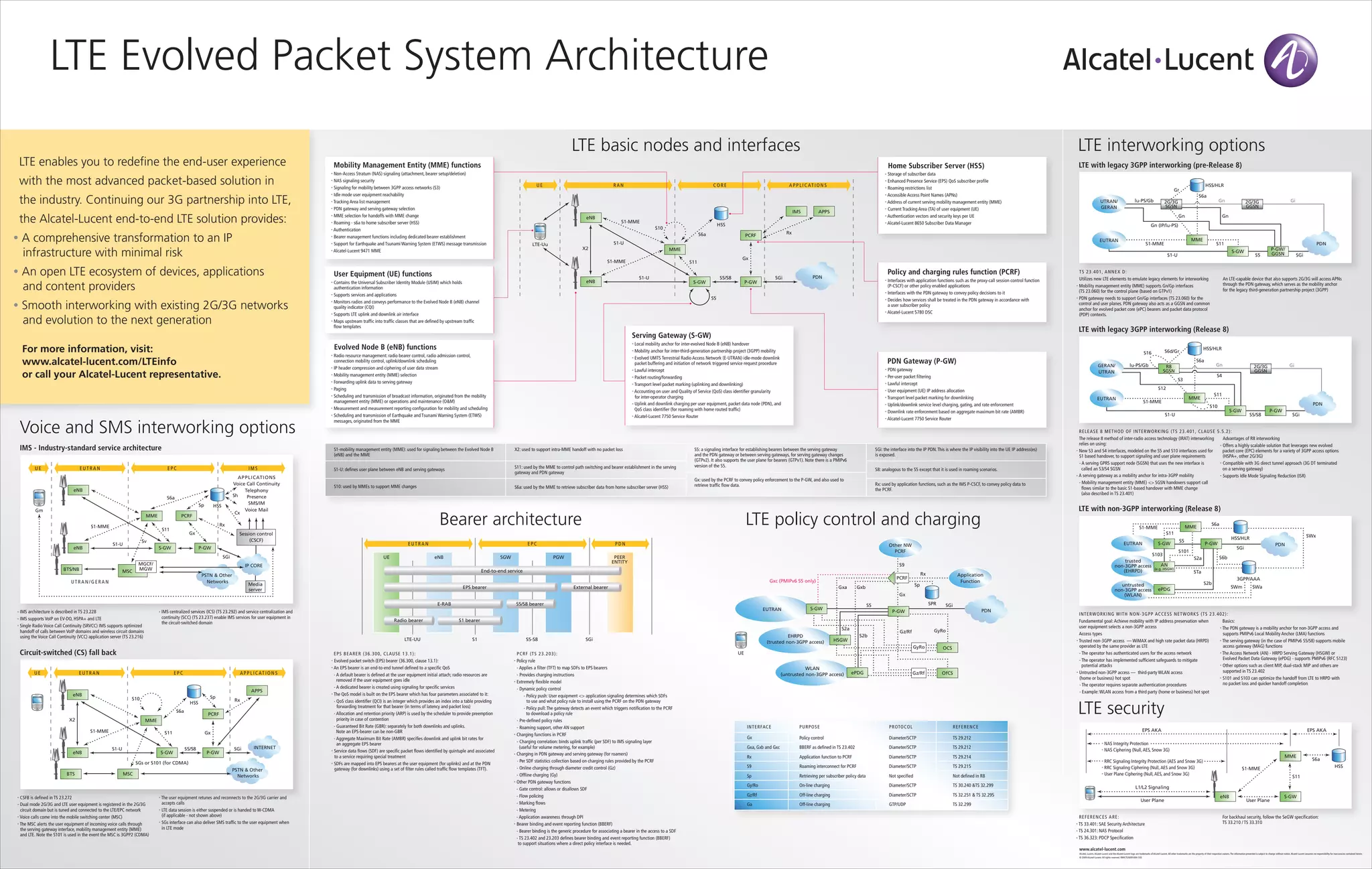
The document discusses LTE Evolved Packet System architecture, including:
- An end-to-end LTE solution from Alcatel-Lucent that provides a transformation to an IP infrastructure, an open ecosystem of devices and applications, and interworking between 2G/3G and LTE networks.
- Key network functions like the Mobility Management Entity (MME), Home Subscriber Server (HSS), Policy and Charging Rules Function (PCRF), Packet Data Network Gateway (P-GW), Serving Gateway (S-GW), Evolved Node B (eNB), and their roles.
- Interworking between LTE and legacy 2G/3G networks using circuit switched fallback (CS