Macro Problems
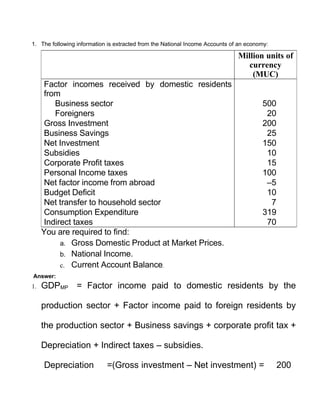
- 1. 1. The following information is extracted from the National Income Accounts of an economy: Million units of currency (MUC) Factor incomes received by domestic residents from Business sector 500 Foreigners 20 Gross Investment 200 Business Savings 25 Net Investment 150 Subsidies 10 Corporate Profit taxes 15 Personal Income taxes 100 Net factor income from abroad –5 Budget Deficit 10 Net transfer to household sector 7 Consumption Expenditure 319 Indirect taxes 70 You are required to find: a. Gross Domestic Product at Market Prices. b. National Income. c. Current Account Balance. Answer: 1. GDPMP = Factor income paid to domestic residents by the production sector + Factor income paid to foreign residents by the production sector + Business savings + corporate profit tax + Depreciation + Indirect taxes – subsidies. Depreciation =(Gross investment – Net investment) = 200
- 2. –150 = 50 Factor income paid abroad = Factor income received from abroad - NFIA = 20 – (– 5) = 25 GDPMP = 500 + 25 + 25 + 15 + 50 + 70 – 10 = 675 b. NI = GDPMP – Indirect taxes + subsidies – Depreciation + NFIA = 675 – 70 + 10 – 50 + (–5)= 560 c. CAB=Domestic savings (DS) – Domestic Investment (DI) DS= Business savings + Government savings + Household savings. Household savings = Personal Disposable income – Personal consumption PDI = NI – Business savings – corporate profit tax + net transfers – Personal income tax PDI = 560 – 25 – 15 + 7 – 100 = 427 PS = 427 – 319 = 108 CAB = (25 – 10 + 108) – 150 = – 27 Current account deficit = 27. 2. The following information is taken from Union Budget for the year 2006 – 07: (Rs. crore)
- 3. Revenue Receipts Tax Revenue (Net) 1,72,965 Non-tax Revenue 72,140 Capital Receipts Recoveries of Loans 17,680 Other Receipts 12,000 Borrowings & Other Liabilities 1,35,524 Non-plan Expenditure On Revenue Account 2,70,169 (Of which, interest payments is Rs.1,17,390 crore) On Capital Account 26,640 Plan Expenditure On Revenue Account 70,313 On Capital Account 43,187 Required: a. Find the Fiscal Deficit, Revenue Deficit and Primary Deficit b. Comment on the significance of these deficits. c. For the economy money multiplier is estimated to be 3. If government plans to monetize 10% of the fiscal deficit, what would be the impact on money supply?(12 points) 2. a. Fiscal Deficit = Borrowings and other liabilities =Rs.1,35,524 Cr Revenue Deficit = Revenue expenditure – Revenue Receipts Revenue Expenditure = Non-plan revenue expenditure + plan revenue expenditure =2,70,169 + 70313=Rs.3,40,482 Cr Revenue Deficit = 3,40,482 – (1,72,965 + 72,140) = Rs.95,377 Cr. Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit – Interest payments = 135,524 – 117,390 = Rs.18,134 Cr.
- 4. b. Fiscal deficit signifies the net addition to the public debt for the current year. Revenue deficit signifies the amount of borrowings required to finance current consumption expenditure of the government. Primary deficit indicates the discretionary component of fiscal deficit. This is because of committed nature of interest payments. c. Fiscal Deficit = Rs.1,35,524 Cr. 10% of fiscal deficit = Rs.13552.4 Cr. Monetization of deficit directly increase the high powered money in the economy DH = Rs.13552.4 Cr. DMs = m. DH = 3 ´ 13552.4 = Rs.40657.2 Monetization of 10% of the fiscal deficit would increase the money supply by Rs.40657.2 Cr. 3. The consumption function estimated for an economy is Ct = 80 + 0.6 + 0.2 Ct – 1 Ytd If increase by 100 and remains at that level, find Ytd the change in steady state level of consumption.(4
- 5. points) Answer: 3. Ct = 80 + 0.6 Y + 0.2 Ct – 1 d t At steady state, Ct = Ct – 1 Ct = 80 + 0.6 Y + 0.2Ct d t 0.8 Ct = 80 + 0.6 Y d t Ct = 100 + 0.75 Y d t DCt = 0.75 ´ D Y = 0.75 ´ 100 = 75 d t If Y increases by 100, steady state level of consumption d t increases by 75. 4. The following relations are estimated for an economy: Savings function (S) = – 380 + 0.35 Yd + 10i Tax function (T) = 0.30Y Investment function (I) = 300 + 0.15Y – 50i Transfer payments (R) = 200 Government Expenditure (G) = 1200 Exports (E) = 900 Import function (M) = 50 + 0.105Y Money Supply (Ms) = 1000 Transaction Demand for Money (Mt) = 0.25Y Speculative Demand for Money (Ma) = 350 – 100i
