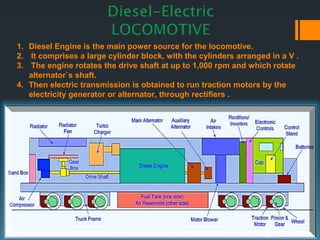
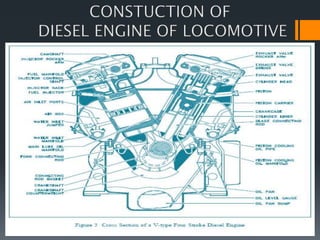
The document discusses the key components of a diesel locomotive. It states that the diesel engine powers the locomotive and can rotate at up to 1,000 rpm, turning the alternator's shaft. The alternator then generates electricity which is used by the traction motors to power the wheels of the locomotive. Some of the main components discussed include the diesel engine, alternator, traction motors, electronic controls, batteries, and various cooling and air systems.