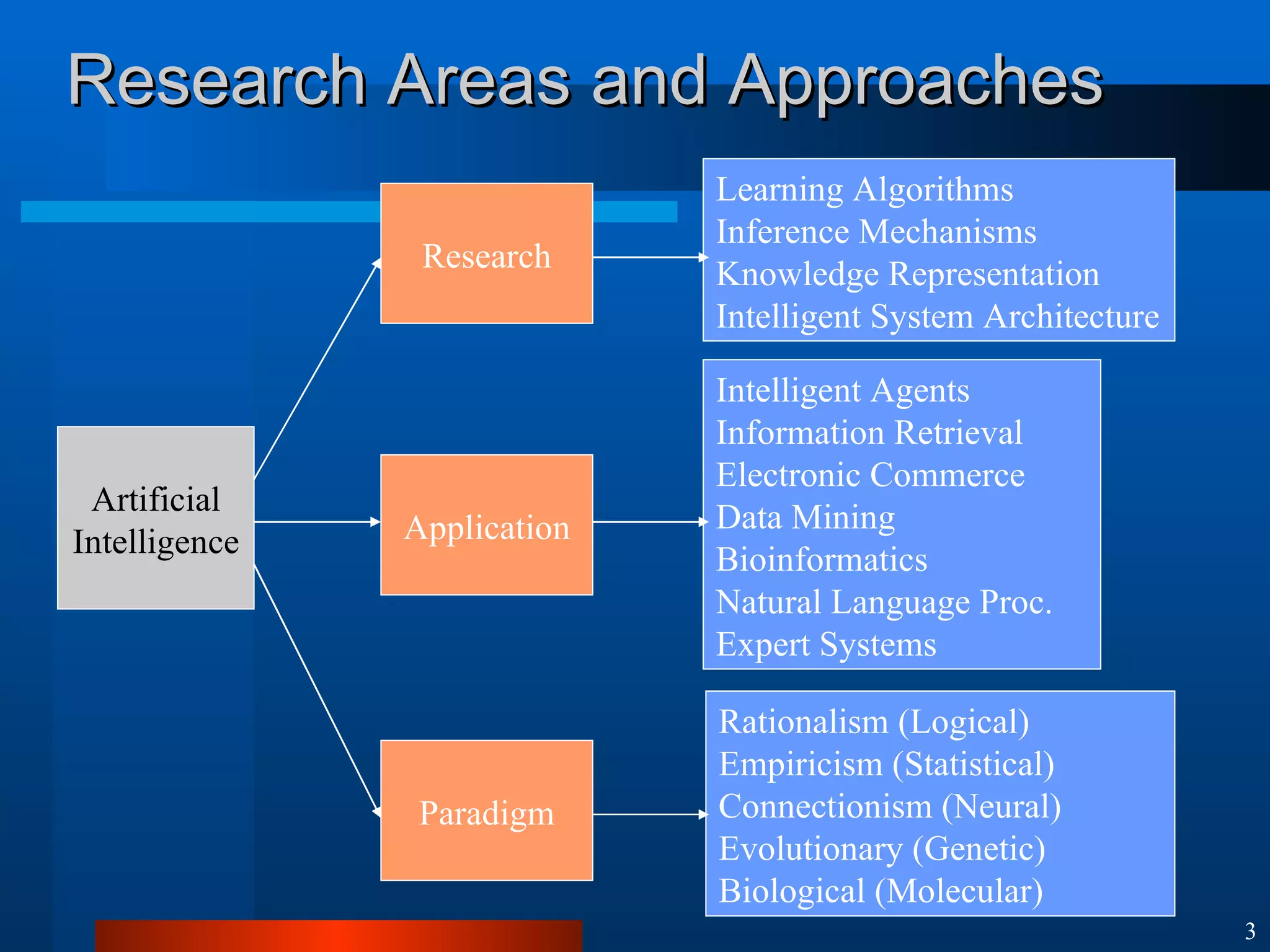
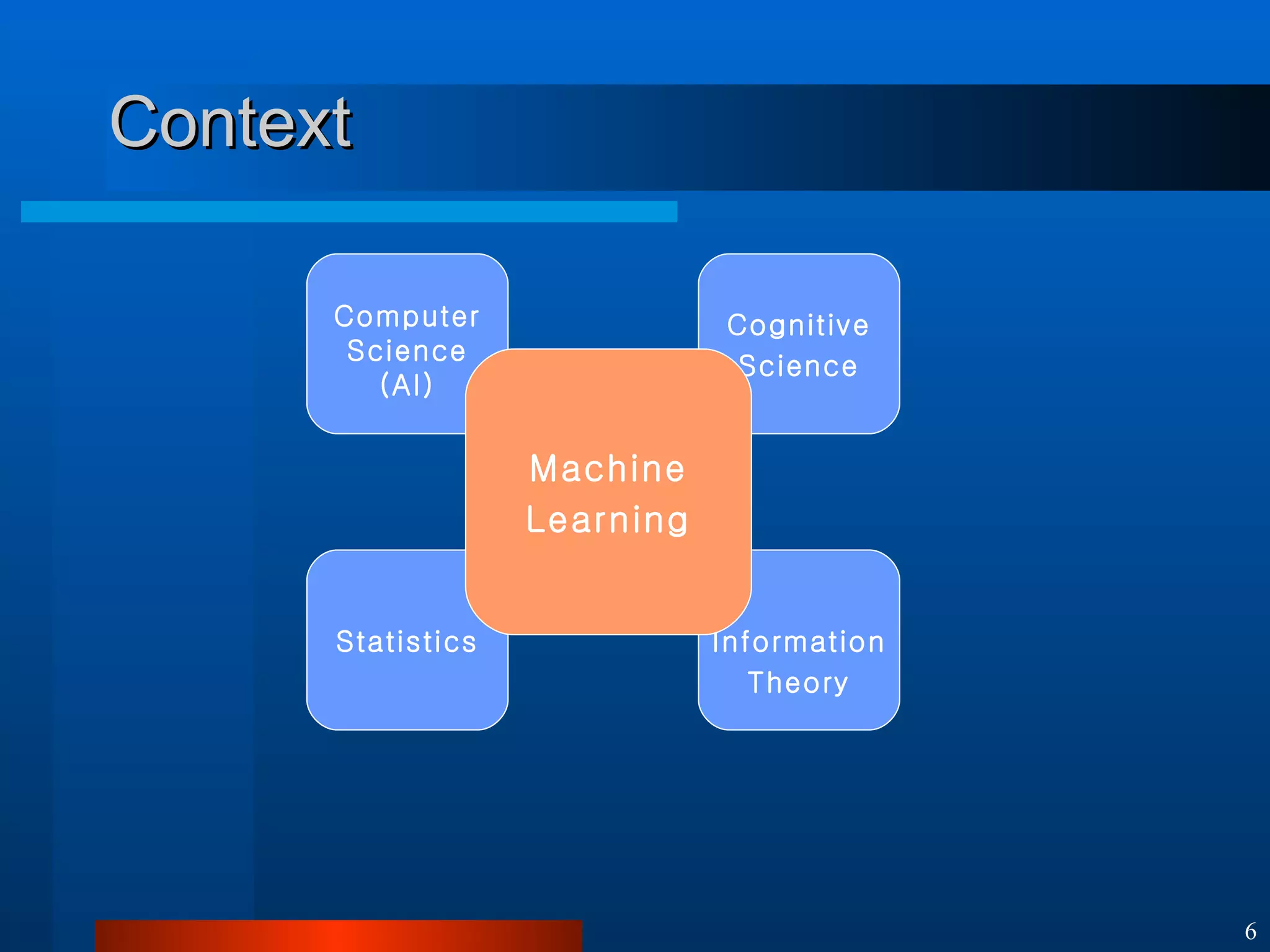
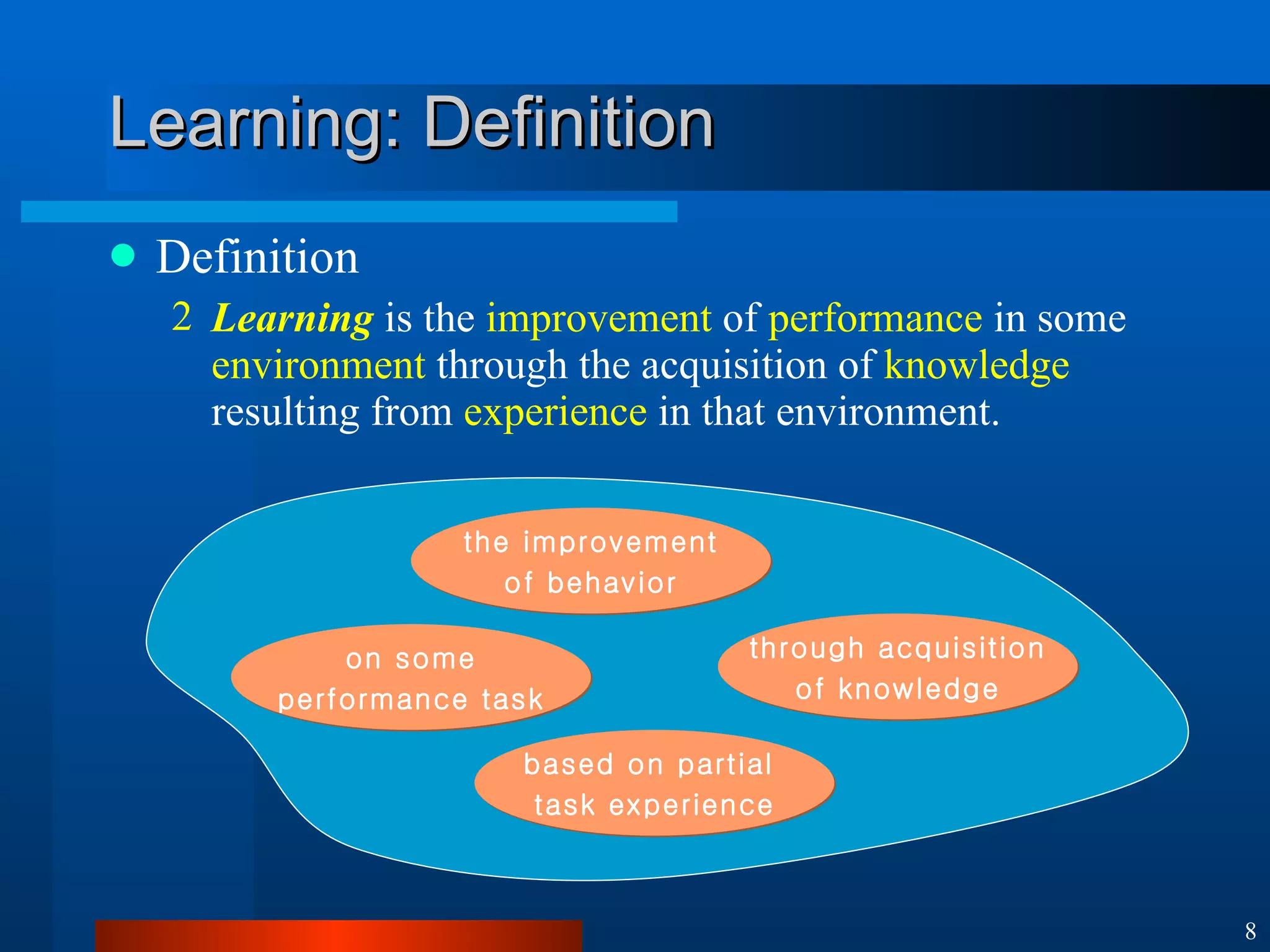
