More Related Content
PPT
Ch no 1 Intro to Management and Organizations PPT
chapter-1 management.ppt competition.pptx competition.pptx PPT
10erobbins_PPT01 - r.ppt chapter 1 principles of management PPT
chapter-1management10theditionbyrobbinsandcoulter-130822064132-phpapp02.ppt PPT
PPT
PPTX
chapter-1management Introduction to management from Stephen P. Robbins PPT
chapter-1 management, theory and concept Similar to Introduction to management Chapter 1.ppt
PPT
PPT
10 introduction to management and organizations ppt01 PPT
PPT
PDF
PDF
Ch1introductiontomanagementandorganizations 130304095937-phpapp01 PPT
Chapter 1management10theditionbyrobbinsandcoulter-130822064132-phpapp02 PPT
PPTX
Introduction to Management Chp 1- r.pptx PPT
PPT
Chapter 1 - Introduction to Management and Organizations PPT
PPT
Management (Complete Book) PPT
Principle of Management - Chapter # 1 PPT
PPT
PPTX
Chapter_01 (Introduction To Management).pptx PPT
PPT
Introduction to management PDF
More from RFZaibiGaming
PPTX
Chap 12 Material Requirement Planning & ERP.pptx.............. PPTX
Chap 14 Recent Developments in OM, OEE, TPM, ERP, FMS,.pptx PPTX
chp 5 Products, Services & Brands...pptx PPTX
IAS_38_Intangible_Assets_Presentation_Updated(1).pptx PPTX
IAS_23_Borrowing_Costs Updated.pptx..... PPTX
GREE VS DAWLANCE Presentation........... PPTX
Economic Issues of Pakistan.pptx........ DOCX
Date Sheet BS Clinical Psychology fall 2023.docx Recently uploaded
PPTX
Nehemiah 1.5-11 6.2-16 GPBC 02.01.26.pptx PPTX
Rooted in Christ, Sabbath School Object lesson PDF
A Brief Introduction About Dr. T. La Mont Holder PDF
UnityNet Champions of the World — Knowledge Note (2026-01-26) PDF
The Legacy of Aspirin - A century-old medicine that shaped therapeutics DOCX
Teacher Induction Program course 1 The Dep ed Teacher PDF
BLU8 Introduction by Ian H. Bates - February 2026 PPTX
Exploring Various Career Pathways powerpoint Introduction to management Chapter 1.ppt
- 1.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–1
Introduction to
Introduction to
Management
Management
and
and
Organizations
Organizations
Chapter
Chapter
1
1
Management
Stephen P. Robbins Mary Coulter
tenth edition
- 2.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–2
Learning Outcomes
Learning Outcomes
Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study
Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study
this chapter.
this chapter.
1.1 Who Are Managers?
• Explain how managers differ from non-managerial
Explain how managers differ from non-managerial
employees.
employees.
• Describe how to classify managers in organizations.
Describe how to classify managers in organizations.
1.2 What Is Management?
• Define management.
Define management.
•
• Explain why efficiency and effectiveness are important
Explain why efficiency and effectiveness are important
to management.
to management.
- 3.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–3
Learning Outcomes
Learning Outcomes
1.3 What Do Managers Do?
• Describe the four functions of management.
Describe the four functions of management.
• Explain Mintzberg’s managerial roles.
Explain Mintzberg’s managerial roles.
• Describe Katz’s three essential managerial skills and
Describe Katz’s three essential managerial skills and
how the importance of these skills changes
how the importance of these skills changes
depending on managerial level.
depending on managerial level.
• Discuss the changes that are impacting manager’s
Discuss the changes that are impacting manager’s
jobs.
jobs.
• Explain why customer service and innovation are
Explain why customer service and innovation are
important to the manager’s job.
important to the manager’s job.
- 4.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–4
Learning Outcomes
Learning Outcomes
1.4 What Is An Organization?
• Explain the characteristics of an organization.
Explain the characteristics of an organization.
• Describe how today’s organizations are structured.
Describe how today’s organizations are structured.
1.5 Why Study Management?
• Discuss why it’s important to understand
Discuss why it’s important to understand
management.
management.
• Explain the universality of management concept.
Explain the universality of management concept.
• Describe the rewards and challenges of being a
Describe the rewards and challenges of being a
manager.
manager.
- 5.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–5
Who Are Managers?
Who Are Managers?
• Manager
Manager
Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of
Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of
other people so that organizational goals can be
other people so that organizational goals can be
accomplished.
accomplished.
- 6.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–6
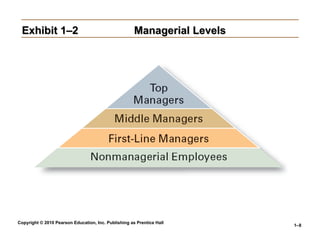
Classifying Managers
Classifying Managers
• First-line Managers
First-line Managers
Individuals who manage the work of non-managerial
Individuals who manage the work of non-managerial
employees.
employees.
