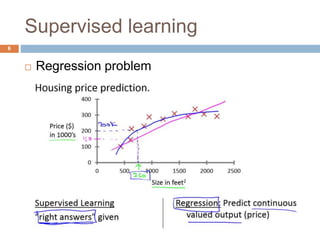
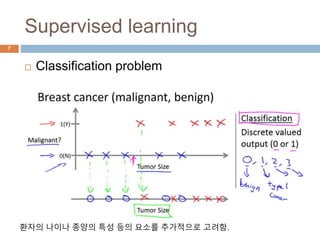
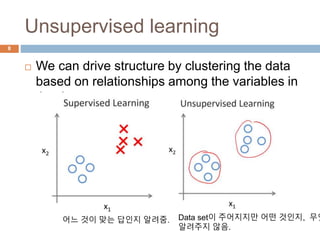
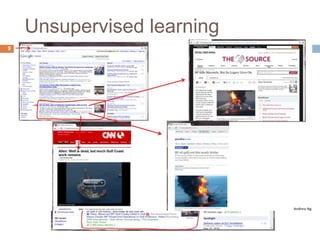
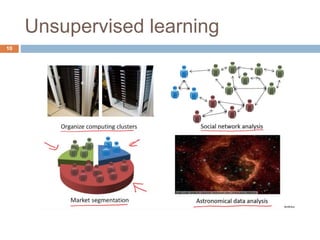
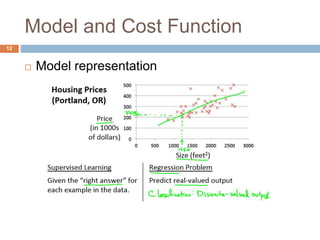
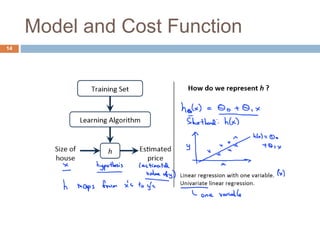
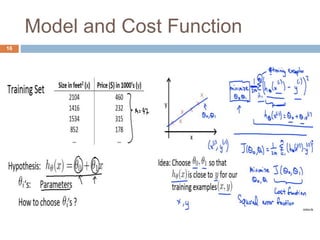
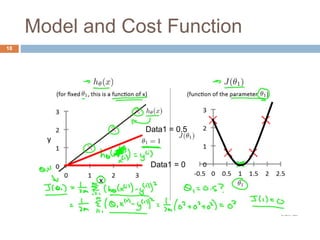
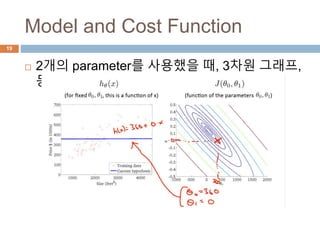
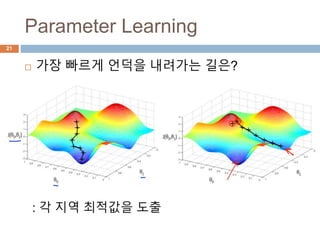
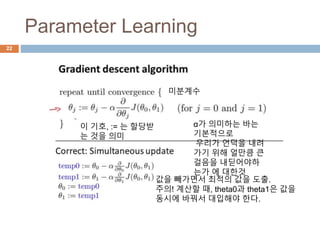
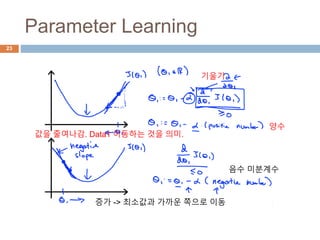
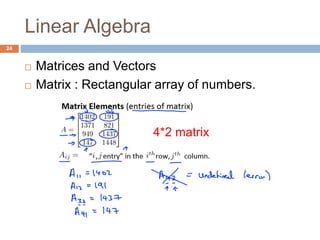
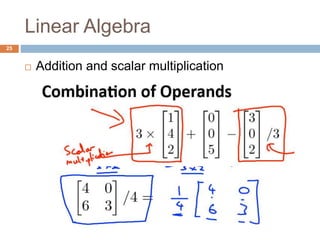
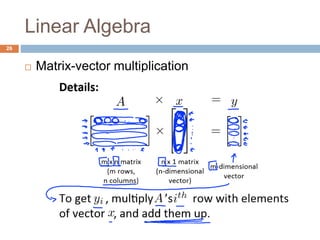
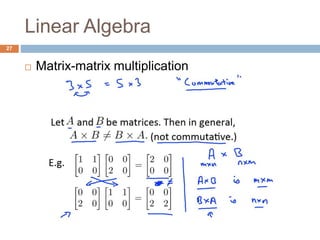
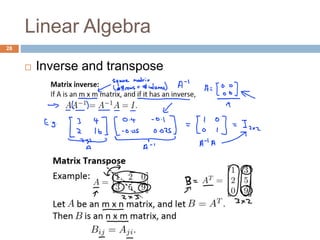
This document provides an introduction to machine learning concepts including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, models and cost functions, and parameter learning. It discusses how machine learning allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Supervised learning uses labeled data to find relationships between inputs and outputs, while unsupervised learning finds structure in unlabeled data through clustering and other methods. Models are represented using functions and parameters, and cost functions measure accuracy by calculating the average difference between predictions and actual values. Parameter learning uses gradient descent to minimize the cost function and find optimal parameter values by iteratively adjusting them based on the cost function's derivative.