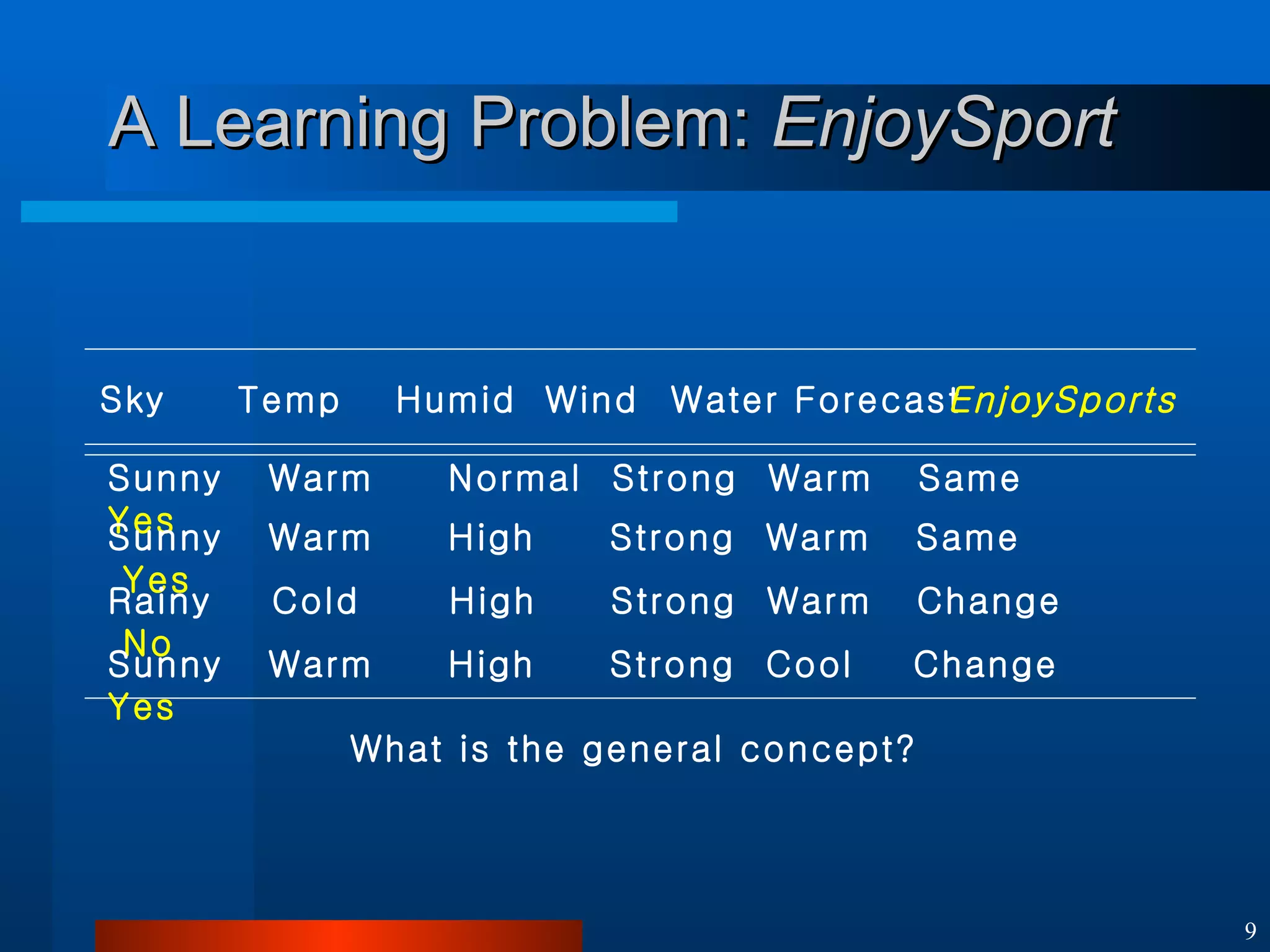
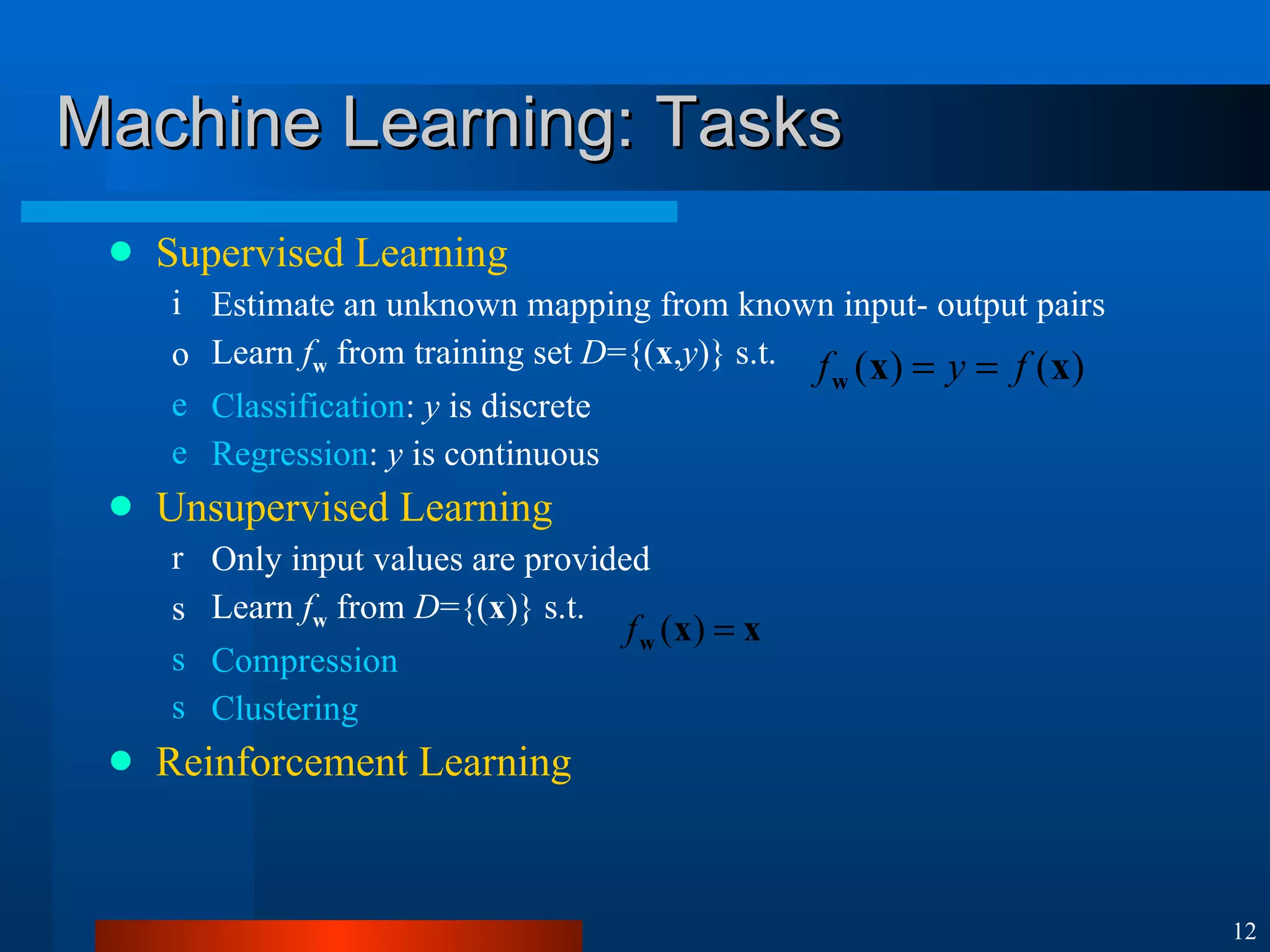
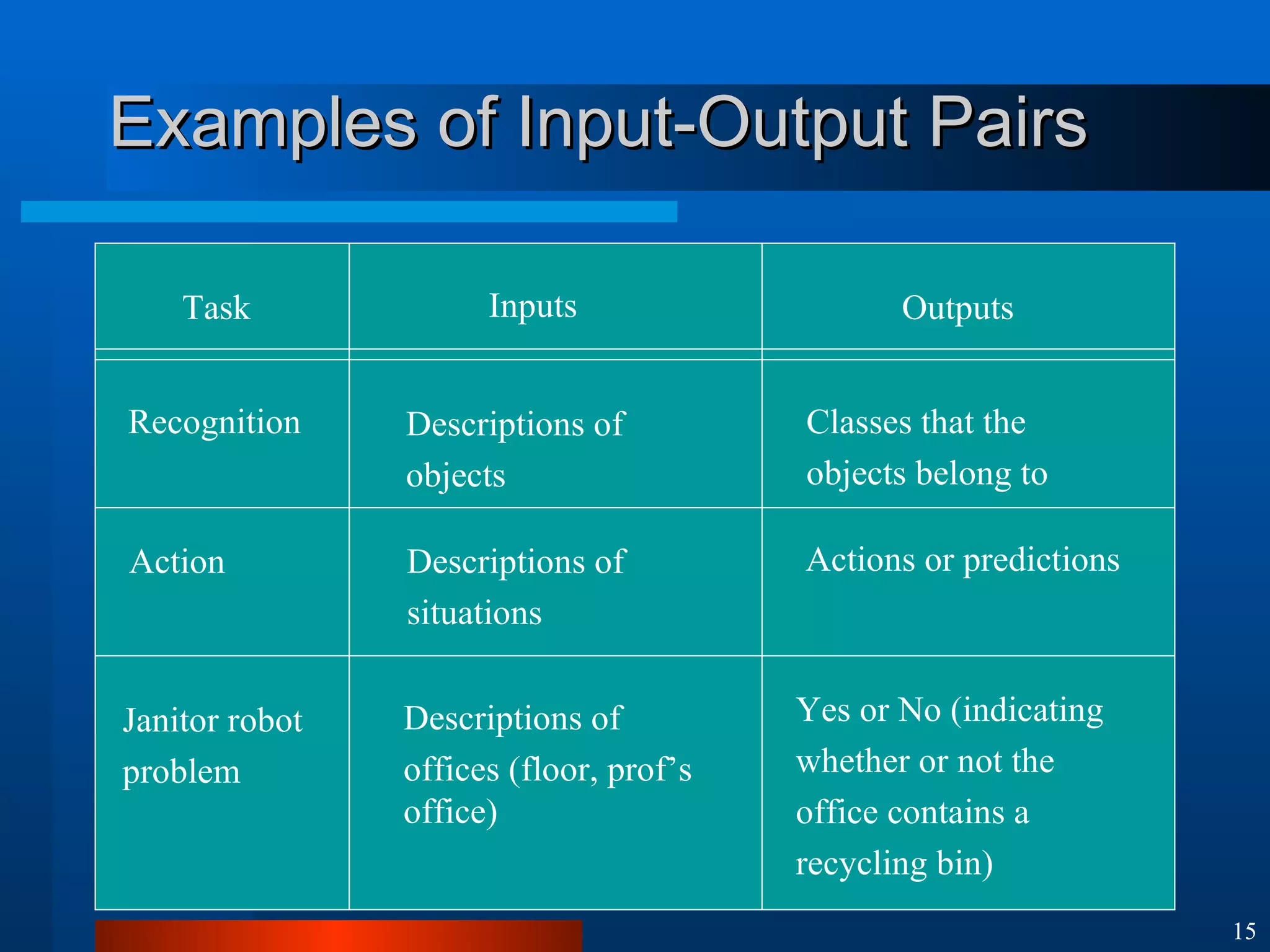
