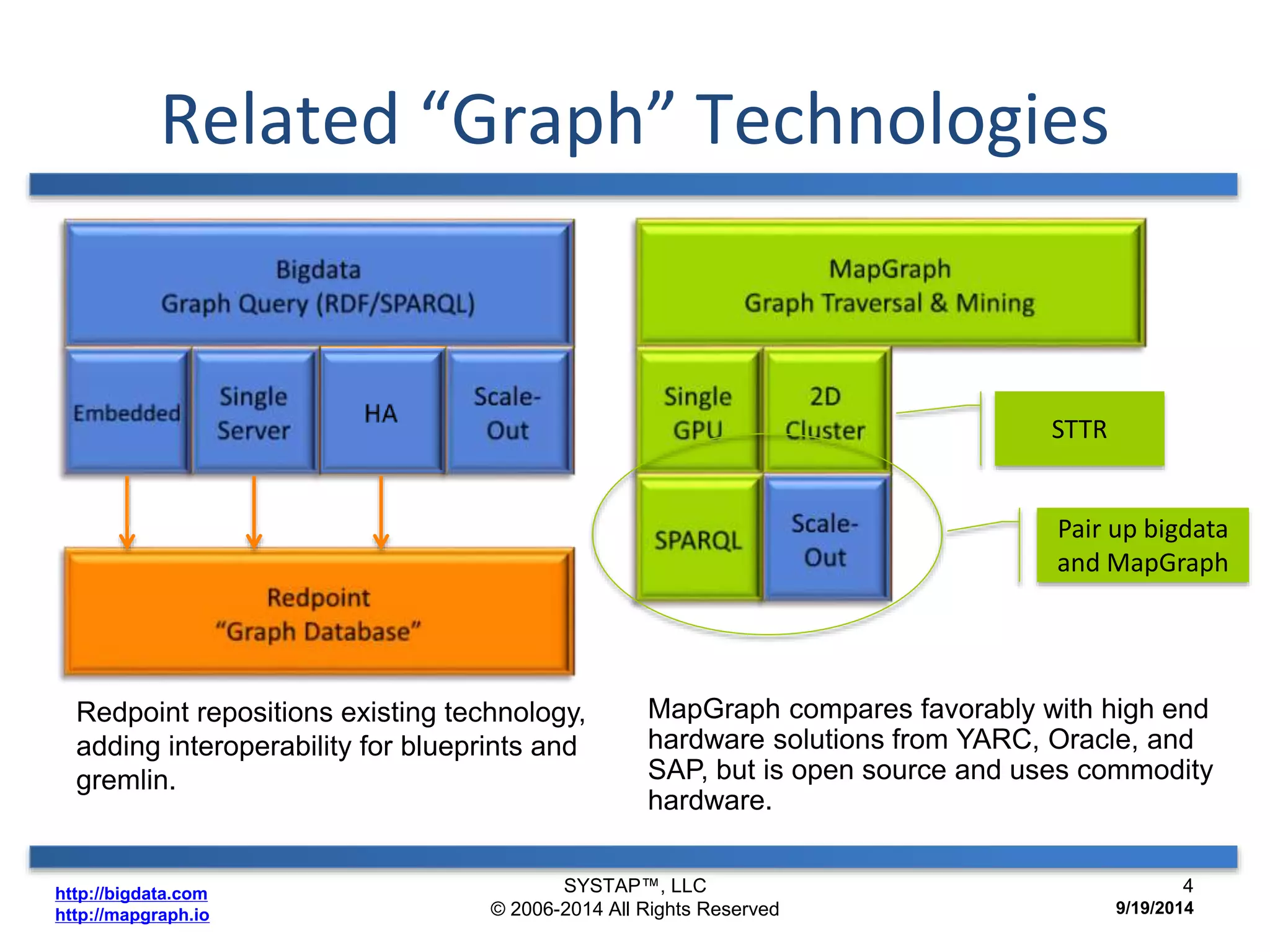
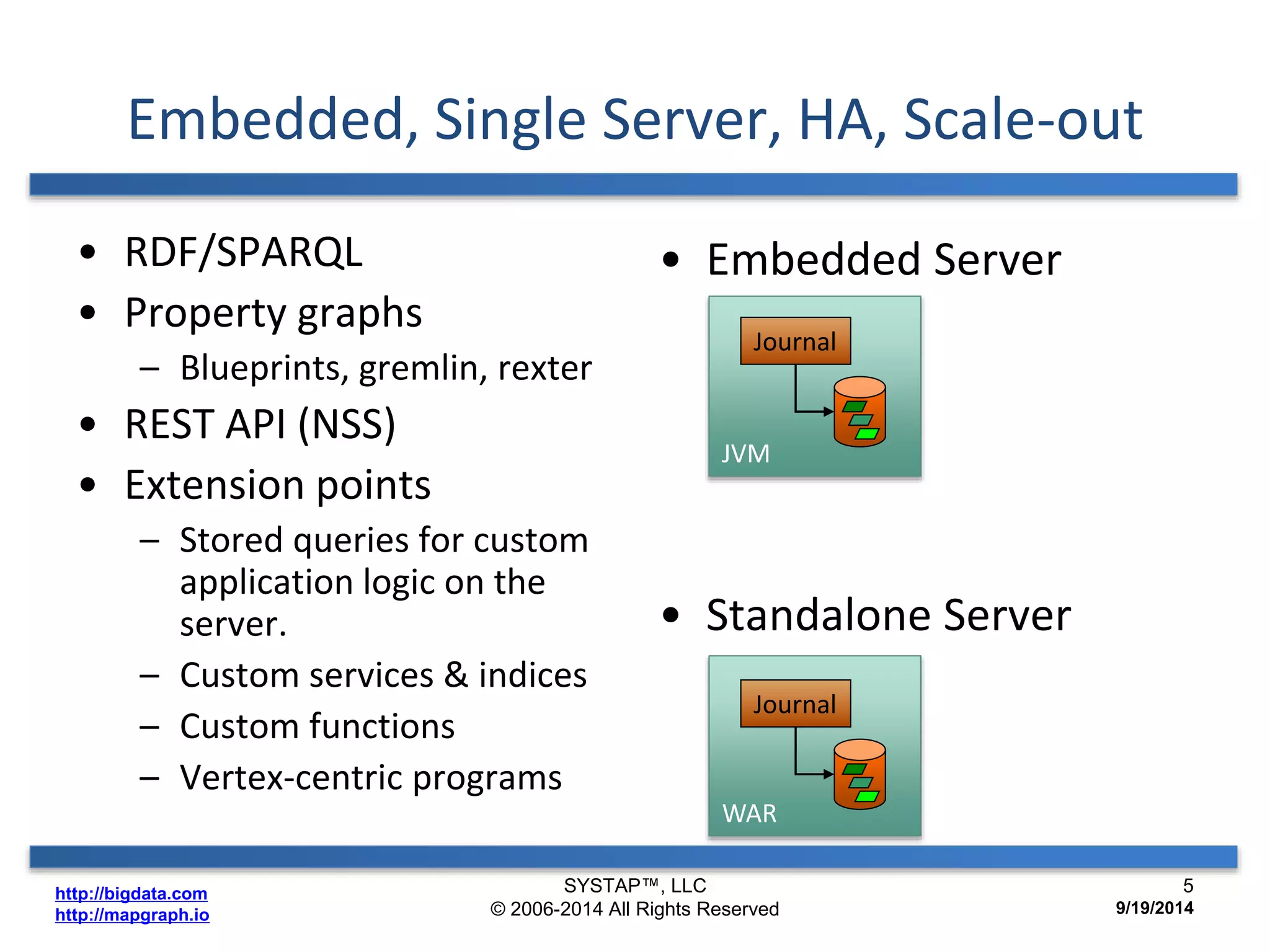
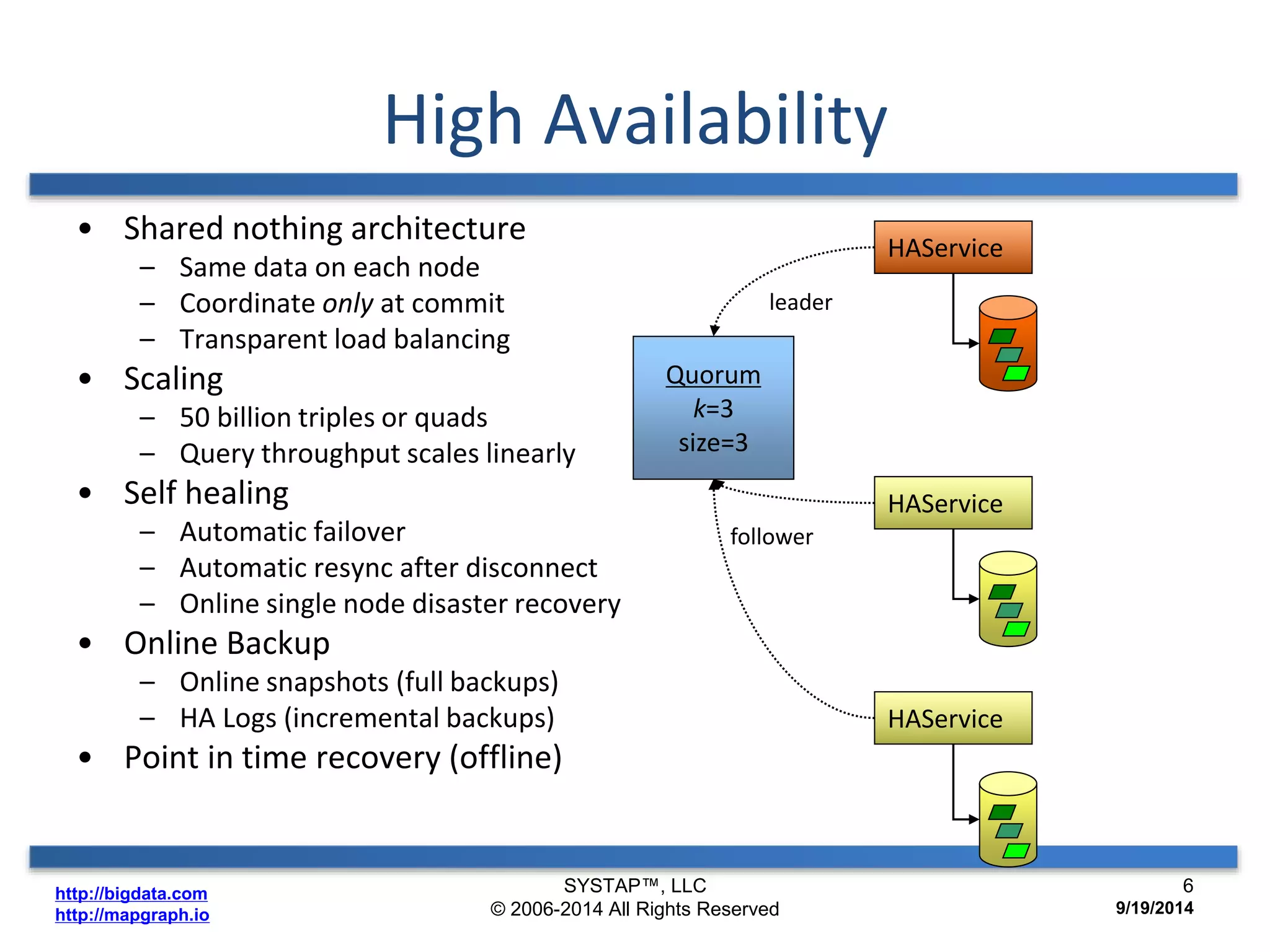
