Embed presentation
Downloaded 29 times





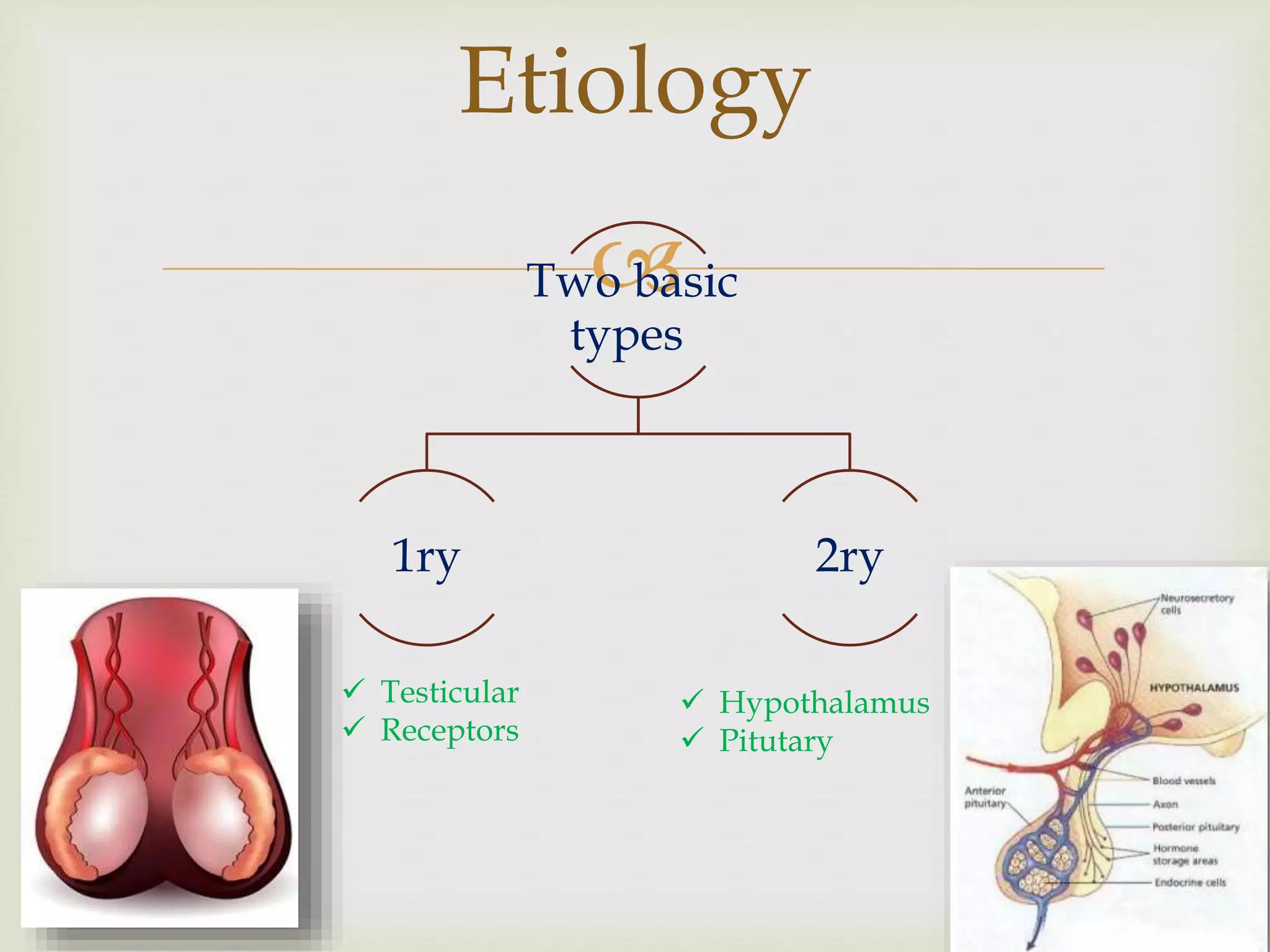










Hypogonadism is a decreased functional activity of the gonads that results in a failure of the testes to produce androgen, sperm, or both. It can occur at any age, with consequences depending on when it starts - before birth, before puberty, or after puberty. There are two types, primary involving the testes and secondary involving the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Causes include genetic conditions, tumors, infections, physical damage to the testes from conditions like mumps, and certain medications or medical treatments that can damage the testes.