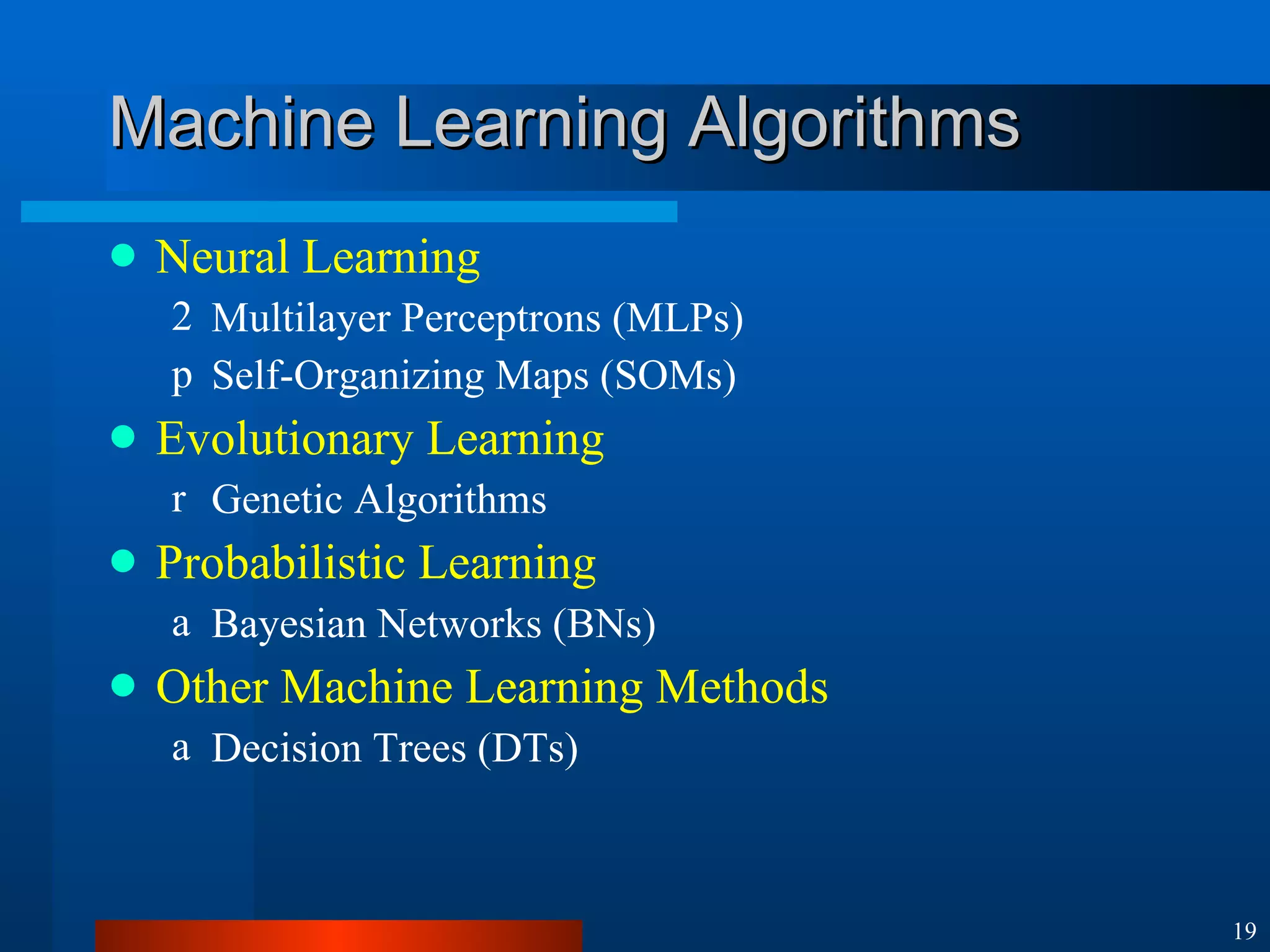
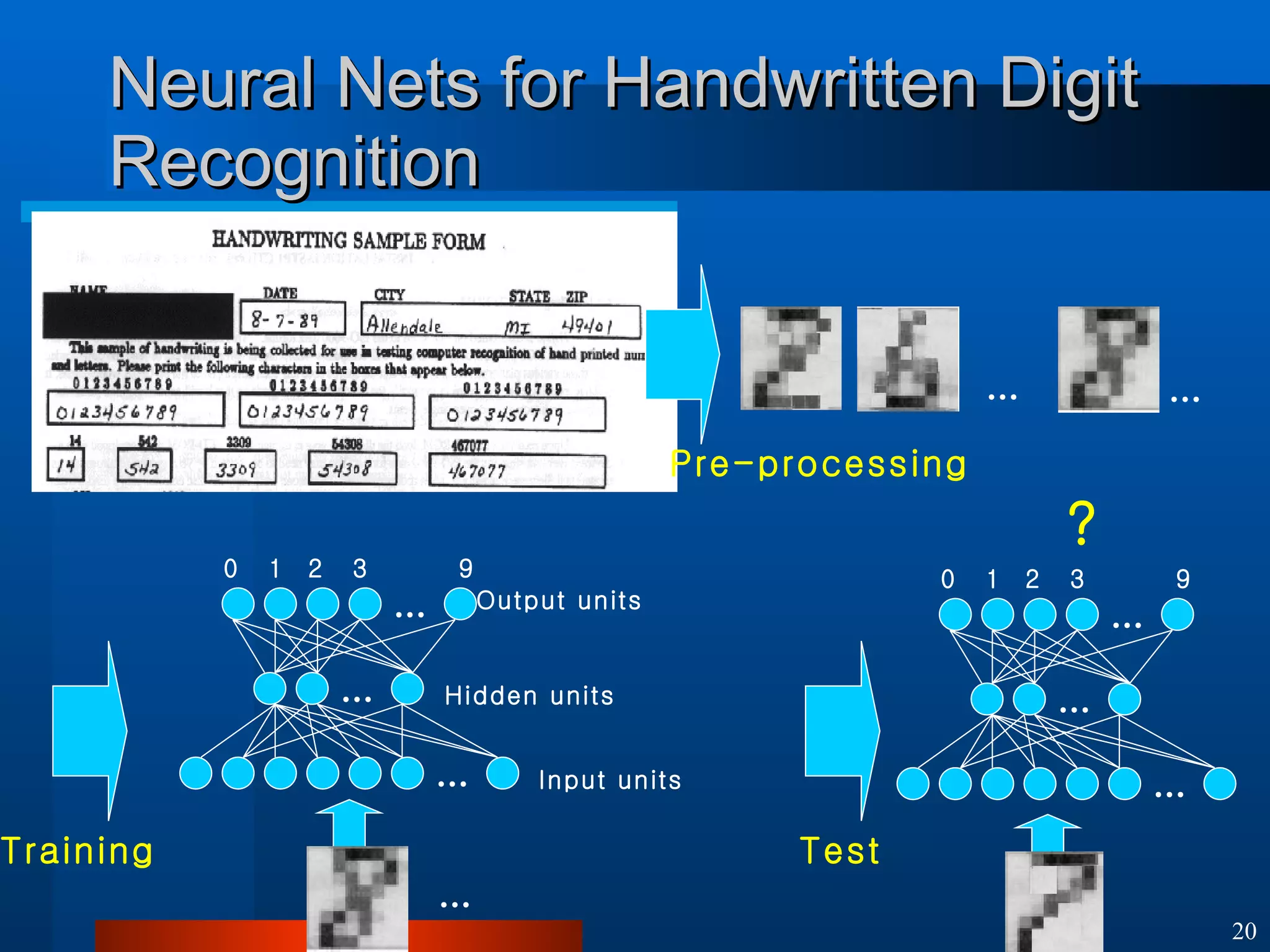
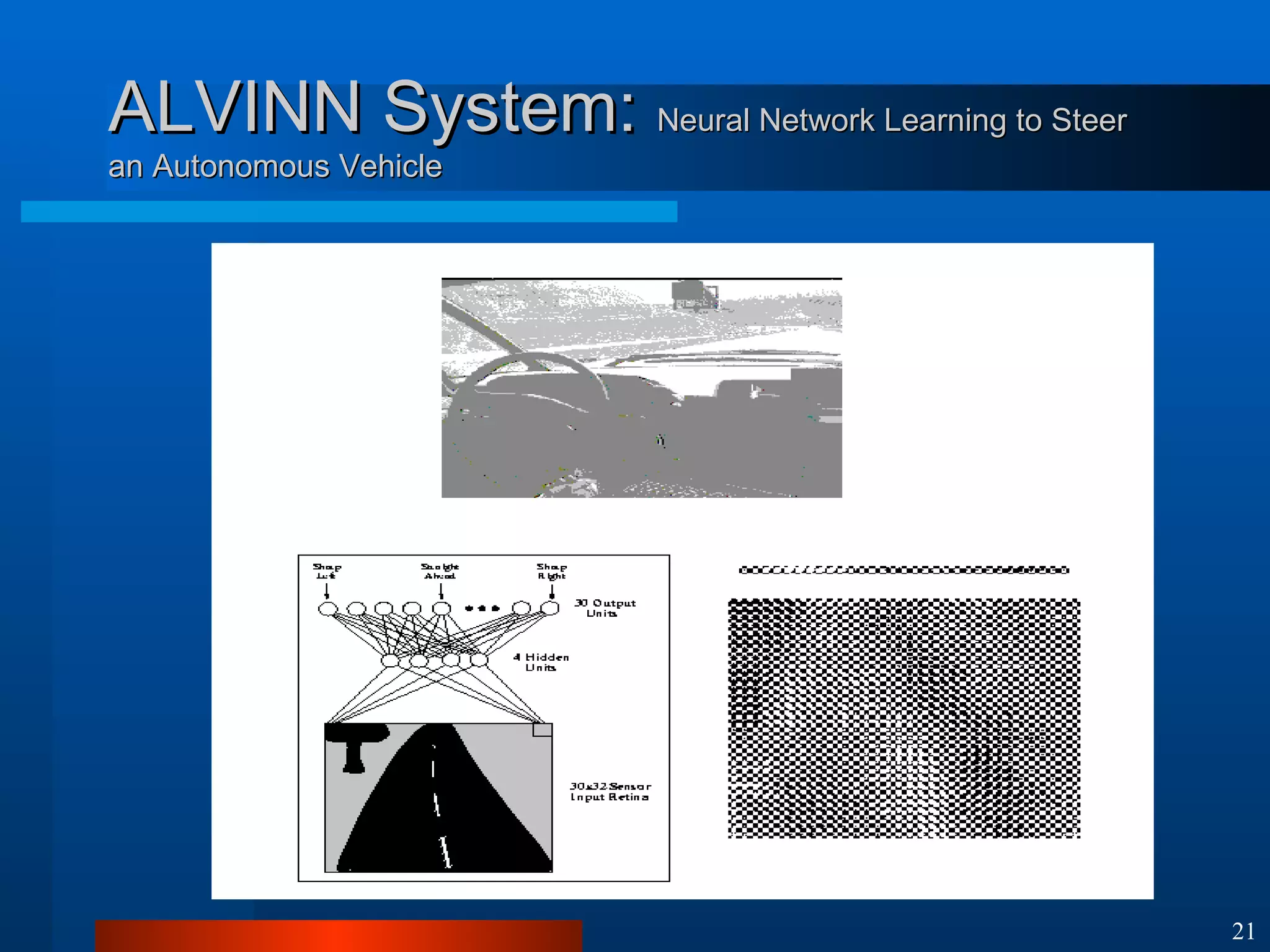