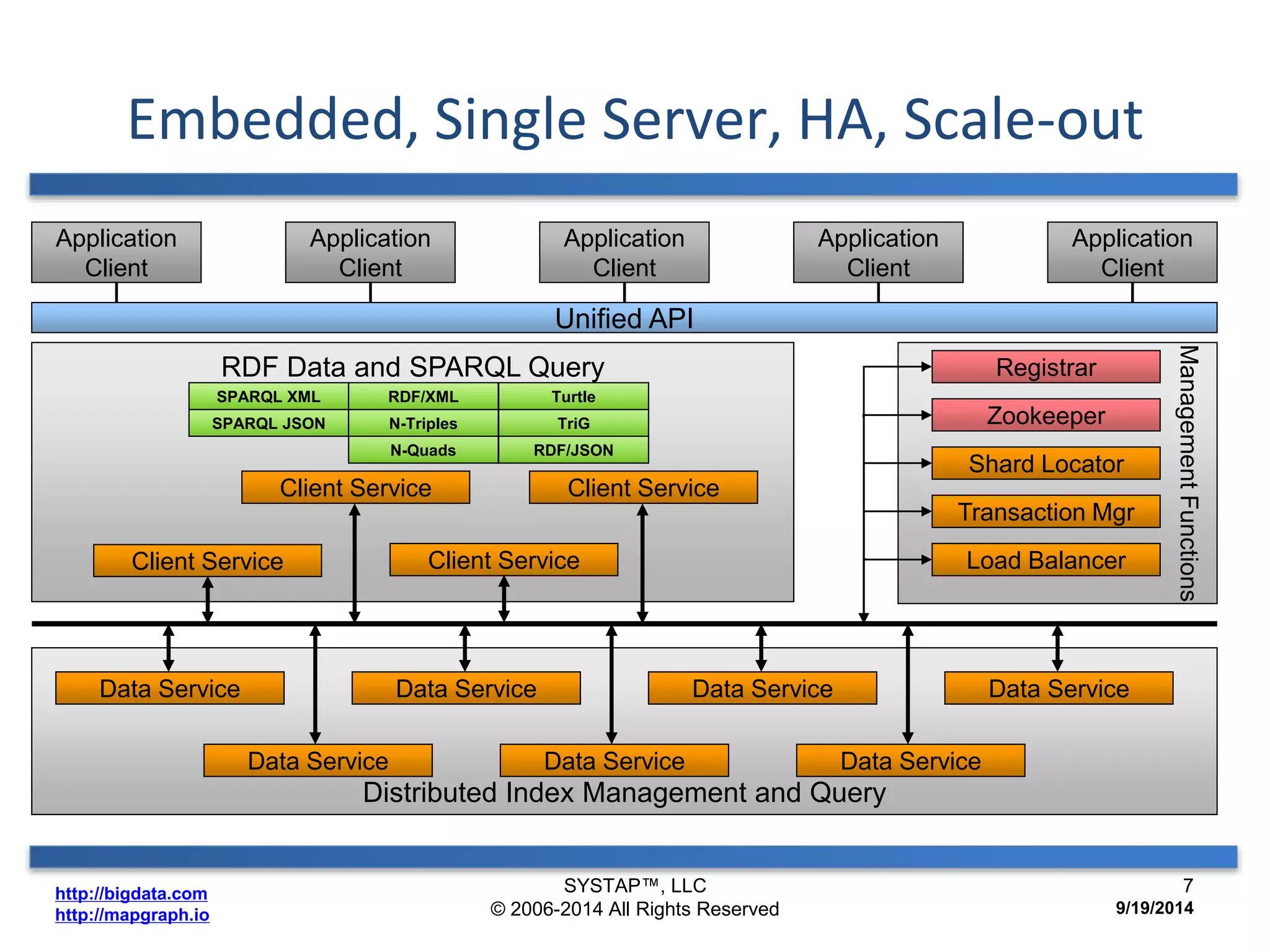
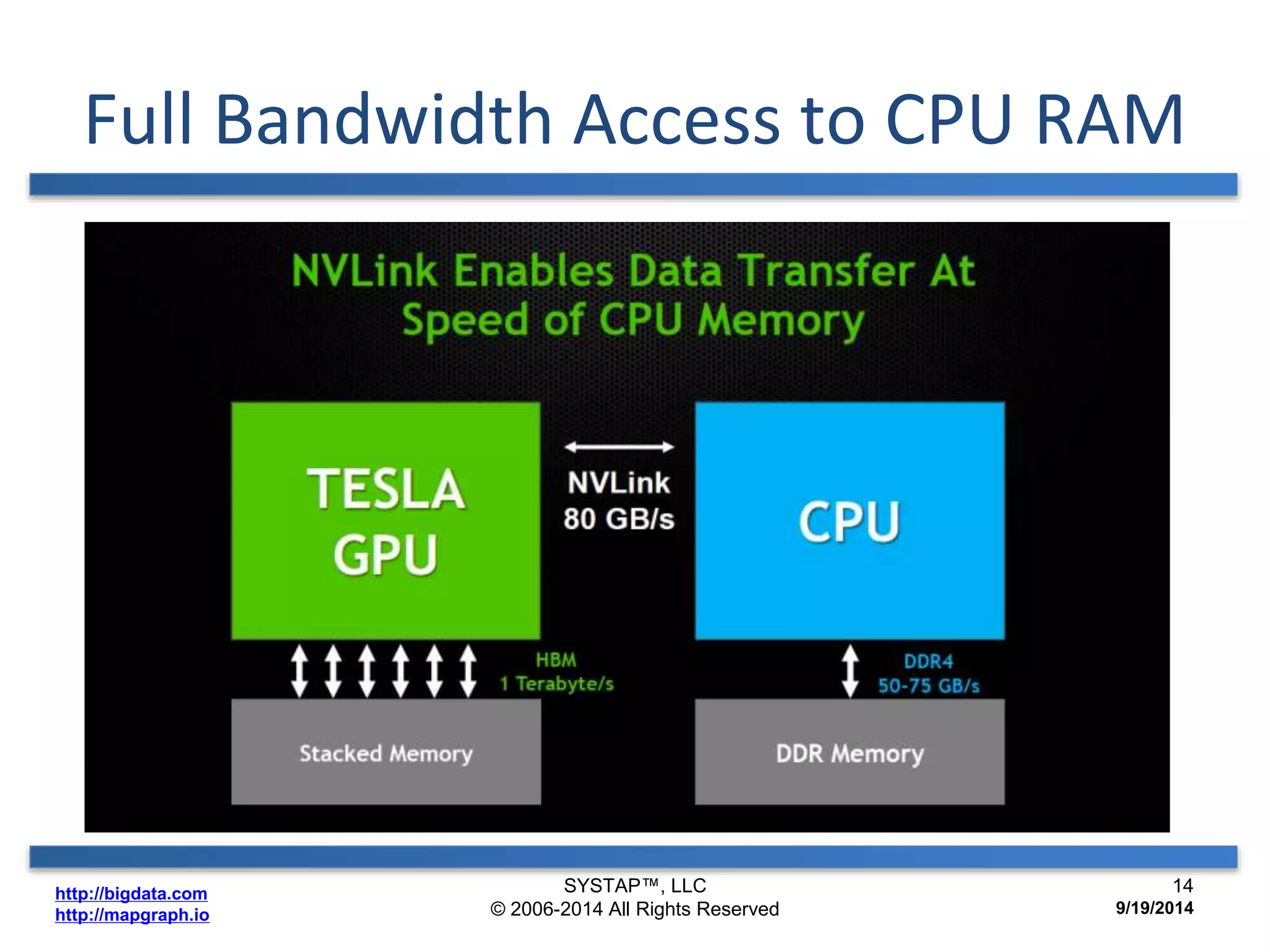
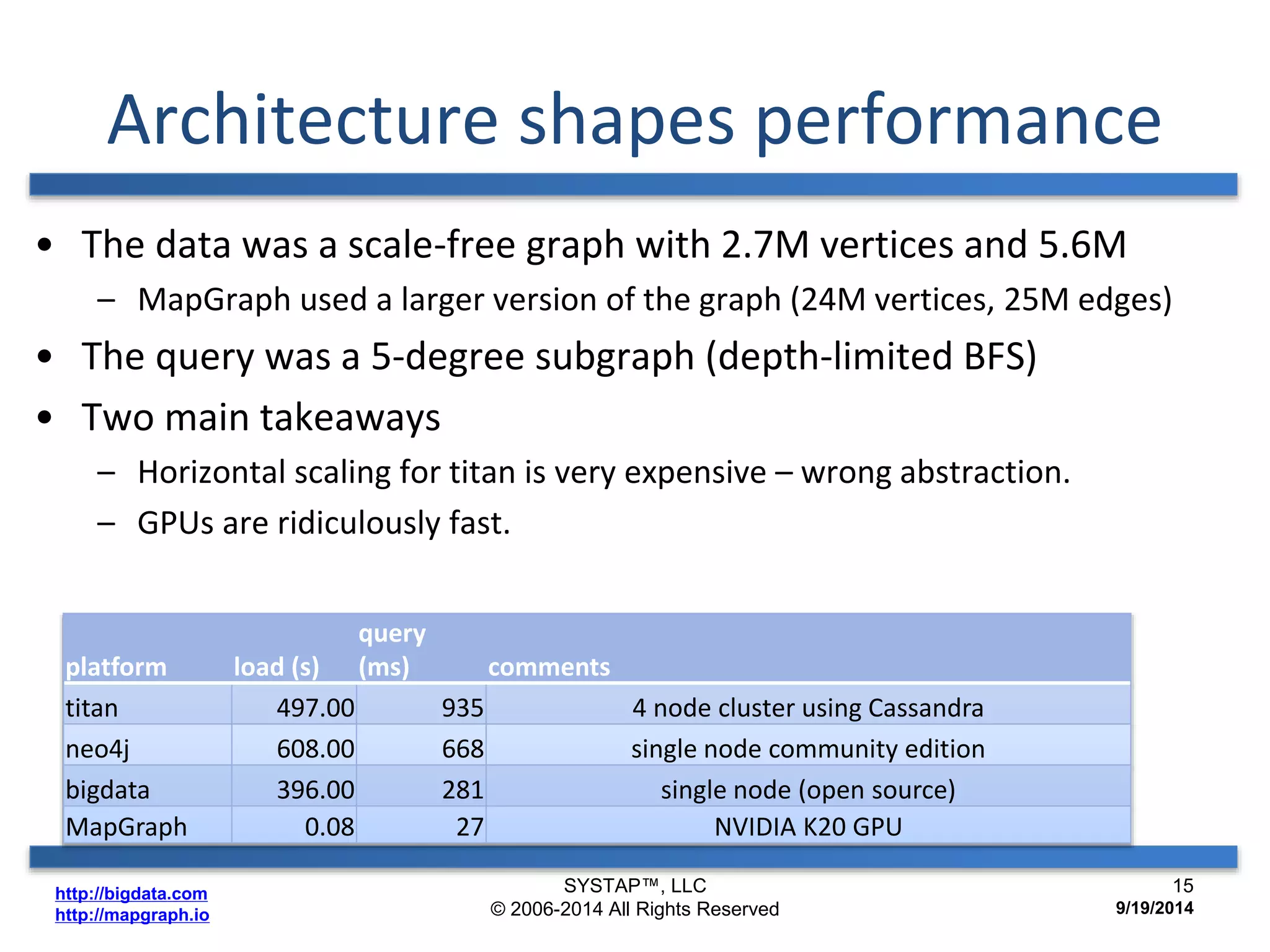
