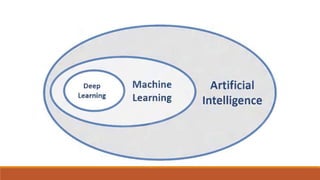
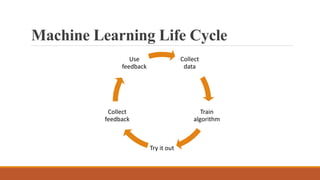
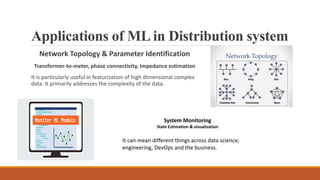
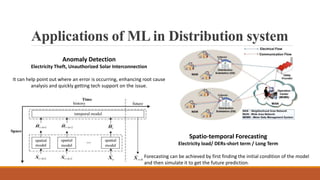
Machine learning has many applications in power systems including equipment monitoring, predictive maintenance, load forecasting, anomaly detection, and more. It can help automate tasks, analyze trends in large datasets, and improve systems over time by learning from experience. While machine learning provides benefits like efficiency and automation, it also has disadvantages such as potential errors, challenges in interpreting results and acquiring data, and significant time and resource requirements.