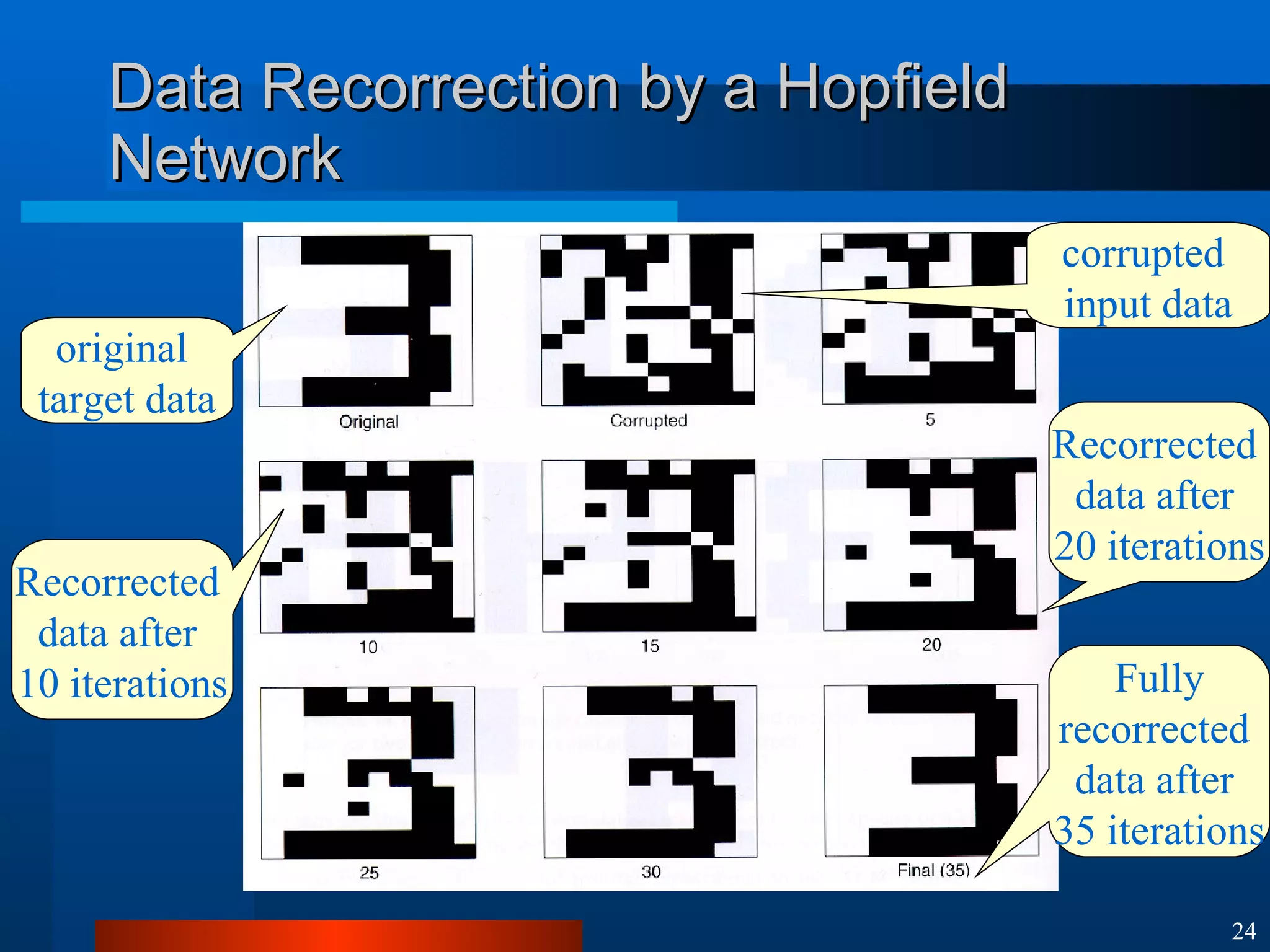
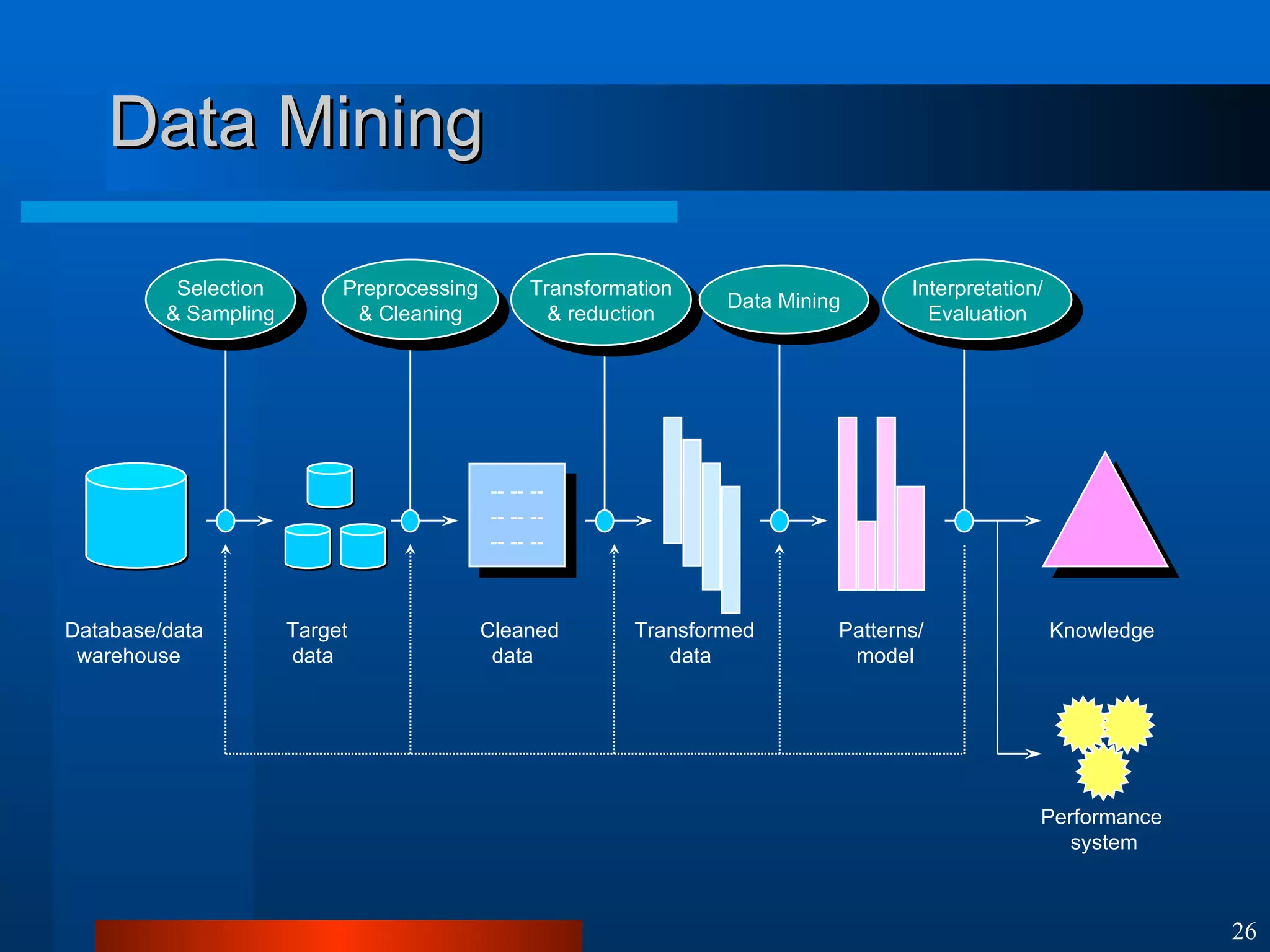
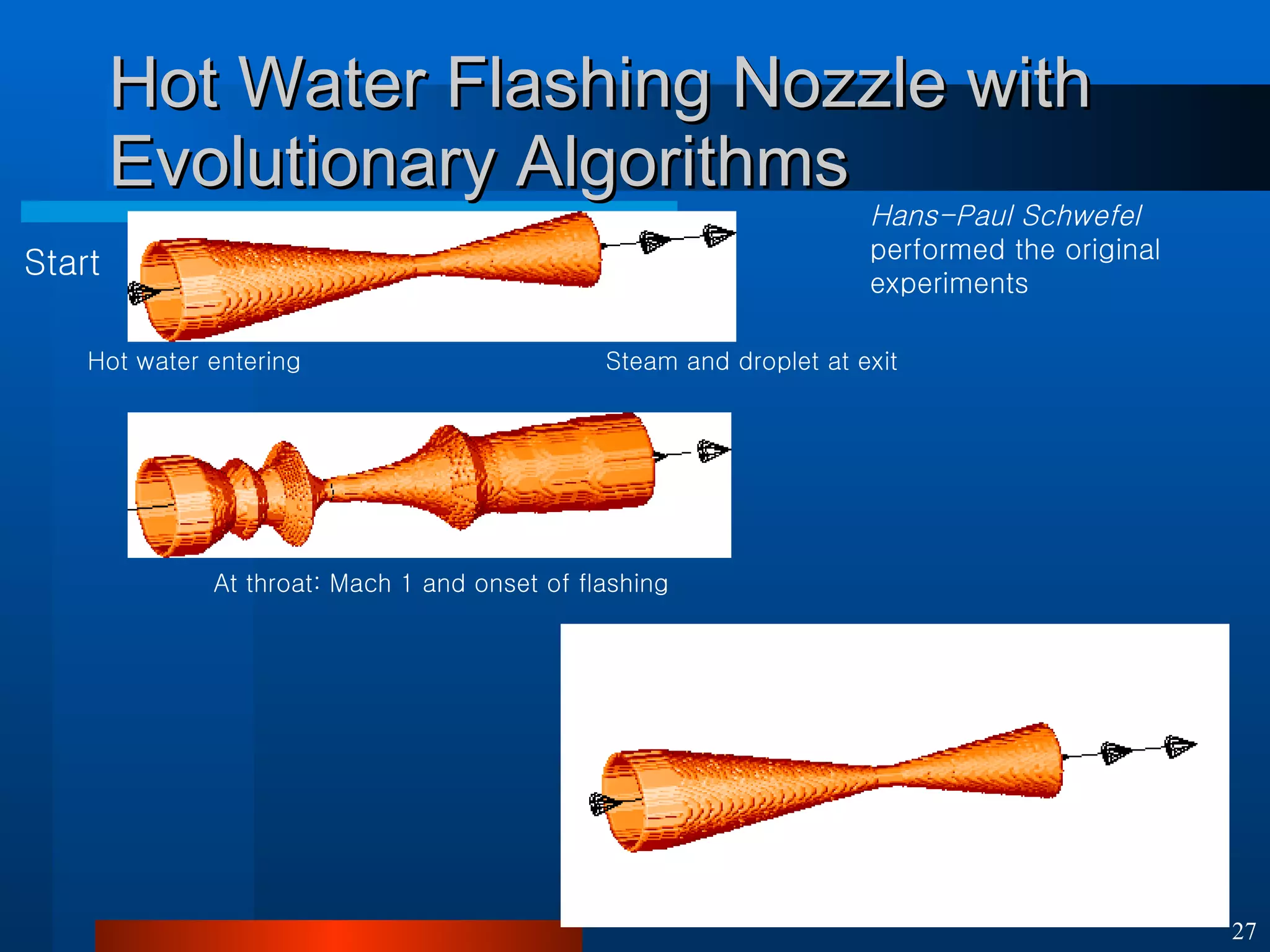
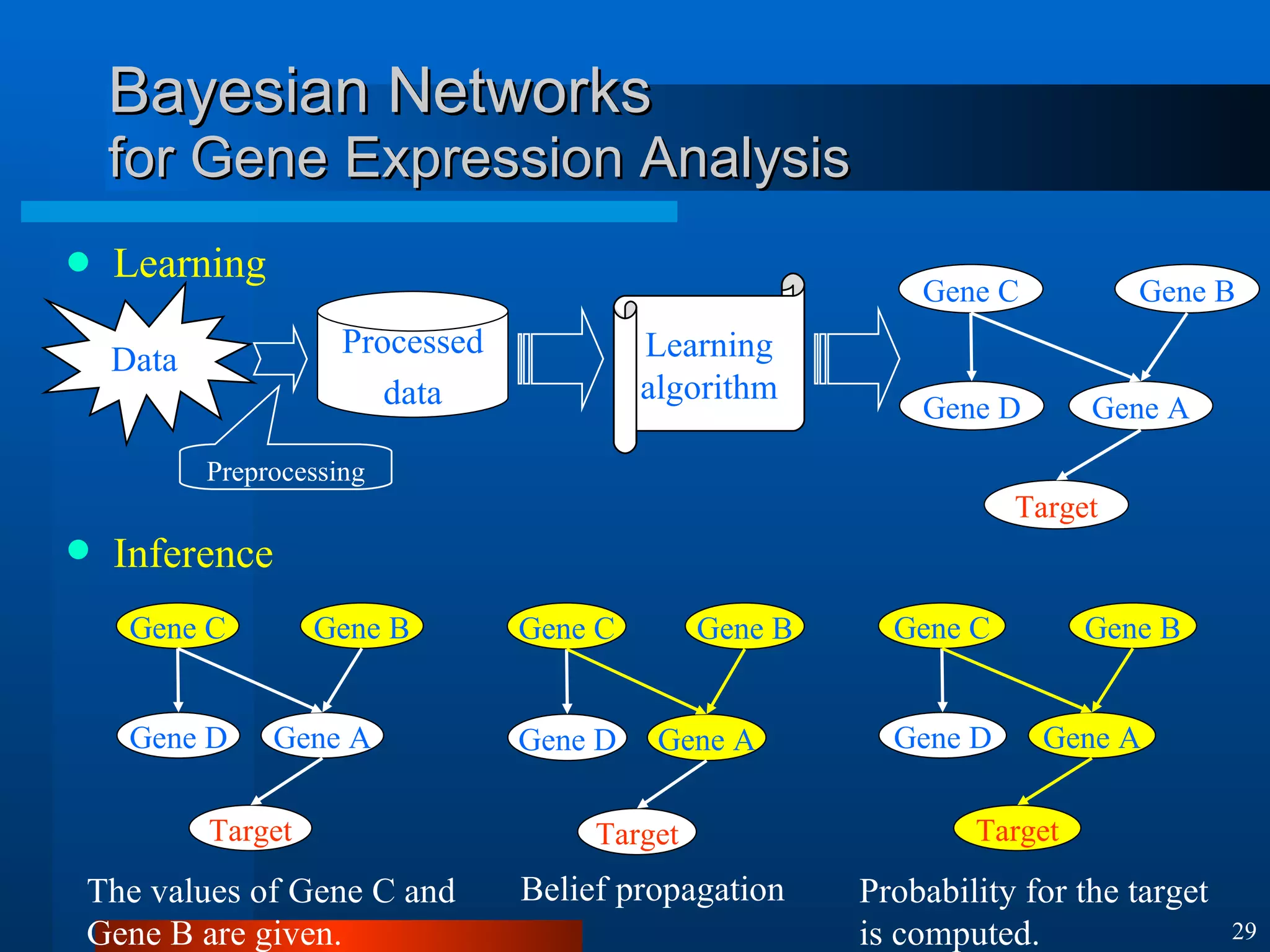
