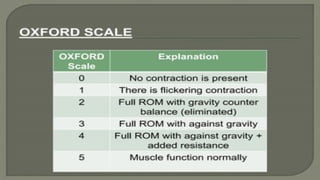
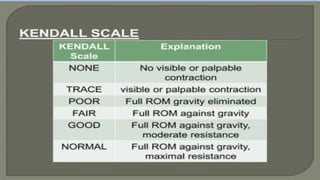
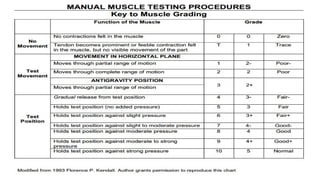
The document outlines a lecture on manual muscle testing, aiming to teach second-year kinesiology students essential definitions, procedures, and grading for assessing muscle strength. It emphasizes the importance of careful examination techniques, the purpose of muscle testing as a diagnostic tool, and the evaluation of muscle functionality and stability. Key components include patient preparation, principles of testing, and grading scales for muscle strength assessment.