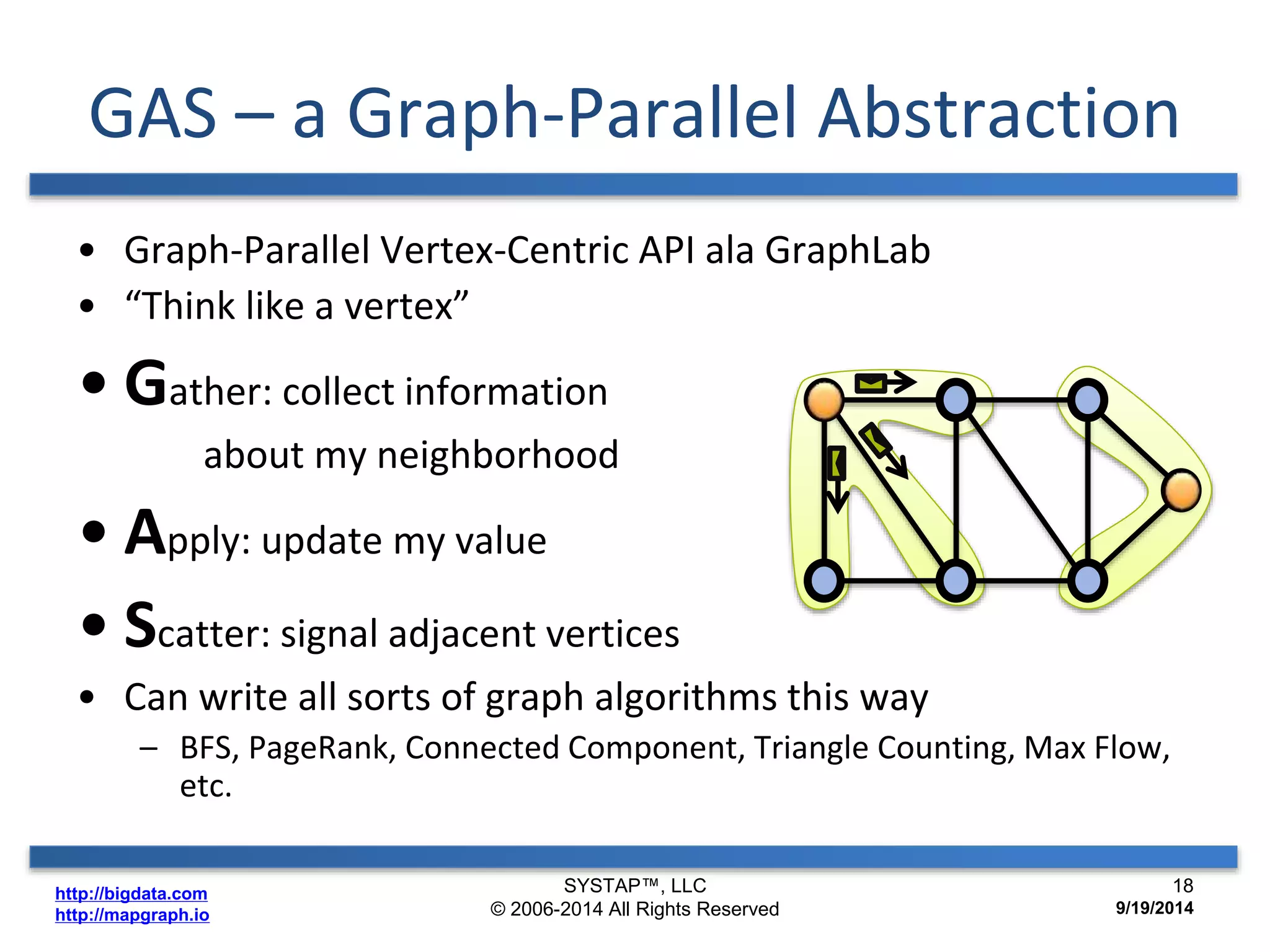
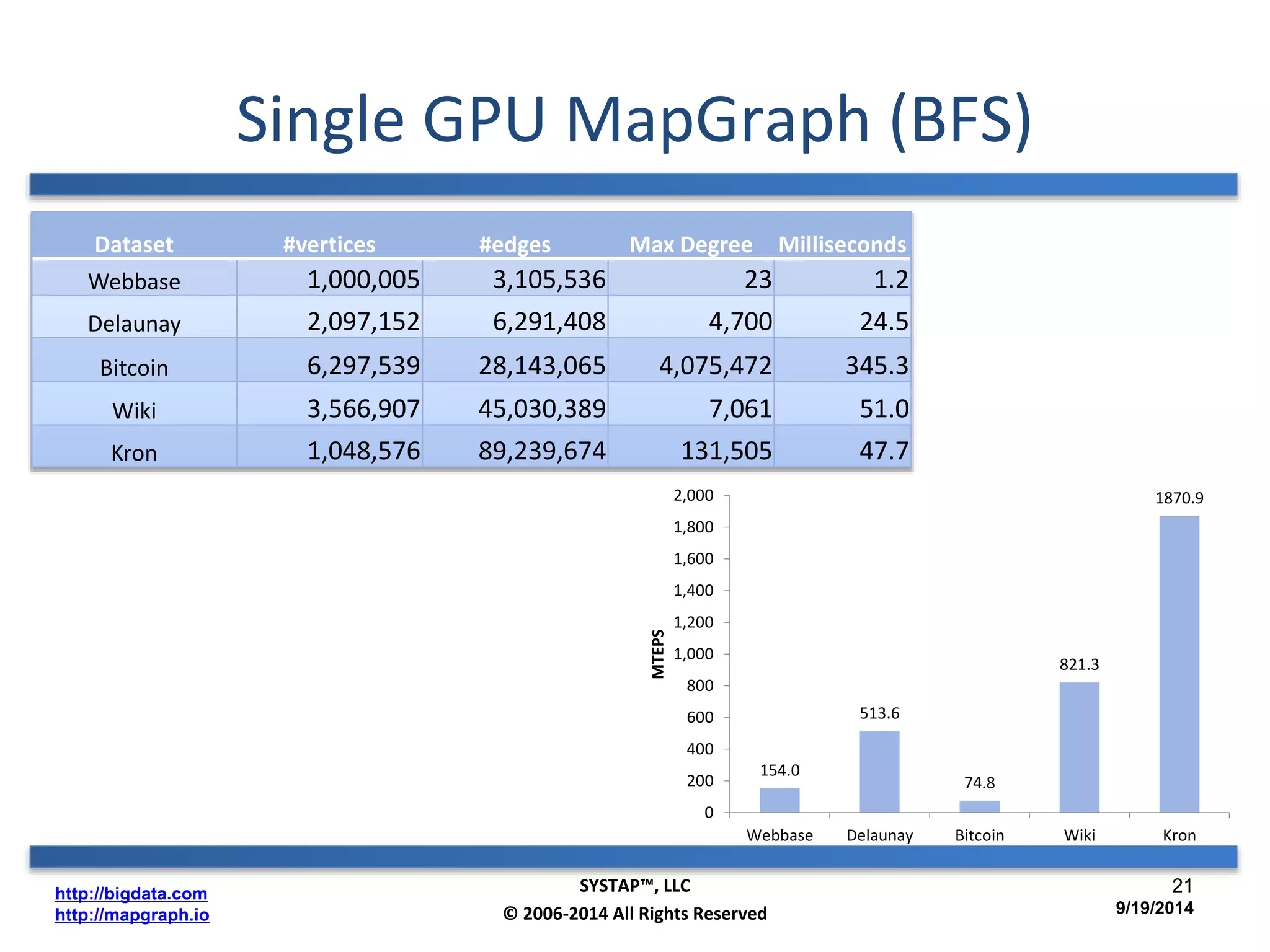
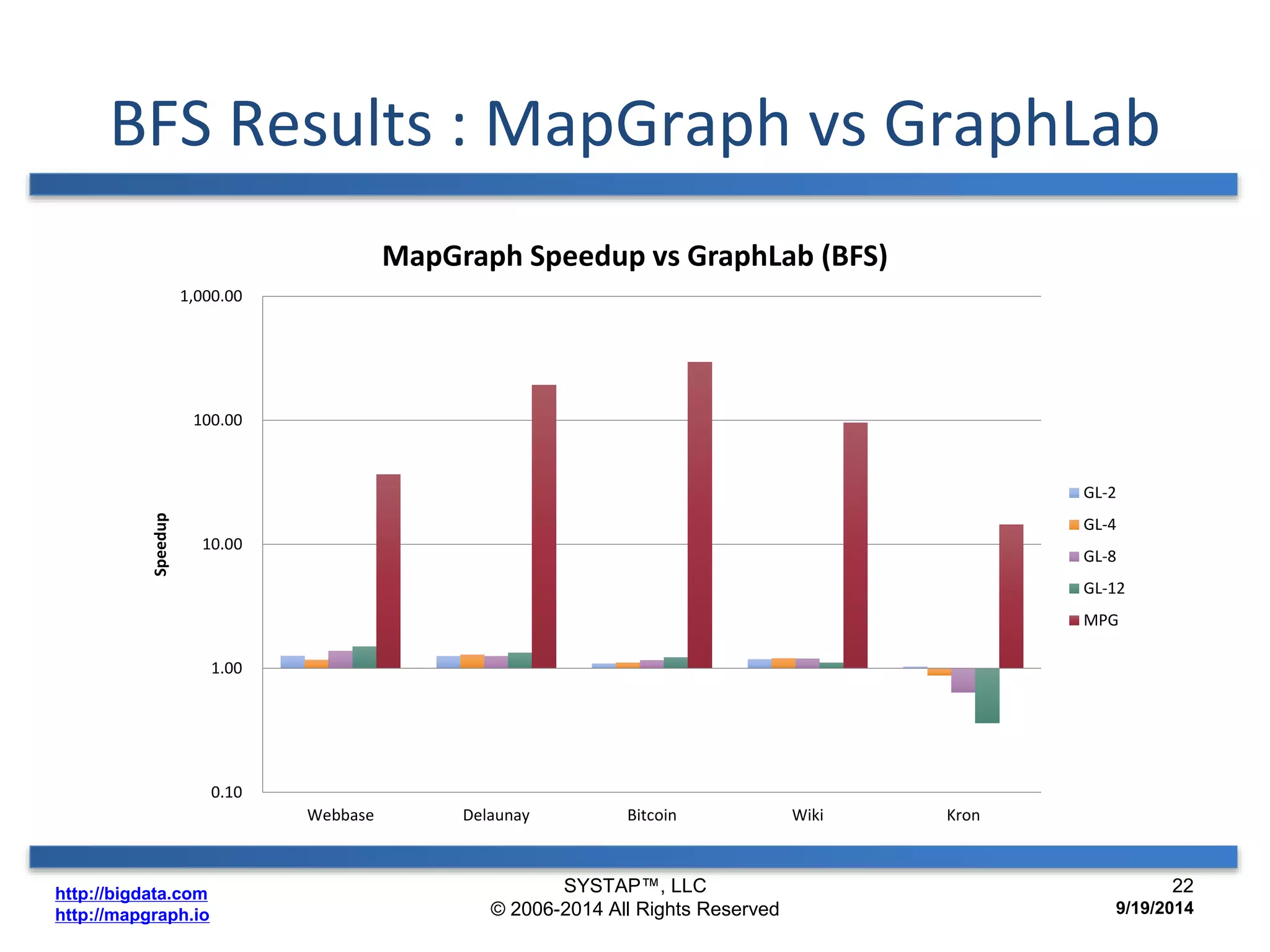
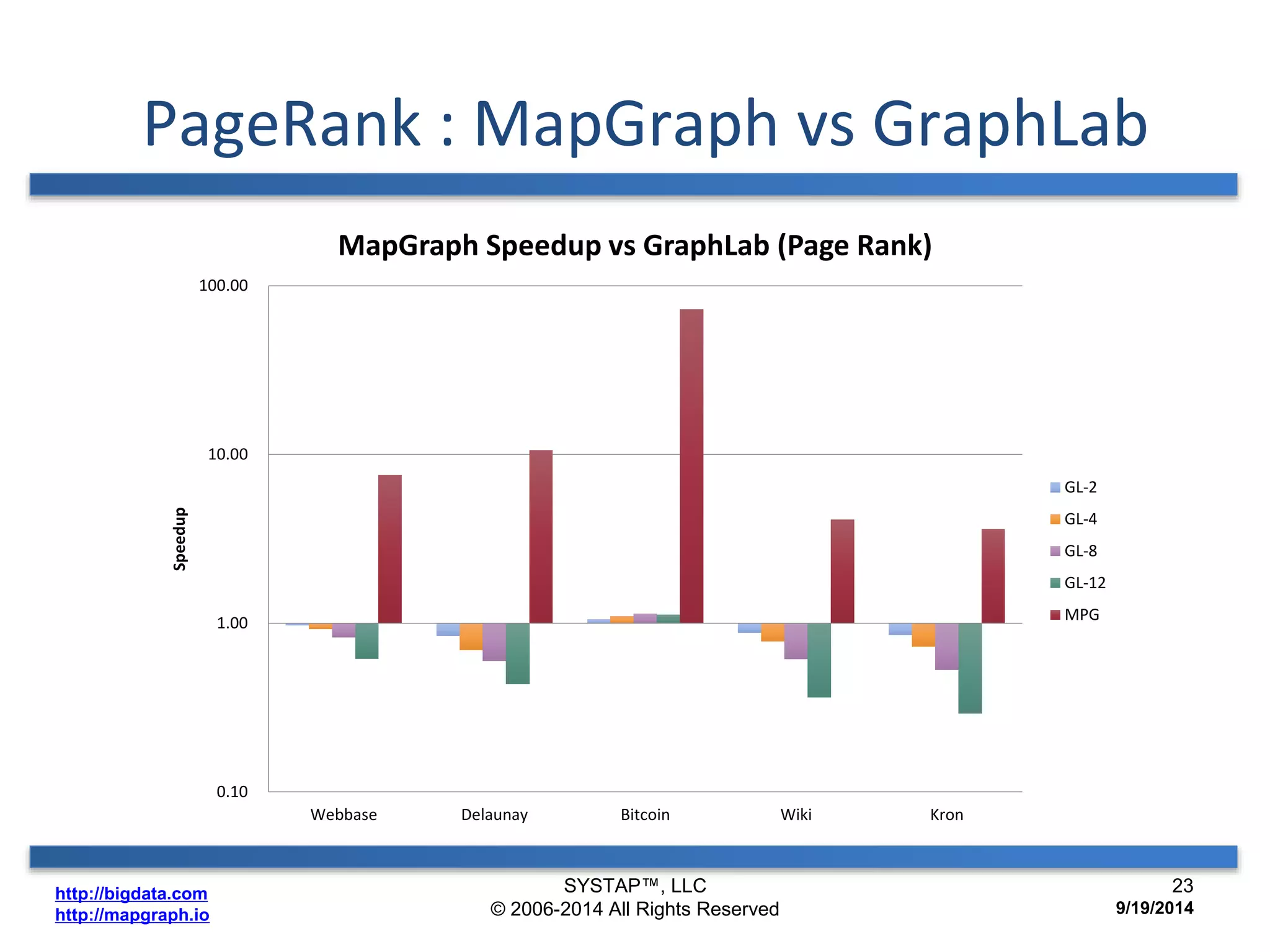
