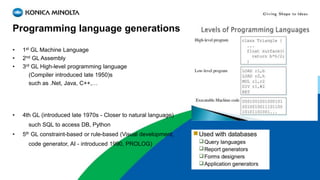
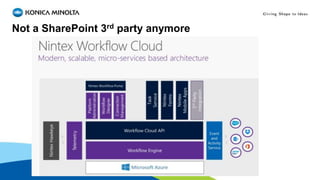
This document discusses and compares low-code development platforms Nintex and PowerApp. It provides an overview of programming language generations and how business application development has evolved from pre-packaged software to low-code platforms. Low-code platforms allow for rapid application development with minimal coding through visual interfaces and drag-and-drop functionality. The document reviews what distinguishes low-code from no-code platforms and provides details on Nintex's products, versions, and components before concluding with a demo of Nintex and PowerApp.