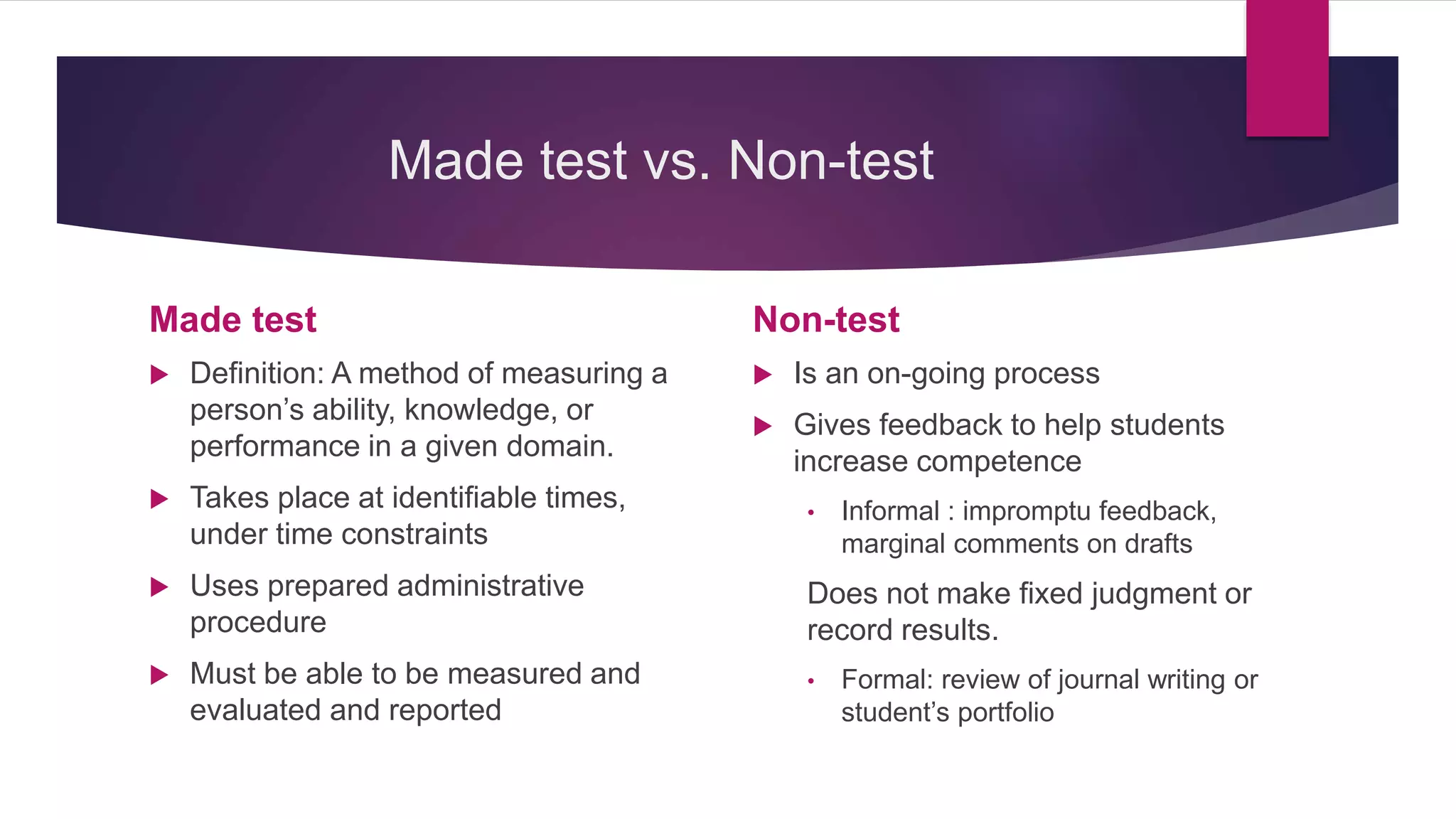
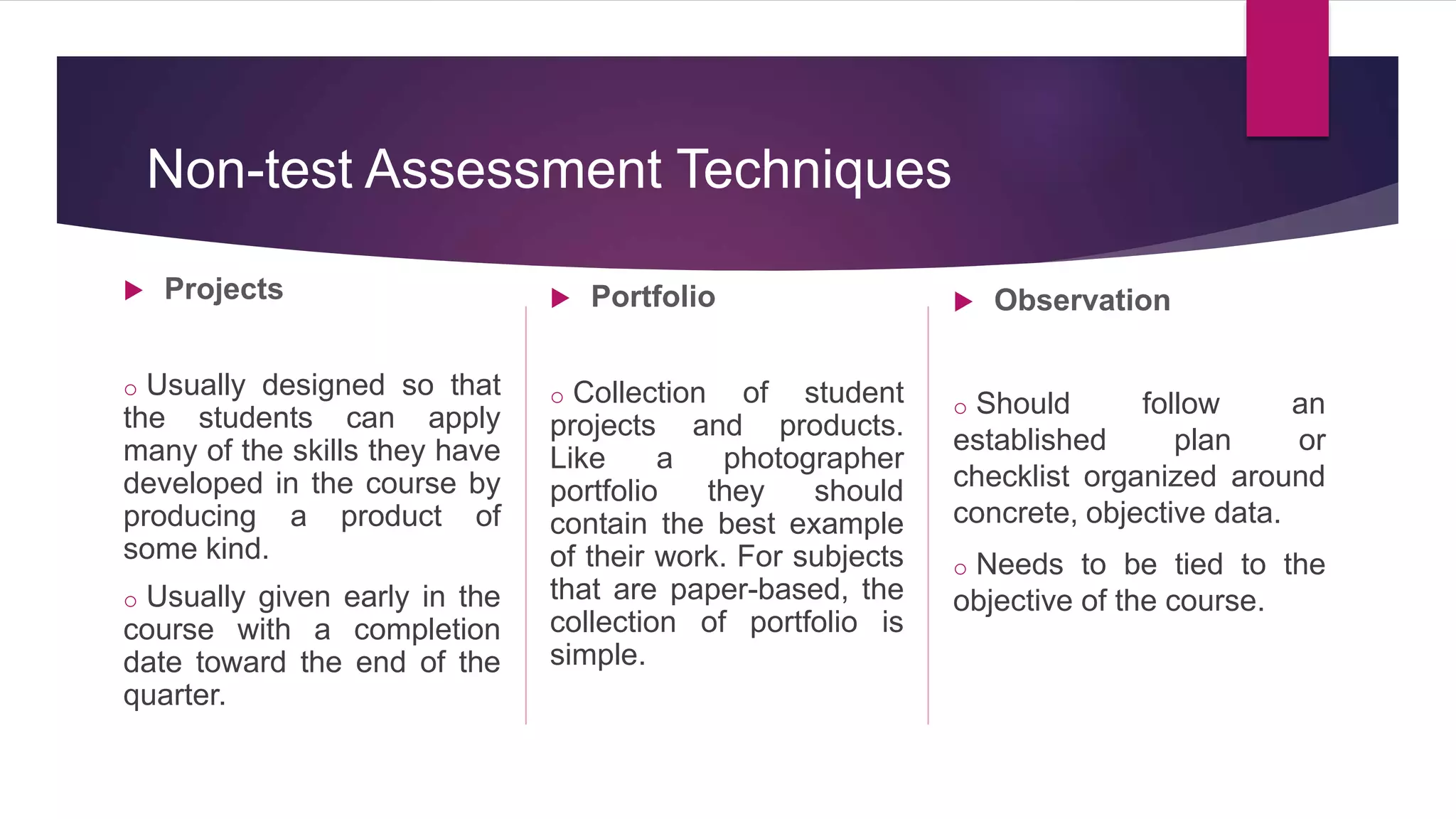
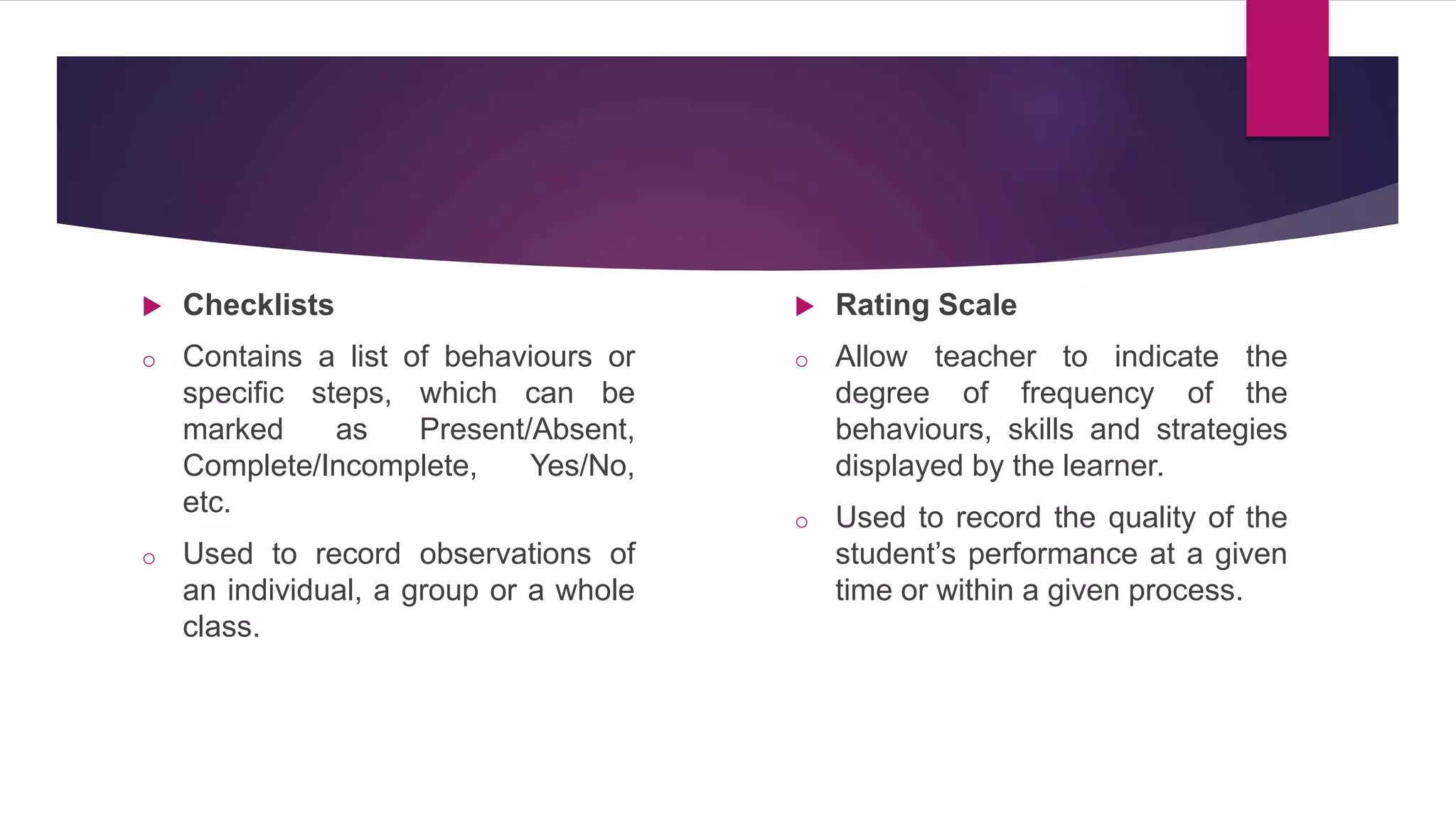
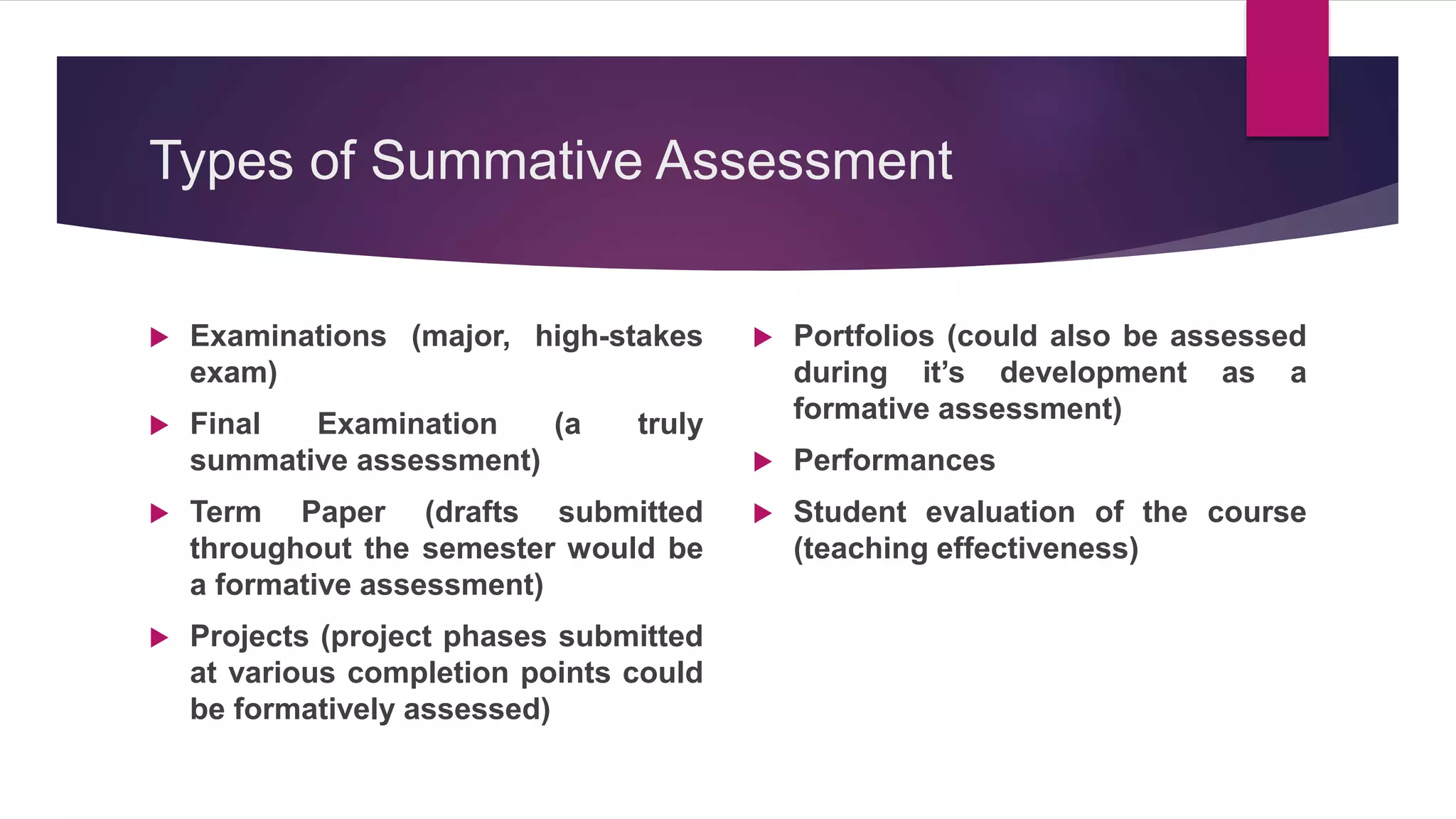
The document outlines the differentiation between made-test and non-test instruments used in educational assessment, highlighting their definitions and applications. It details various forms of teacher-made tests, such as multiple choice and essay questions, as well as non-test methods like case studies and portfolios. Additionally, it explains the four roles of assessment in instructional decisions: placement, diagnostic, formative, and summative assessments.