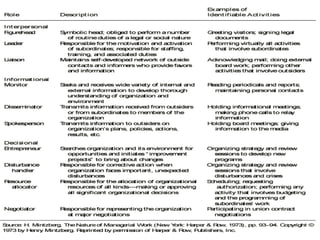
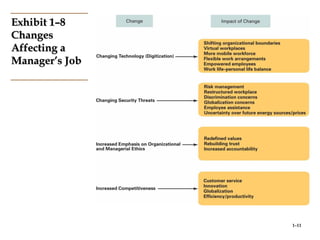
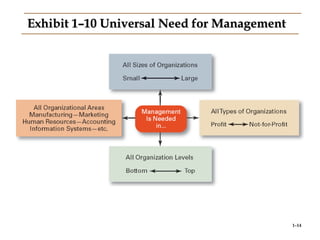
This document provides an introduction to management and organizations. It defines key management terms like managers, levels of managers, and functions of management. It describes what managers do, including their functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It also outlines management roles and skills. The document notes how the manager's job is changing with a focus on customers and innovation. It concludes with defining organizations and discussing why studying management is important.