• Middle Managers
Middle Managers
Individuals who manage the work of first-line
Individuals who manage the work of first-line
managers.
managers.
• Top Managers
Top Managers
Individuals who are responsible for making
Individuals who are responsible for making
organization-wide decisions and establishing plans
organization-wide decisions and establishing plans
and goals that affect the entire organization.
and goals that affect the entire organization.
- 7.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–7
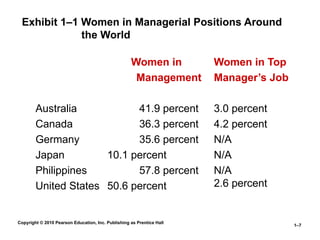
Exhibit 1–1 Women in Managerial Positions Around
the World
Women in
Management
Australia 41.9 percent
Canada 36.3 percent
Germany 35.6 percent
Japan 10.1 percent
Philippines 57.8 percent
United States 50.6 percent
Women in Top
Manager’s Job
3.0 percent
4.2 percent
N/A
N/A
N/A
2.6 percent
- 8.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–8
Exhibit 1–2
Exhibit 1–2 Managerial Levels
Managerial Levels
- 9.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–9
What Is Management?
What Is Management?
• Management involves coordinating and
overseeing the work activities of others so that
their activities are completed efficiently and
effectively.
- 10.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–10
What Is Management?
What Is Management?
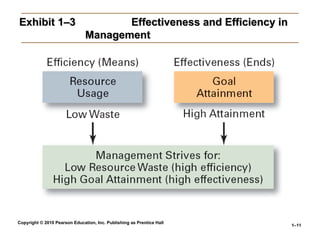
• Managerial Concerns
Managerial Concerns
Efficiency
Efficiency
“
“Doing things right”
Doing things right”
– Getting the most output
Getting the most output
for the least inputs
for the least inputs
Effectiveness
Effectiveness
“
“Doing the right things”
Doing the right things”
– Attaining organizational
Attaining organizational
goals
goals
- 11.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–11
Exhibit 1–3
Exhibit 1–3 Effectiveness and Efficiency in
Effectiveness and Efficiency in
Management
Management
- 12.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–12
What Managers Do?
What Managers Do?
• Three Approaches to Defining What Managers
Three Approaches to Defining What Managers
Do.
Do.
Functions they perform.
Functions they perform.
Roles they play.
Roles they play.
Skills they need.
Skills they need.
- 13.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–13
What Managers Do?
What Managers Do?
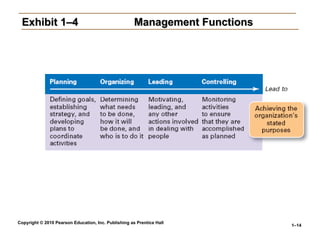
• Functions Manager’s Perform
Functions Manager’s Perform
Planning
Planning
Defining goals, establishing strategies to achieve goals,
Defining goals, establishing strategies to achieve goals,
developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities.
developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities.
Organizing
Organizing
Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational
Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational
goals.
goals.
Leading
Leading
Working with and through people to accomplish goals.
Working with and through people to accomplish goals.
Controlling
Controlling
Monitoring, comparing, and correcting work.
Monitoring, comparing, and correcting work.
- 14.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–14
Exhibit 1–4
Exhibit 1–4 Management Functions
Management Functions
- 15.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–15
What Managers Do?
What Managers Do?
• Roles Manager’s Play
Roles Manager’s Play
Roles are specific actions or behaviors expected of a
manager.
Mintzberg identified 10 roles grouped around
interpersonal relationships, the transfer of information,
and decision making.
- 16.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–16
What Managers Do?
What Managers Do?
• Management Roles
Management Roles
(Mintzberg)
(Mintzberg)
Interpersonal roles
Interpersonal roles
Figurehead, leader, liaison
Figurehead, leader, liaison
Informational roles
Informational roles
Monitor, disseminator,
Monitor, disseminator,
spokesperson
spokesperson
Decisional roles
Decisional roles
Entrepreneur, disturbance
Entrepreneur, disturbance
handler, resource allocator,
handler, resource allocator,
negotiator
negotiator
- 17.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–17
What Managers Do (Mintzberg)
What Managers Do (Mintzberg)
• Actions
Actions
thoughtful thinking
thoughtful thinking
practical doing
practical doing
- 18.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–18
• Interpersonal Roles
• Figurehead
• Leader
• Liaison
• Interpersonal Roles
• Monitor
• Disseminator
• Spokesperson
• Decisional Roles
• Entrepreneur
• Disturbance handler
• Resource allocator
• Negotiator
Exhibit 1.5 Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles
Adapted from Mintzberg, Henry,
The Nature of Managerial Work,
1st Edition, © 1980, pp. 93–94..
