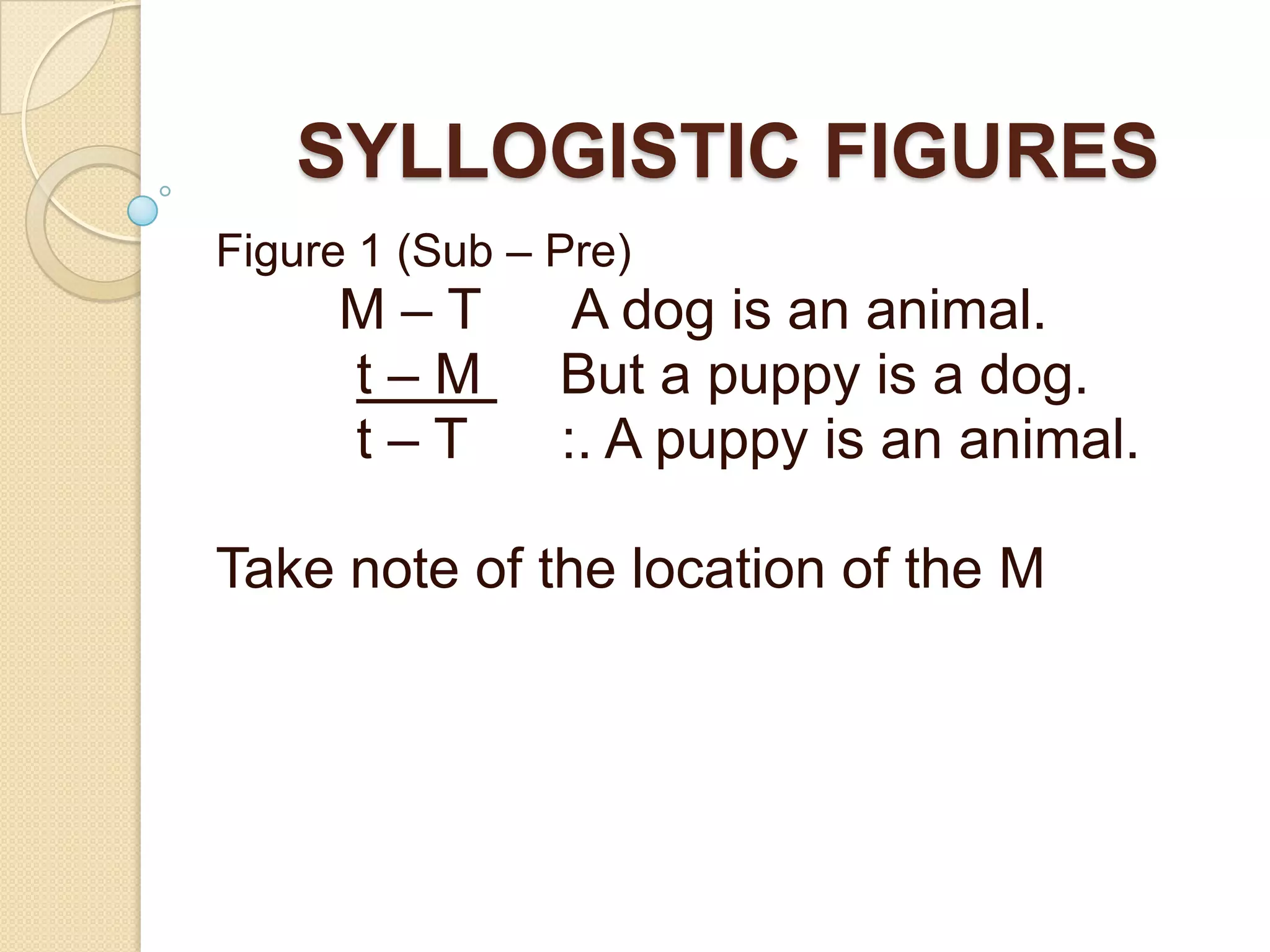
The document discusses syllogistic figures and principles of categorical syllogism. It explains:
1) Four syllogistic figures defined by the location of the middle term in the premises.
2) Five principles of categorical syllogism including reciprocal identity, reciprocal non-identity, dictum de omni, dictum de nullo, and contradiction.
3) Basic rules of categorical syllogism requiring three terms, limitations on negatives, and conclusions matching premises.
4) For a syllogism to be valid it must be correct in form and have true content.