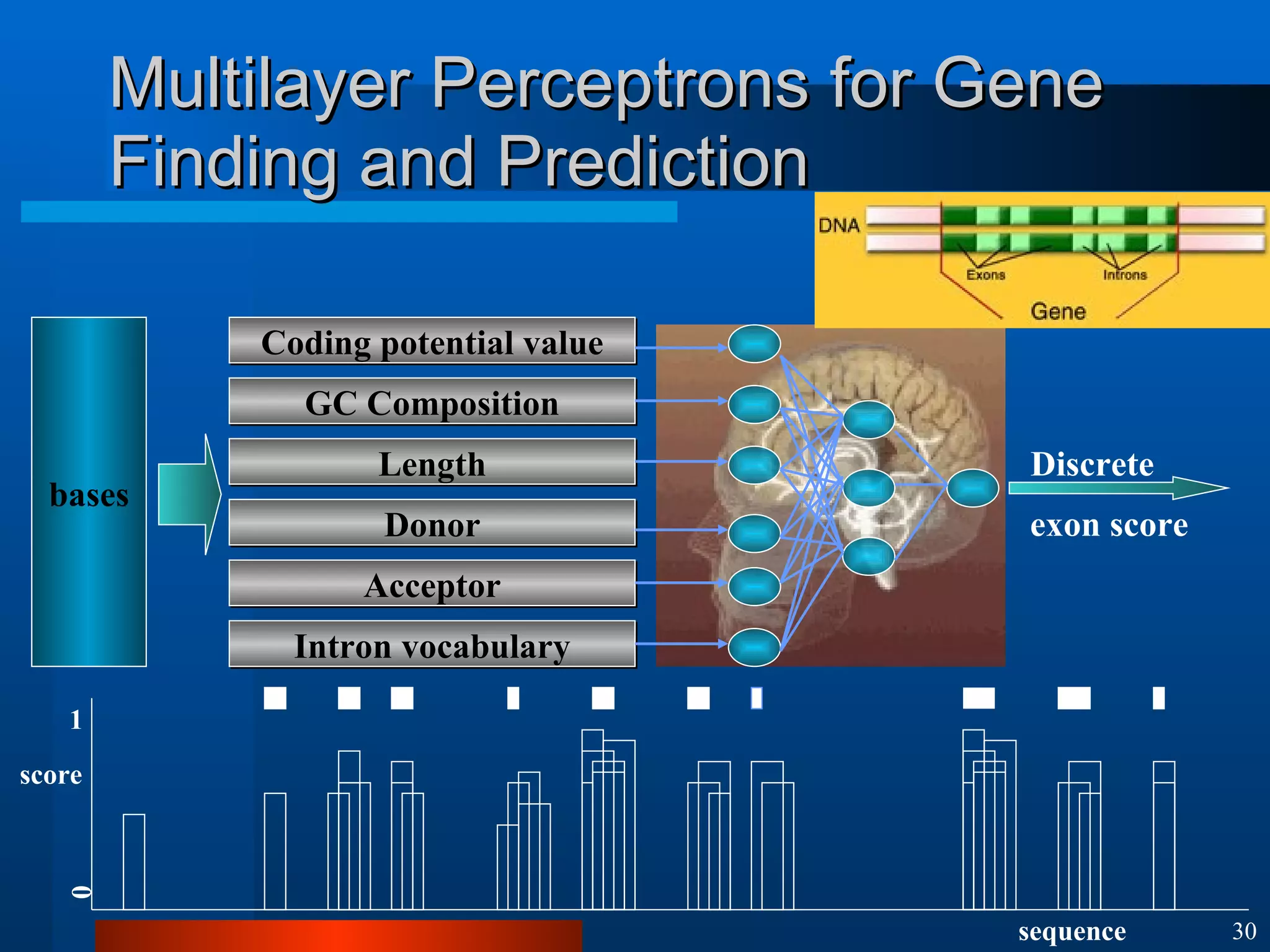
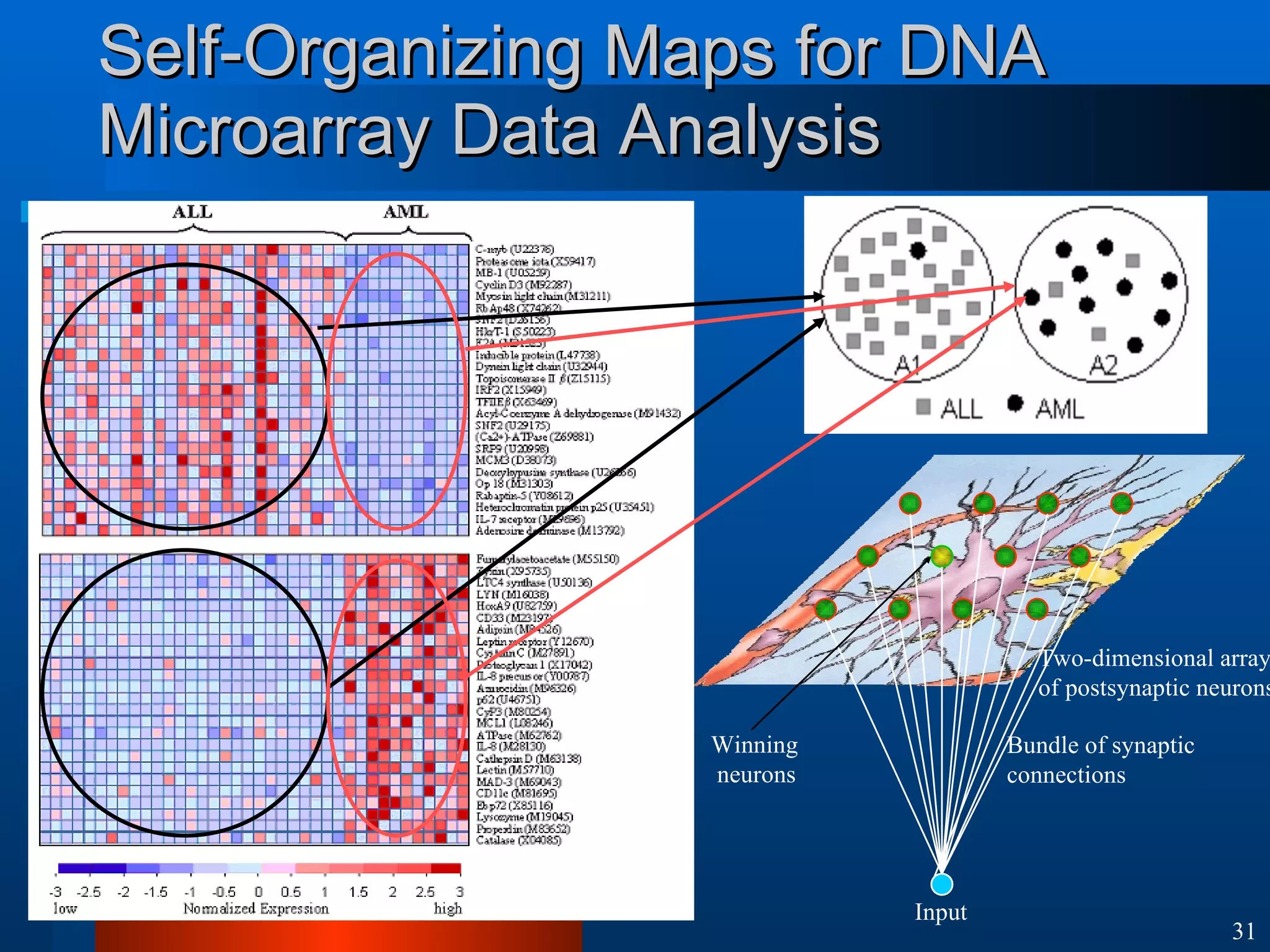
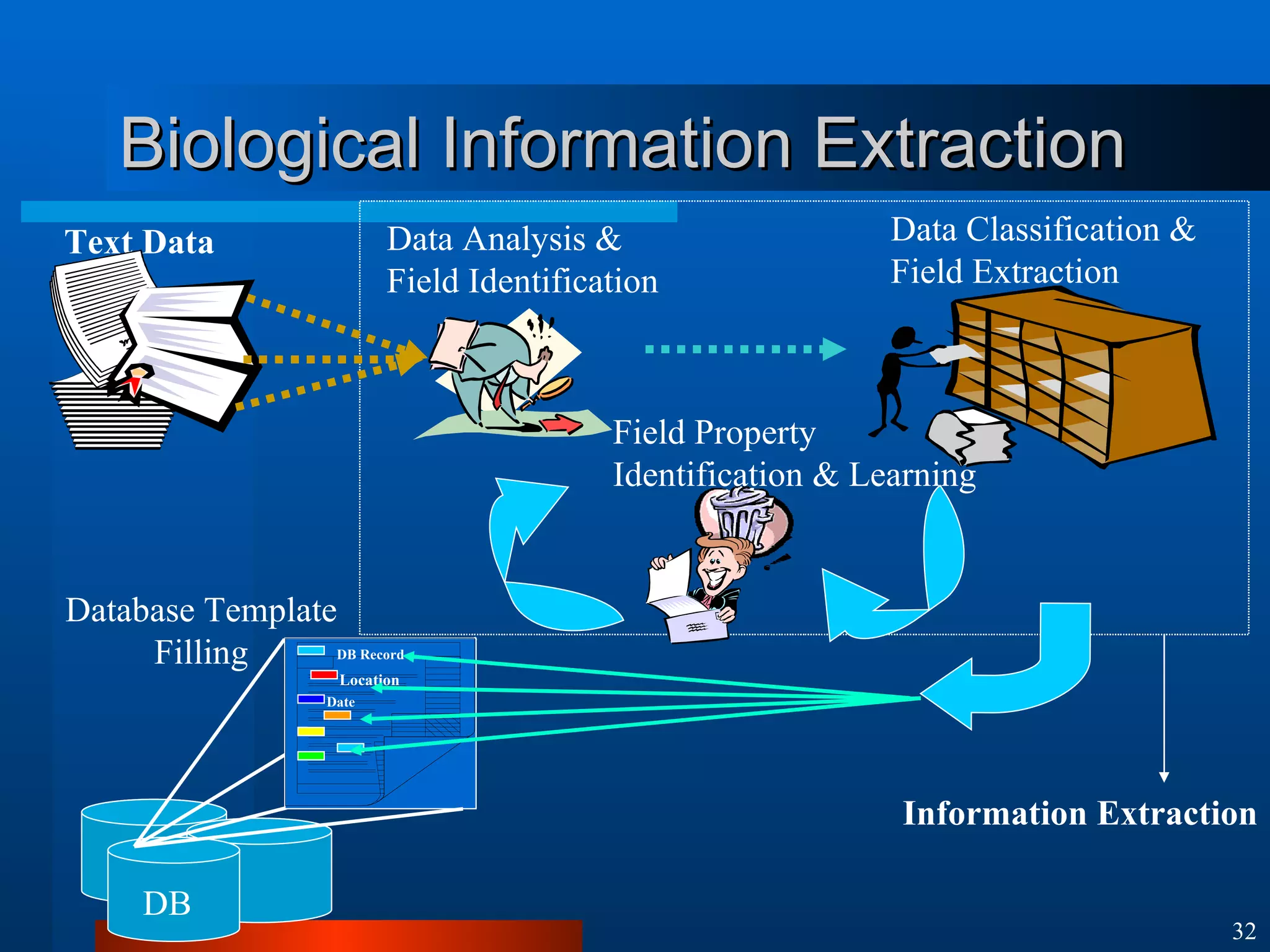
