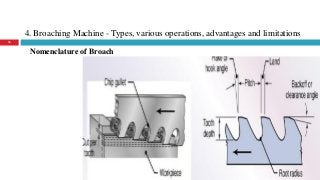
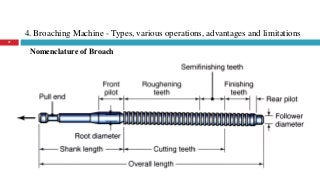
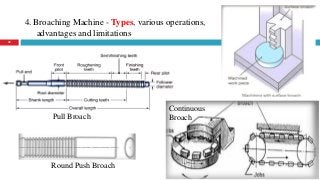
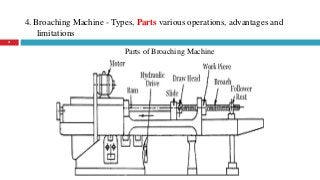
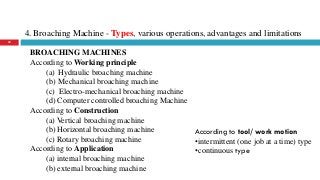
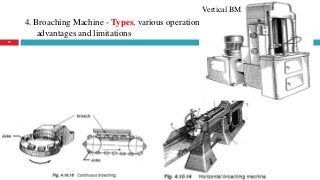
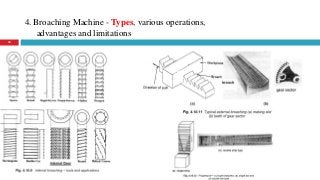
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various machine tools used in manufacturing, specifically focusing on shaping, planning, slotting, and broaching machines. It details their types, mechanisms, operations, and applications, with emphasis on the principles of each machine and the advantages and limitations associated with them. Additionally, it discusses distinct features and functionalities, including the movements of cutting tools and workpieces during the machining processes.