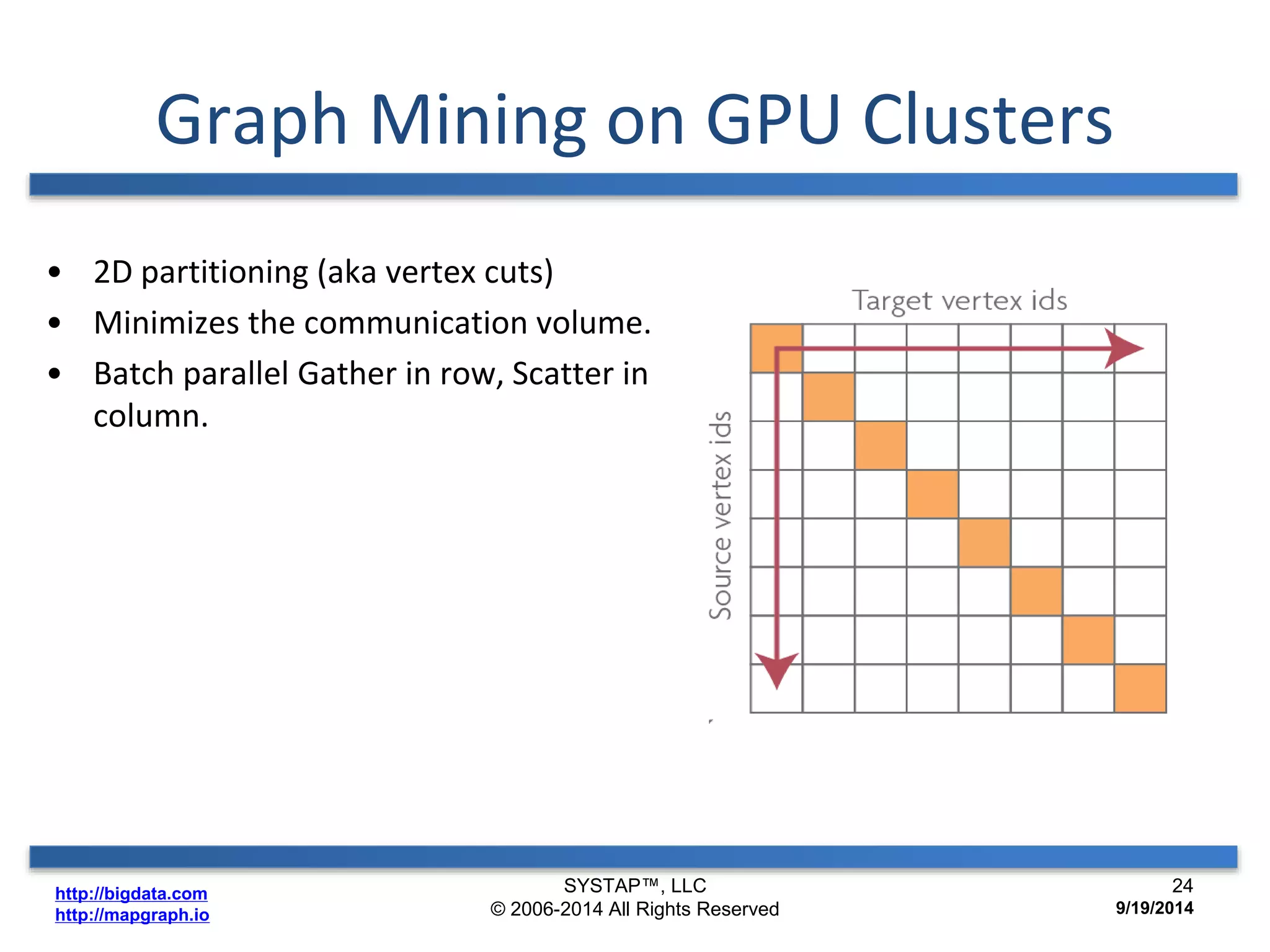
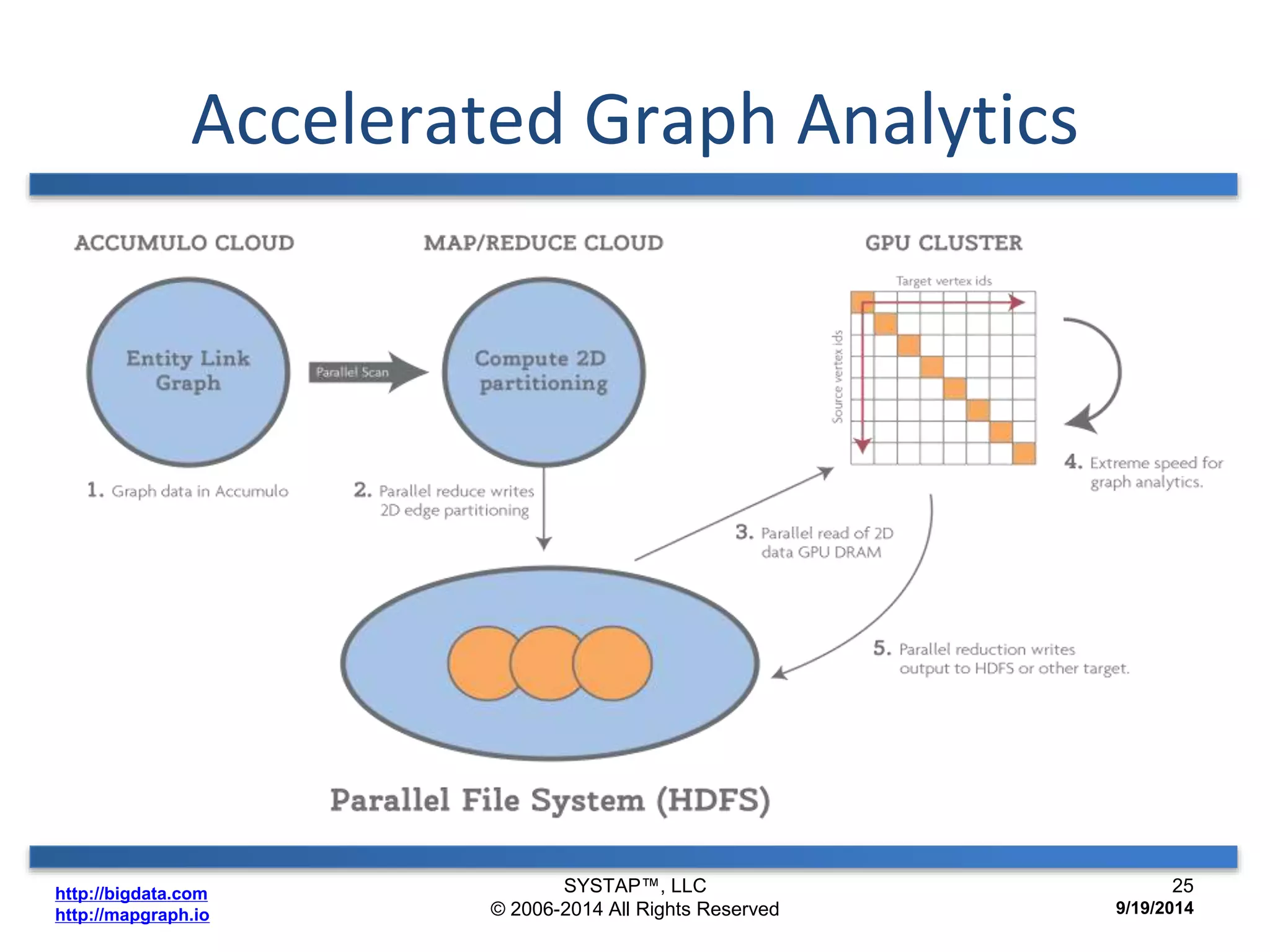
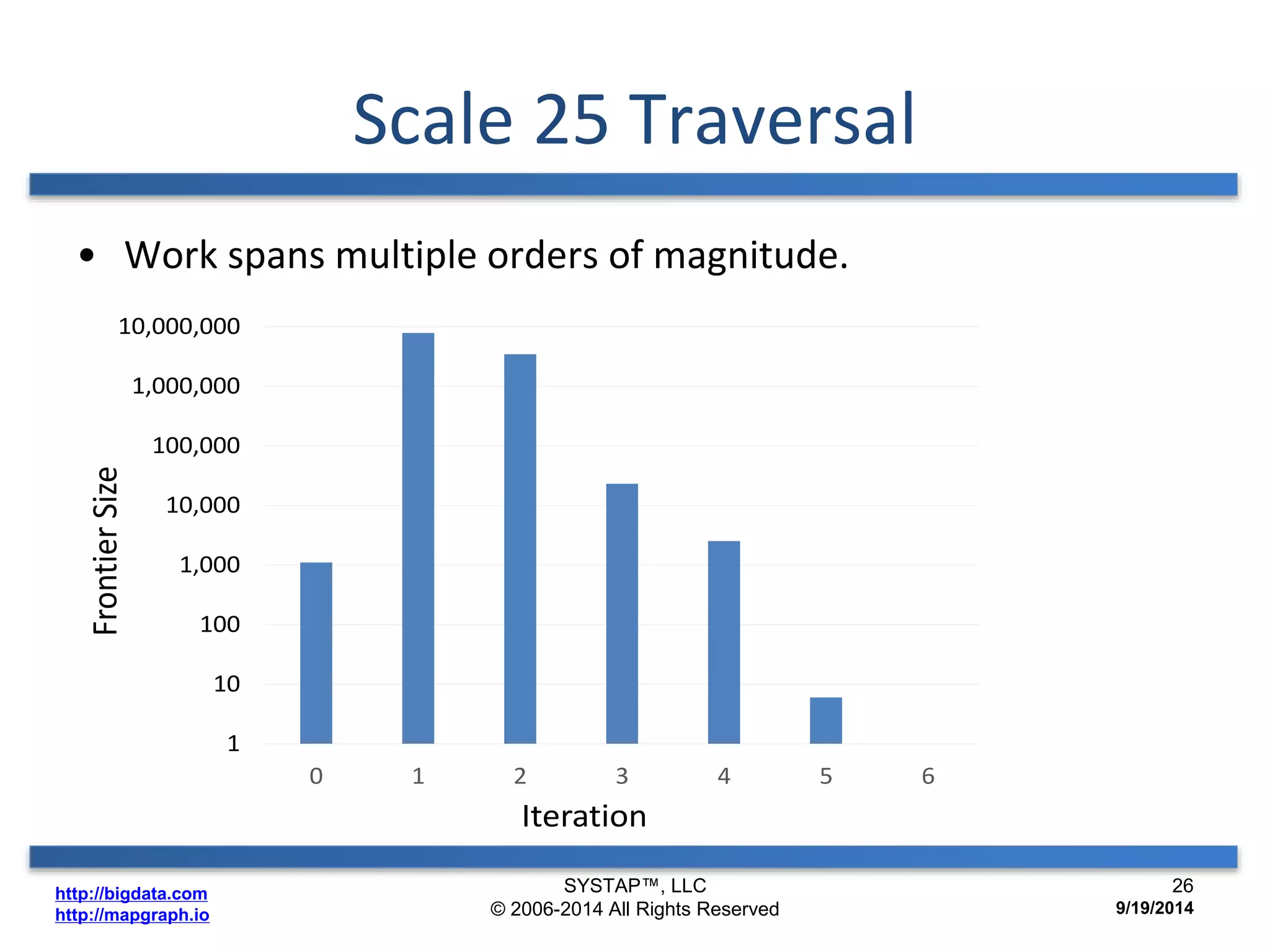
