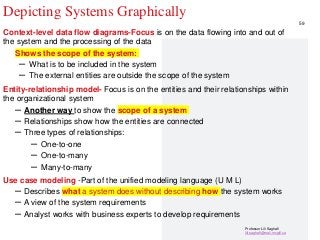
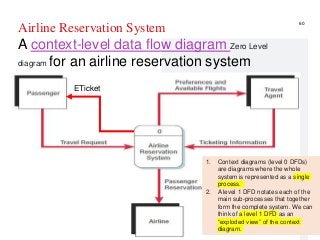
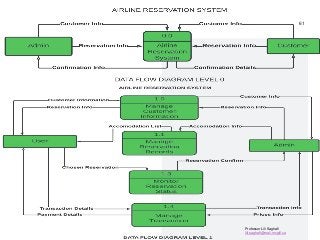
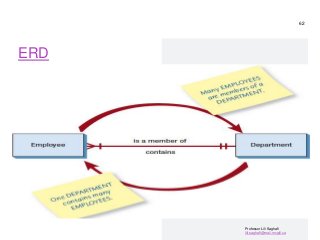
STEP1-Understanding and Modeling Organizational Systems
Big Data, BI , power of Analytic in software development
System Analyst role , in defining root problem or opportunity
Software’s Project Management , workload , activities , team , risks
STEP2-Determining Priorities and Feasibility
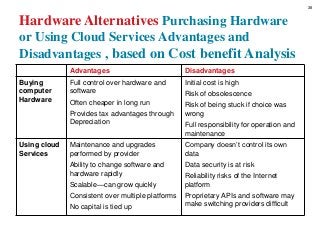
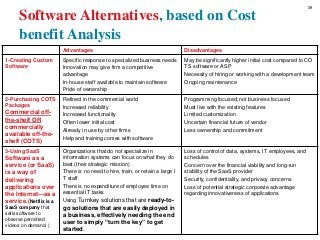
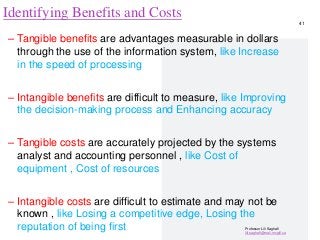
Software and Hardware Alternatives, based on Cost benefit Analysis for tangible and intangible cost and benefits. Payback, ROI,….
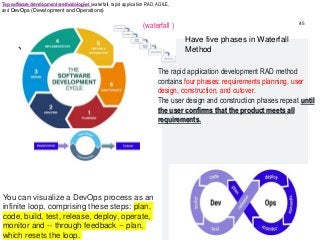
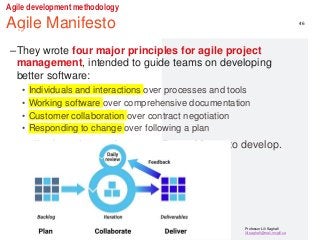
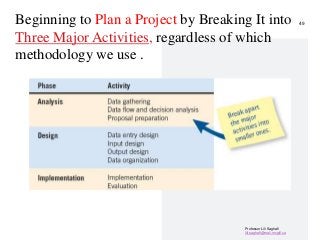
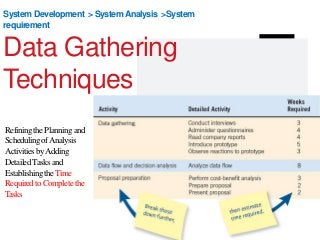
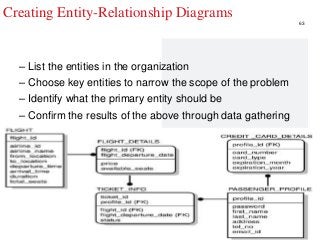
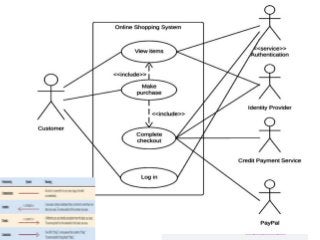
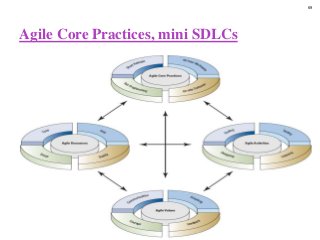
STEP3-Software Development Projects, Methodology , Data gathering, Modeling , Agile