- 19.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–19
What Managers Do?
What Managers Do?
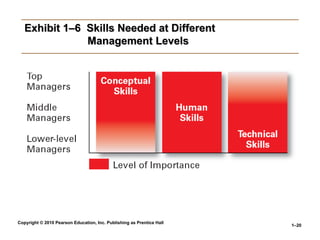
• Skills Managers Need
Skills Managers Need
Technical skills
Technical skills
Knowledge and proficiency in a specific field
Knowledge and proficiency in a specific field
Human skills
Human skills
The ability to work well with other people
The ability to work well with other people
Conceptual skills
Conceptual skills
The ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and
The ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and
complex situations concerning the organization
complex situations concerning the organization
- 20.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–20
Exhibit 1–6 Skills Needed at Different
Exhibit 1–6 Skills Needed at Different
Management Levels
Management Levels
- 21.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–21
How The Manager’s Job Is
How The Manager’s Job Is
Changing
Changing
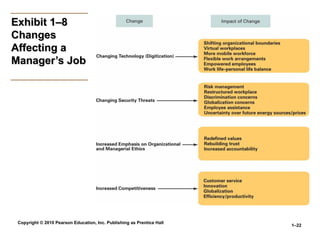
• The Increasing Importance of Customers
The Increasing Importance of Customers
Customers: the reason that organizations exist
Customers: the reason that organizations exist
Managing customer relationships is the responsibility of all
Managing customer relationships is the responsibility of all
managers and employees.
managers and employees.
Consistent high quality customer service is essential for
Consistent high quality customer service is essential for
survival.
survival.
• Innovation
Innovation
Doing things differently, exploring new territory, and
Doing things differently, exploring new territory, and
taking risks
taking risks
Managers should encourage employees to be aware of and
Managers should encourage employees to be aware of and
act on opportunities for innovation.
act on opportunities for innovation.
- 22.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–22
Exhibit 1–8
Exhibit 1–8
Changes
Changes
Affecting a
Affecting a
Manager’s Job
Manager’s Job
- 23.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–23
What Is An Organization?
What Is An Organization?
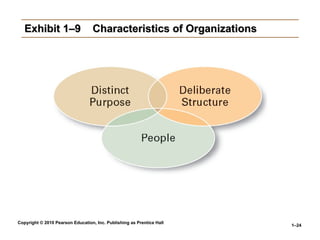
• An Organization Defined
An Organization Defined
A deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish
A deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish
some specific purpose (that individuals independently
some specific purpose (that individuals independently
could not accomplish alone).
could not accomplish alone).
• Common Characteristics of Organizations
Common Characteristics of Organizations
Have a distinct purpose (goal)
Have a distinct purpose (goal)
Composed of people
Composed of people
Have a deliberate structure
Have a deliberate structure
- 24.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–24
Exhibit 1–9 Characteristics of Organizations
Exhibit 1–9 Characteristics of Organizations
- 25.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–25
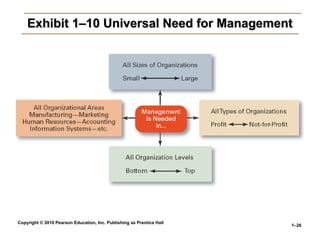
Why Study Management?
Why Study Management?
• The Value of Studying Management
The Value of Studying Management
The universality of management
The universality of management
Good management is needed in all organizations.
Good management is needed in all organizations.
The reality of work
The reality of work
Employees either manage or are managed.
Employees either manage or are managed.
Rewards and challenges of being a manager
Rewards and challenges of being a manager
Management offers challenging, exciting and creative
Management offers challenging, exciting and creative
opportunities for meaningful and fulfilling work.
opportunities for meaningful and fulfilling work.
Successful managers receive significant monetary rewards
Successful managers receive significant monetary rewards
for their efforts.
for their efforts.
- 26.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–26
Exhibit 1–10 Universal Need for Management
Exhibit 1–10 Universal Need for Management
- 27.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–27
Exhibit 1–11 Rewards and Challenges of
Exhibit 1–11 Rewards and Challenges of
Being A Manager
Being A Manager
- 28.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–28
Terms to Know
Terms to Know
• manager
manager
• first-line managers
first-line managers
• middle managers
middle managers
• top managers
top managers
• management
management
• efficiency
efficiency
• effectiveness
effectiveness
• planning
planning
• organizing
organizing
• leading
leading
• controlling
controlling
• management roles
management roles
• interpersonal roles
interpersonal roles
• informational roles
informational roles
• decisional roles
decisional roles
• technical skills
technical skills
• human skills
human skills
• conceptual skills
conceptual skills
• organization
organization
• universality of
universality of
management
management
- 29.
Copyright © 2010Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
1–29
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by
any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Printed in the United States of America.
Printed in the United States of America.