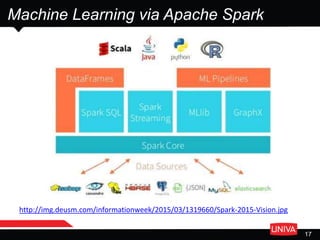
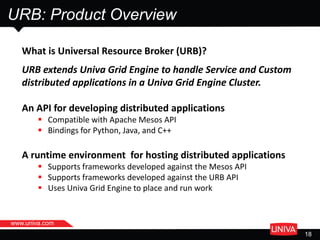
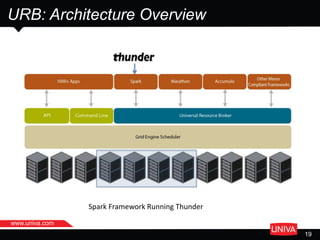
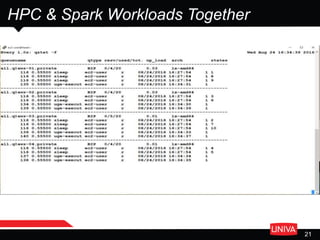
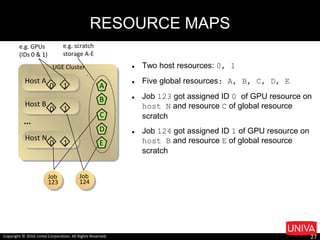
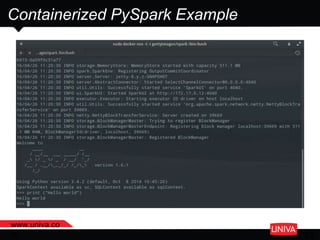
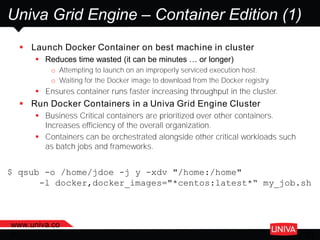
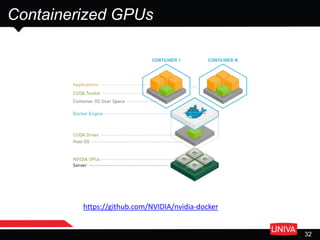
The document discusses machine learning and its applications in big data analytics, specifically focusing on earthquake and tsunami predictions using a pipeline that includes Apache Spark and Univa's Universal Resource Broker. It highlights the significance of GPUs for deep learning and containerization for efficient resource management within a cluster. The presentation concludes with a summary of scaling solutions to transition from prototypes to production environments.