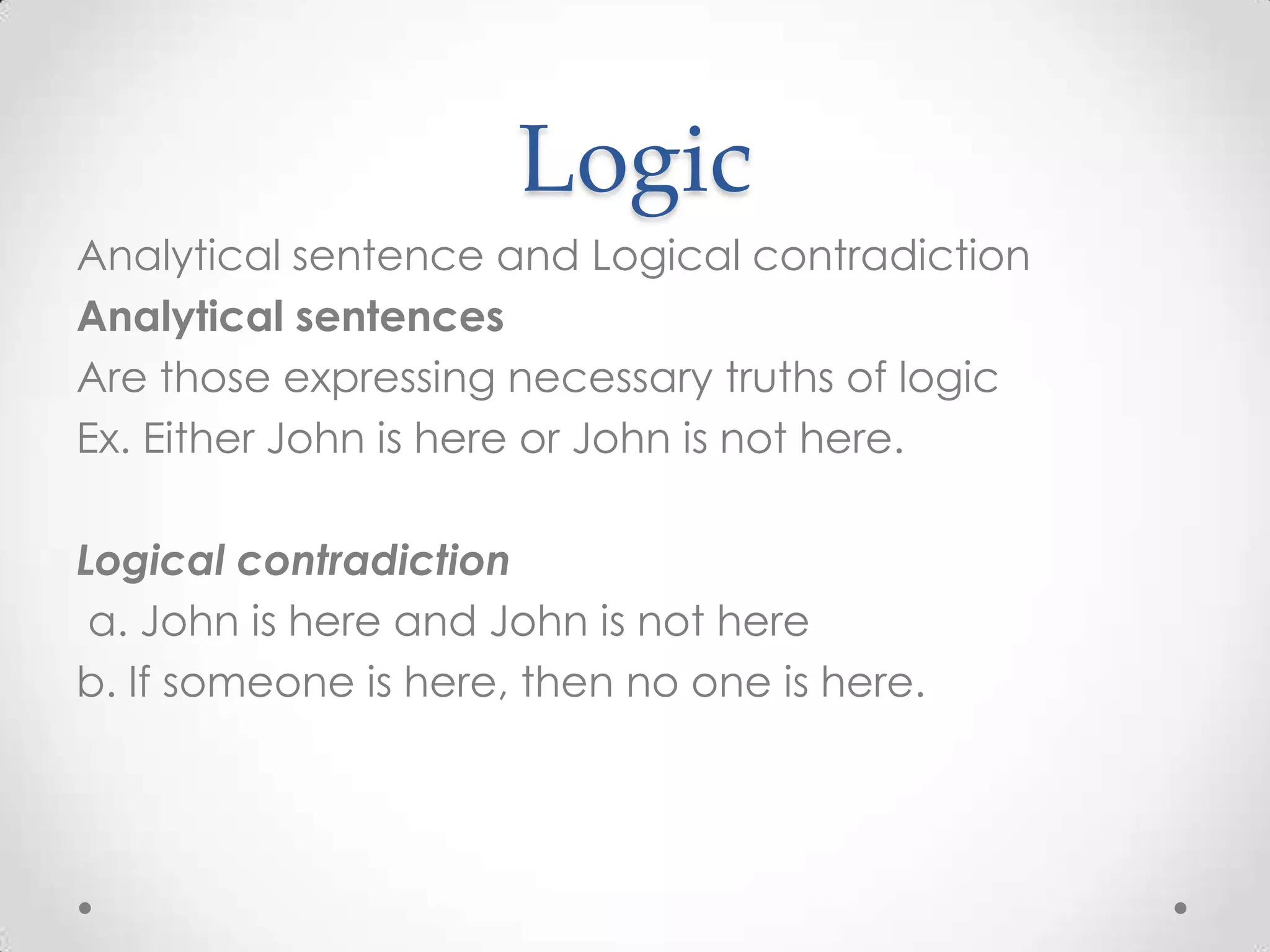
Logic deals with meanings in a language system rather than actual behavior. A proposition is the meaning of a declarative sentence describing a state of affairs. While logic provides rules for calculations, rational behavior involves goals, assumptions, knowledge, and calculations to achieve goals. Logic is one factor in rational behavior but does not equate to it. Analytical sentences express necessary logical truths, while contradictions express inconsistent statements. Simple propositions represent predicators in capital letters and arguments in lowercase.