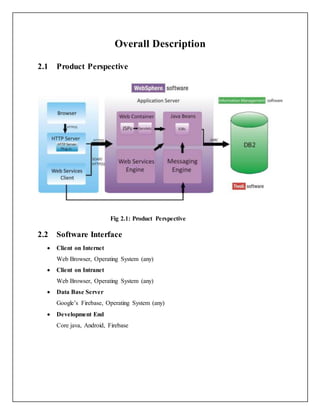
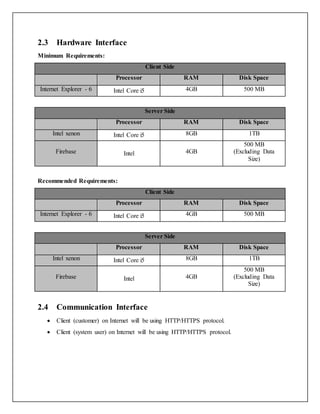
This document provides a software requirements specification for a mobile application to support India's Clean India Mission. It describes the purpose, scope, methodology, tools and technologies to be used in the application. The overall description outlines the product perspective, interfaces, constraints, E-R diagram, use cases and architecture. Specific requirements covered include use case reports, activity diagrams and sequence diagrams. The application will allow citizens to interact with local officials, upload photos of garbage areas, and help coordinate clean-up efforts.