- 6. (All macroeconomic aggregates are in million units of currency (MUC) and the rate of interest is in percentage.) Required: a. Compute the equilibrium level of income and rate of interest b. The government desires to have an increase in the equilibrium output by 10% in the next period and for this purpose, the following alternatives are under consideration i. Increase in government expenditure (G) ii. Increase in money supply (Ms) Compute the required increase in G and Ms to achieve the objective of the government. c.Compute the impact of the two alternative measures in (b) above on private investment. Answer: 4. a. S= – 380 + 0.35 Yd + 10i C = 380 + 0.65Yd – 10i Yd = (Y – tY + R) = (Y – 0.3Y + 200) C = 380+ 0.65 (Y – 0.3Y + 200) – 10i = 510 + 0.455Y – 10i IS function Y = C + I + G + (E – M) =510 + 0.455Y – 10i + 300 + 0.15Y – 50i + 1200 + 900 – 50 – 0.105Y Y = 2860 + 0.5Y – 60i Y = 5720 – 120i IS function. LM function Ms = Md Md = Mt + M a = 0.25Y + 350 – 100i
- 7. 1000 = 0.25Y + 350 – 100i 650 100i Y = 0.25 = 2600 + 400i LM function At equilibrium LM = IS 2600 + 400i = 5720 – 120i 520i = 3120 i = 6% Y = 5000. b. If Y is to increase by 10% new equilibrium income is 5000 (1 + 0.10) = 5500 Option I: Increase in G Y = 2600 + 400i LM function If Y = 5500 400i = 5500 – 2600 i = 7.25% IS function with G as a variable is Y = (2860 – 1200 + G) + 0.5Y –60i (1660 G 60i) Y = 0.5 Y = 3320 + 2G – (120 ´ 7.25) 2G = 3050 G = 1525. Increase in G = 1525 – 1200 = 325. Option II: Increase in Money Supply
- 8. Y = 5720 – 120i IS function If Y = 5500, 120i = 5720 – 5500 i = 1.83% Ms = 0.25Y + 350 – 100i LM function If Y = 5500 and i = 1.83% Ms = (0.25 ´ 5500) + 350 – (100 ´ 1.83) = 1542 Increase in G: Change in Investment (DI) = I1 – I0 I1 = 300 + (0.15 ´ 5500) – (50 ´ 7.25) = 762.50 I0 = 300 + (0.15 ´ 5000) – (50 ´ 6.0) = 750 DI= 762.50 –750 = 12.50 Increase in Money Supply DI = I1 – I0 I1 = 300 + (0.15 ´ 5500) – (50 ´ 1.83) = 1033.50 I0 = 750 DI = 1033.50 –750 = 283.50 5. The following balances are taken from balance sheet of the Central Bank of a country.
- 9. Million units of currency Particulars (MUC) Credit to Government 7,000 Credit to Banks 4,000 Government Deposits 500 Other non-monetary liabilities 25 Net worth 1,000 Credit to commercial sector 2,000 Net foreign exchange assets 11,000 Other assets 100 Deposits of banks 6,000 Other Deposits 600 The currency/deposit ratio has been ascertained as 0.24. Reserve ratio imposed by the central bank is 7%. The amount of Government money is 25 million units of currency. Required: a. Find the money supply in the economy b. Because of intervention in the foreign exchange market, net worth of the central bank is expected to erode by 50% in the next period. If the Central bank desires to maintain the current level of money supply by changing the reserve ratio, what should be the new reserve ratio? Answer: 5. a. High powered money = Monetary Liabilities of RBI + Government Money Monetary liabilities of RBI =(Financial Assets + Other Assets – Non-monetary liabilities) Financial Assets = (Credit to Government + Credit to Banks + Credit to commercial sector + Net Foreign exchange assets) =7000 + 4000 + 2000 + 11000=24000. Other Assets =100 Non-monetary liabilities = Government deposits + other non-monetary liabilities + Net worth = 500 + 25 + 1000 = 1525 Monetary liabilities = 24000 + 100 – 1525 = 22575 Government money = 25 High powered money (H) = 22575 + 25 = 22600 Money Supply =H ´ m Money multiplier (m) =(1+c)/(c+r)= 4 Money Supply in the economy = 22600 ´ 4 =90400 MUC
- 10. b. If net worth is eroded by 50%, Net worth = 500 MUC. Monetary liabilities = 22575 + 500 = 23075 H = 23100. If money supply is held constant, 90400 = 23100 /m. r is found out by the equation m=(1+c)/(c+r) r = 0.0769 =7.69% The central bank should increase the reserve ratio to 7.69%.