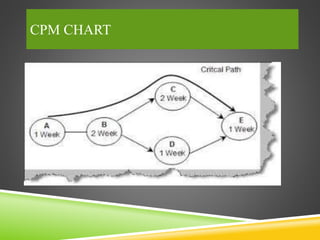
This document discusses controlling in project management. It defines controlling as evaluating performance and applying corrective measures to ensure plans are followed. The control process involves establishing standards, measuring actual results against standards, and taking corrective actions. The document also discusses ITC, a large Indian conglomerate, as a case study. It outlines ITC's diverse businesses and how it uses techniques like CPM, PERT, auditing, and ISO standards to control quality across its operations.