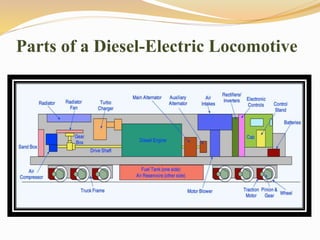
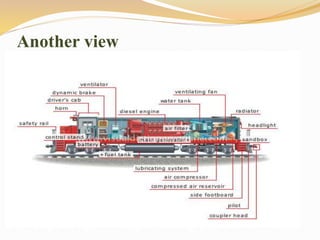
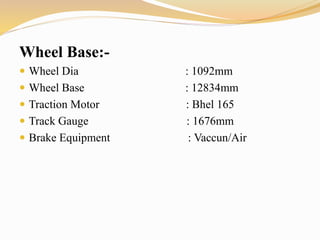
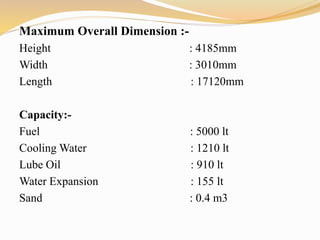
The document provides information about the key components and systems of a diesel-electric locomotive. It describes the main components including the diesel engine that powers the main alternator, traction motors on the trucks, fuel tank, radiator, air compressors, and other auxiliary systems. It also provides specifications for a typical WDM2 class locomotive used in India, including its power output, maximum speed, wheel configuration, and dimensions.