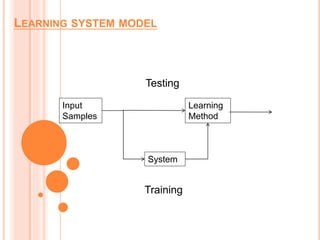
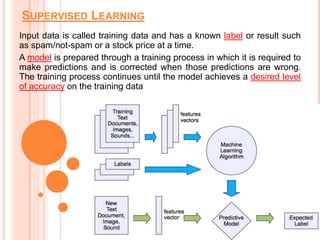
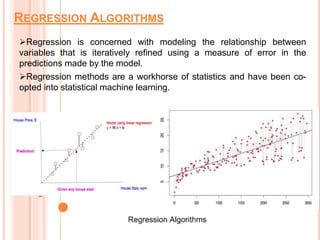
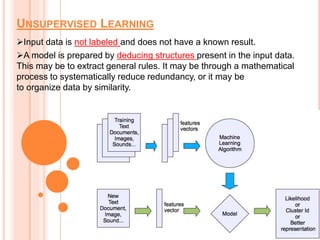
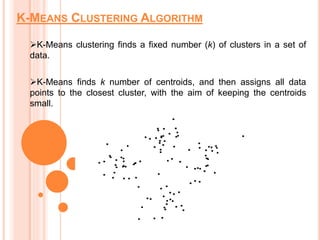
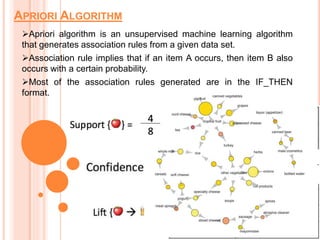
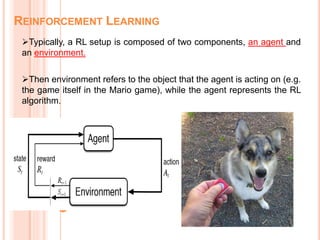
Soft computing encompasses methodologies that leverage tolerance for imprecision and uncertainty, aiming to replicate human-like decision-making in machines. Machine learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, enables systems to learn from data autonomously, with various algorithms like supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning addressing diverse data problems. Applications of machine learning include virtual assistants, social media services, search engine optimization, and product recommendations.