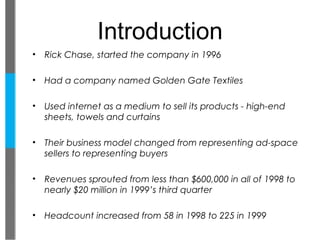
- Madison Media started in 1996 selling high-end home goods but later transitioned to selling advertising space on websites.
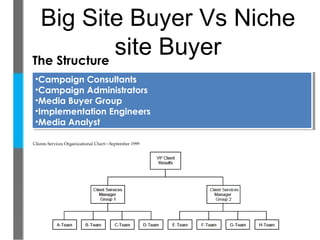
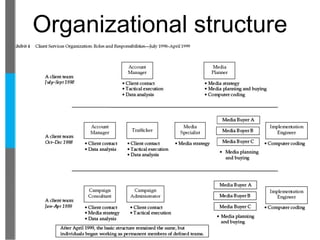
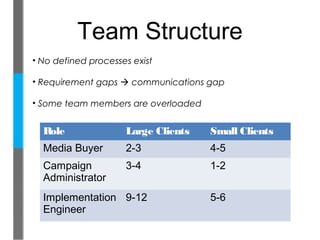
- They evolved their business model from selling advertising space to buying and consulting on ad space for advertisers.
- Their revenues grew from less than $600,000 in 1998 to nearly $20 million in the third quarter of 1999 as their business model changed and headcount increased.