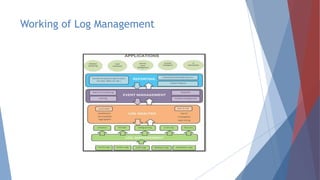
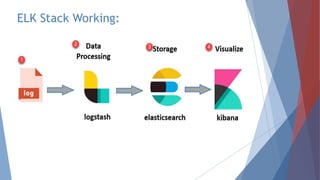
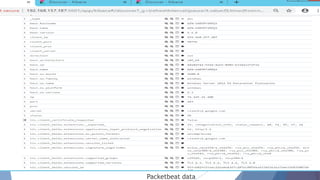
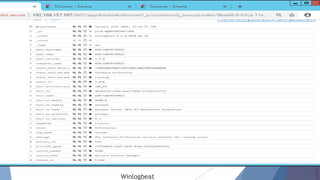
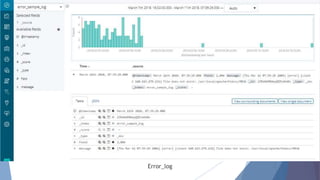
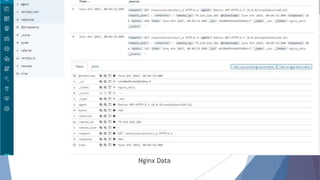
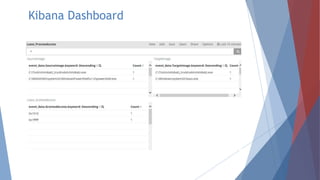
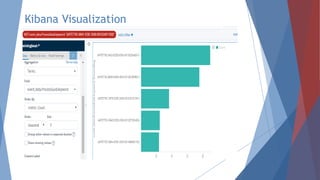
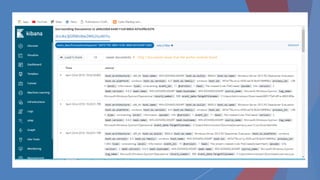
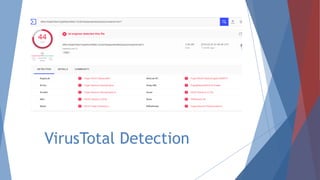
The document provides a comprehensive overview of log management and analysis using the ELK stack, which consists of Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. It discusses the importance of log analysis in debugging, predictive analysis, and security, as well as detailing various log management tools and the functionalities of different beats for collecting logs. Furthermore, it covers practical setup instructions for implementing the ELK stack on both Ubuntu and Windows systems, including examples of analyzing server logs and detecting malicious activities.