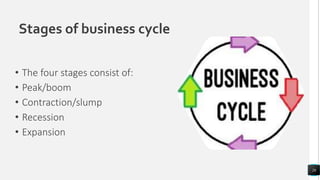
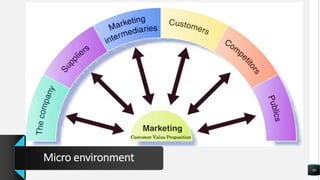
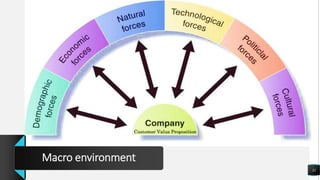
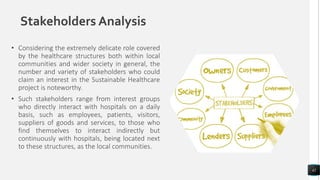
The document discusses various marketing concepts including integrated marketing communication, market segmentation, branding, digital marketing, customer relationship management, and sales. It explains that political factors can impact businesses and effective branding creates enduring customer perceptions. Market segmentation involves dividing markets into groups with common characteristics to create customized marketing. Relationship marketing focuses on loyalty and engagement rather than just sales.