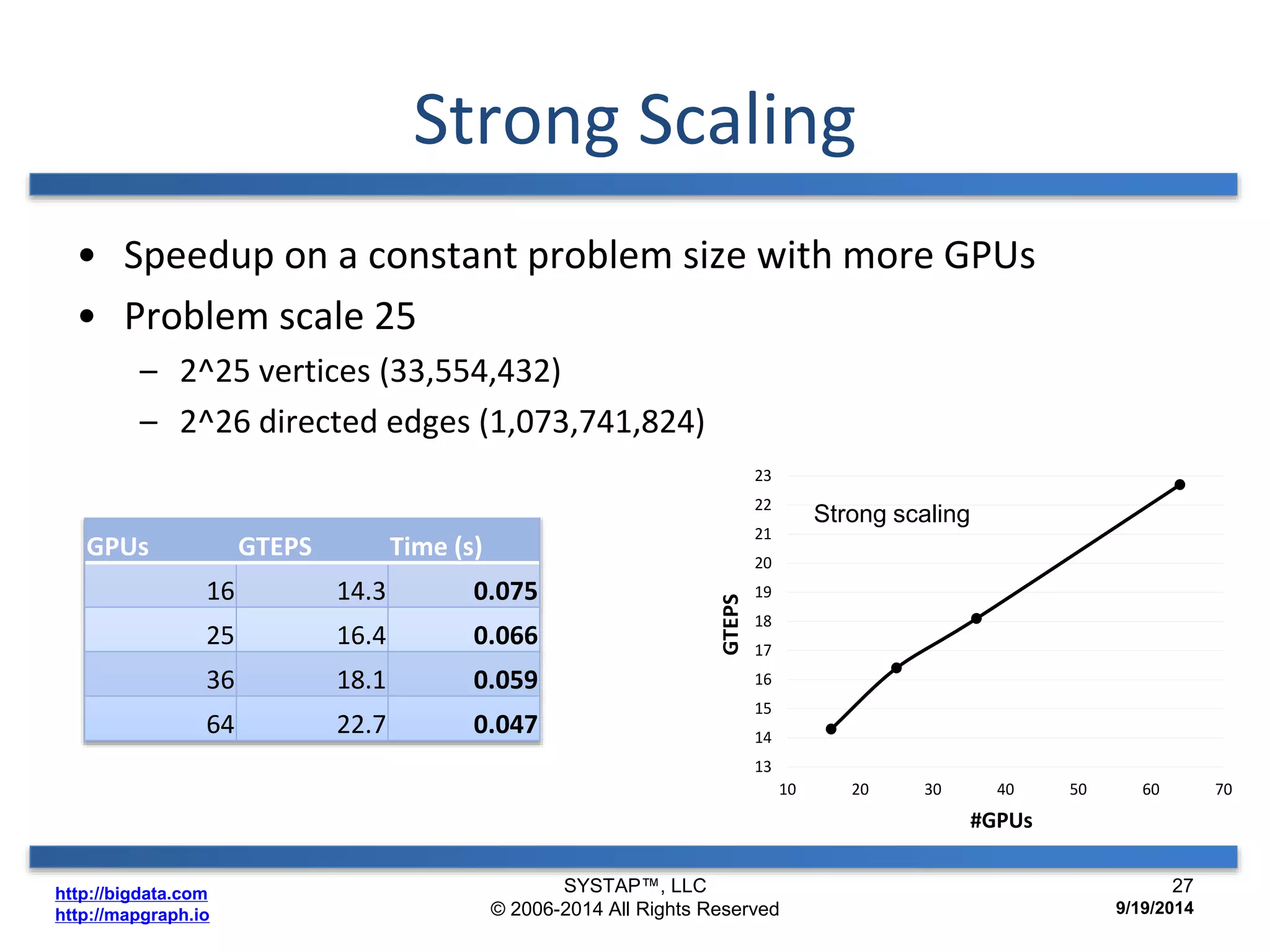
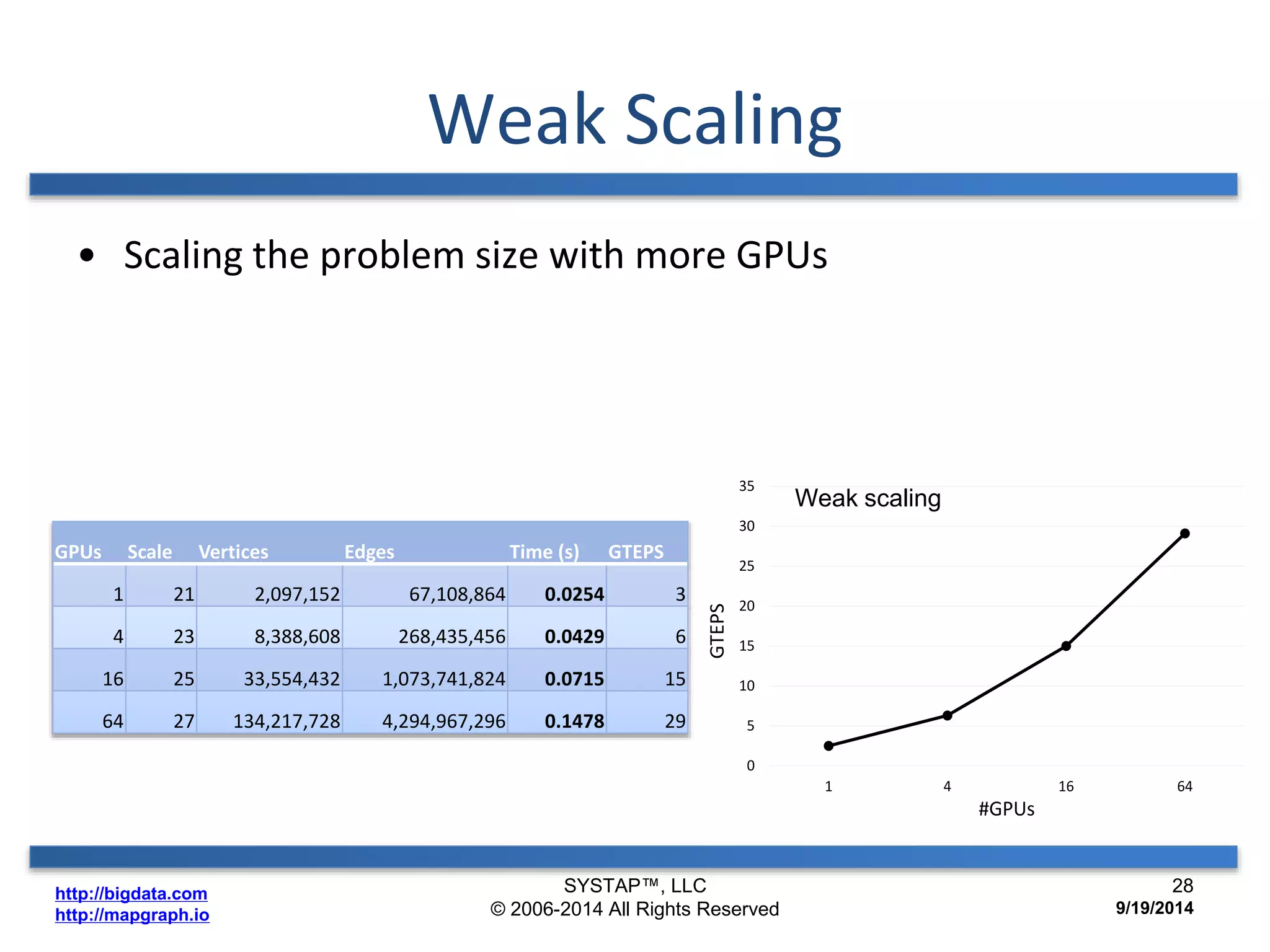
The document discusses the advancements in large-scale graph processing on GPUs, highlighting the high performance and scalability of graph databases and analytics. It emphasizes the advantages of using GPU architecture for graph algorithms, achieving significant speed improvements over traditional methods. Additionally, it outlines the necessity of optimizing storage and computation patterns for efficient performance in graph analytics.