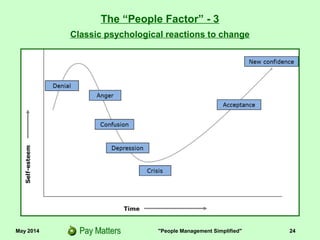
The document outlines the importance of managing organizational change and the various reasons organizations undergo change, including crises, technology advancements, and market opportunities. It details a 15-step change process for effectively implementing change while addressing potential resistance from employees. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of communication, engagement, and understanding the 'people factor' in successful change management.