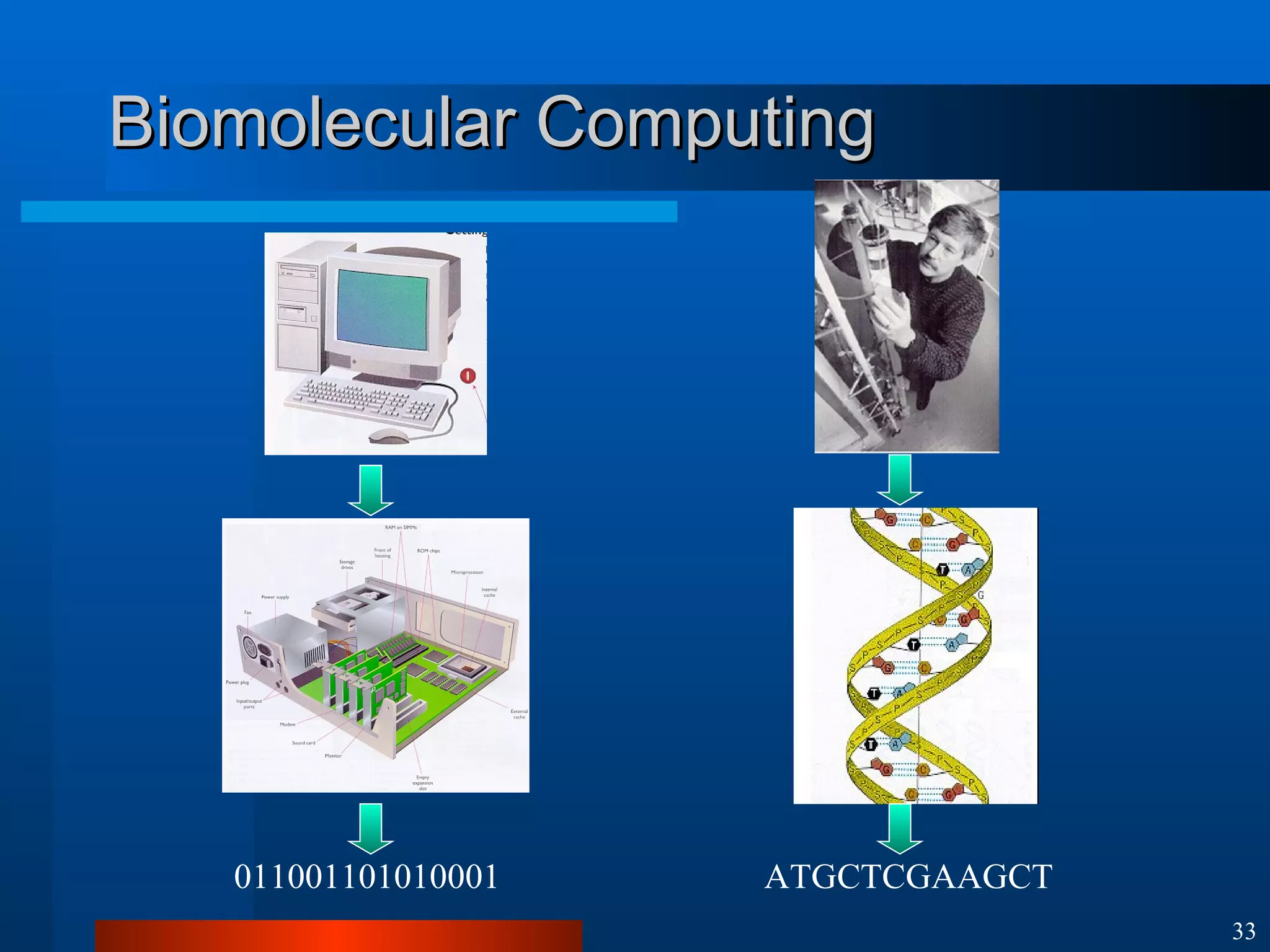
This document introduces machine learning algorithms. It discusses supervised and unsupervised learning problems and strategies. It provides examples of machine learning applications including neural networks for handwritten digit recognition, evolutionary algorithms for nozzle design, and Bayesian networks for gene expression analysis.